
The phenotypic ratio of trihybrid cross in F2 generation is?
A. \[27{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}1\]
B. \[9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}1\]
C. \[1{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}4{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}6{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}4{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}1\]
D. \[27{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}1{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}2{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}1\]
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: A trihybrid cross is a cross between individuals of the same type who are heterozygous for three pairs of alleles at three different loci. The number of possible genotypic combinations is 64.
Complete Answer:
The F1 generation refers to the first generation of a cross between two parents. Filial generations are the designation given to successive sets of offspring. The letter 'P' is designated for the parent generation. The first set of offspring from these parents is known as the F1 generation. The generation of F1 can reproduce to create the F2 generation, and so on.
For a dihybrid cross, the phenotypic ratio is \[9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}1\] .
The chart below represents a cross of F2 generation between organisms with genotype AaBbCc.
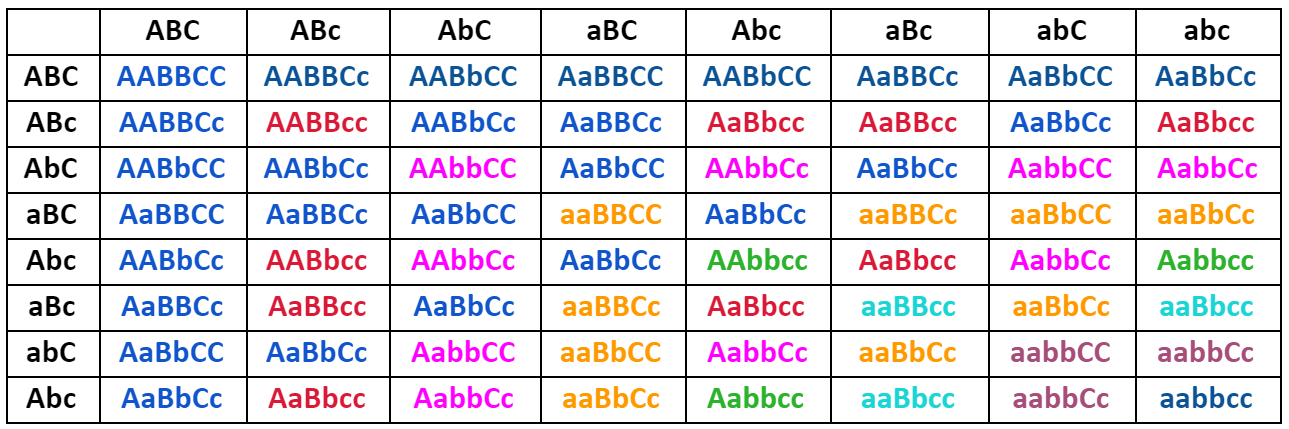
As shown in the figure the phenotypic ratio of a trihybrid cross in F2 generation will be \[27{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}1\] .
Thus, the correct answer is option A i.e., \[27{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}1\] .
Note: A monohybrid cross is a genetic mixture between two individuals who have homozygous genotypes or genotypes that have completely dominant or completely recessive alleles, resulting in opposite phenotypes for a certain genetic trait. The dihybrid cross is a cross between two organisms with two different observable traits.
Complete Answer:
The F1 generation refers to the first generation of a cross between two parents. Filial generations are the designation given to successive sets of offspring. The letter 'P' is designated for the parent generation. The first set of offspring from these parents is known as the F1 generation. The generation of F1 can reproduce to create the F2 generation, and so on.
For a dihybrid cross, the phenotypic ratio is \[9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}1\] .
The chart below represents a cross of F2 generation between organisms with genotype AaBbCc.

As shown in the figure the phenotypic ratio of a trihybrid cross in F2 generation will be \[27{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}1\] .
Thus, the correct answer is option A i.e., \[27{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}:{\text{ }}1\] .
Note: A monohybrid cross is a genetic mixture between two individuals who have homozygous genotypes or genotypes that have completely dominant or completely recessive alleles, resulting in opposite phenotypes for a certain genetic trait. The dihybrid cross is a cross between two organisms with two different observable traits.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




