
The peristaltic movements of the alimentary canal are controlled by
(a)Cerebrum
(b)Pons
(c)Medulla
(d)Cerebellum
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: The wall of the gastrointestinal tract consists of smooth muscles that are regulated by the autonomic nervous system. The activity of these muscles is independent and not affected by voluntary nerve activity.
Complete answer:
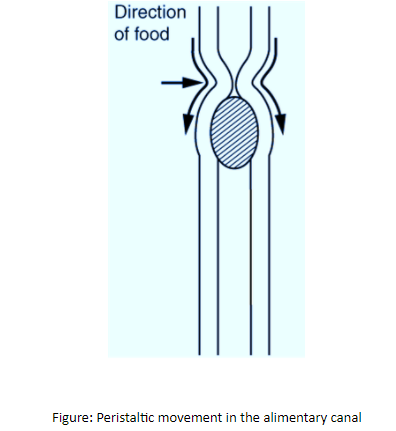
The process of peristalsis in the esophagus is controlled by the medulla oblongata. The peristaltic movement includes circular and longitudinal smooth muscles. The movement starts with the relaxation of circular muscles and then their contraction by the chewed food to keep it from moving backward and then longitudinal contraction to push it forward. The synchronized efforts of these muscles control the movement of digestive substances unidirectionally from one location to another.
Medulla oblongata and its function:
The medulla oblongata is situated in the lower half of the brainstem, anterior to the cerebellum that connects the brain to the spinal cord. It controls a number of involuntary functions.
-The medulla helps in the transfer of messages from the body to the spinal cord and the thalamus which is also the part of the brain.
-The medulla oblongata controls breathing, heart rate, digestion, blood pressure, sneezing, and swallowing.
-The medulla region comprises both myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers that are also called white matter and gray matter, respectively.
-It is the primary respiratory control center. The main purpose of the medulla is to send signals to the muscles that control respiration to cause breathing to occur.
So, the correct answer is ‘Medulla’.
Note: -Peristaltic helps in the churning of swallowed food and mixes it with the gastric juices in the stomach.
-Peristaltic waves also help in compaction and movement of waste and indigestible foodstuffs by the large intestine for elimination.
Complete answer:
The process of peristalsis in the esophagus is controlled by the medulla oblongata. The peristaltic movement includes circular and longitudinal smooth muscles. The movement starts with the relaxation of circular muscles and then their contraction by the chewed food to keep it from moving backward and then longitudinal contraction to push it forward. The synchronized efforts of these muscles control the movement of digestive substances unidirectionally from one location to another.
Medulla oblongata and its function:
The medulla oblongata is situated in the lower half of the brainstem, anterior to the cerebellum that connects the brain to the spinal cord. It controls a number of involuntary functions.
-The medulla helps in the transfer of messages from the body to the spinal cord and the thalamus which is also the part of the brain.
-The medulla oblongata controls breathing, heart rate, digestion, blood pressure, sneezing, and swallowing.
-The medulla region comprises both myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers that are also called white matter and gray matter, respectively.
-It is the primary respiratory control center. The main purpose of the medulla is to send signals to the muscles that control respiration to cause breathing to occur.
So, the correct answer is ‘Medulla’.
Note: -Peristaltic helps in the churning of swallowed food and mixes it with the gastric juices in the stomach.
-Peristaltic waves also help in compaction and movement of waste and indigestible foodstuffs by the large intestine for elimination.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




