
The plant body of a liverwort is thalloid
(a) True
(b) False
Answer
577.5k+ views
hHint: Liverworts tend to grow on moist and shady areas which may include banks of rivers, moist and damp soil. The thallus of the Liverworts is flattened dorsoventrally and are appressed closely to the substratum.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
You may come across various names like Marchantia, Porella, who are non- vascular terrestrial plants of damp and moist habitats with a diploid sporophyte. They spend their lives like a parasite on haploid gametophytes. These are classified as bryophytes and the particular two examples which you saw above, belong to a further sub- classification of bryophytes known as liverworts. The liverworts have thalloid as their plant body which is seen in the case of Marchantia.
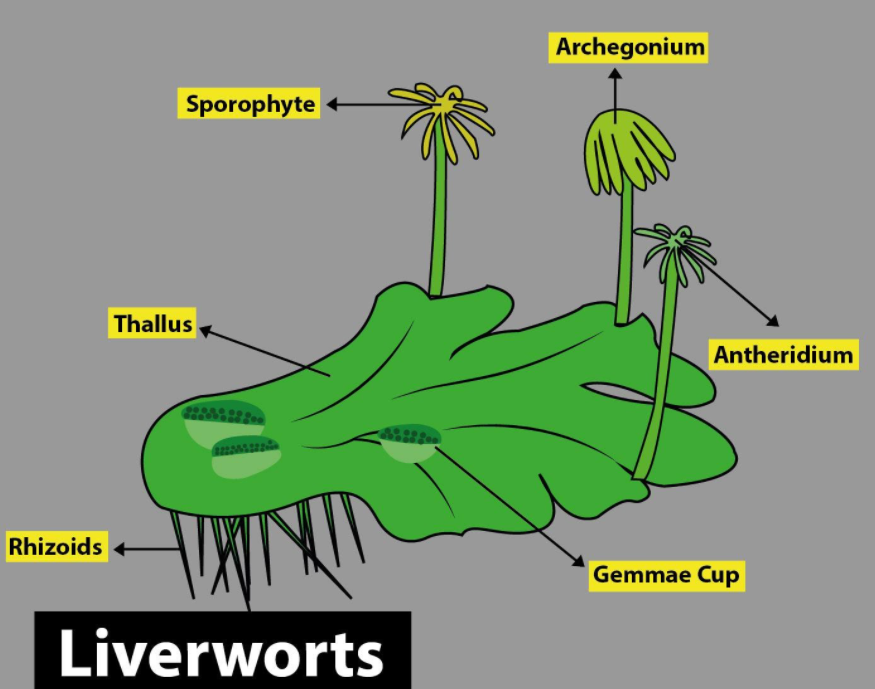
They grow in a moist habitat. They have two modes of reproduction, viz. Asexual, which usually occurs by fragmentation or they can also form special structures known as gemmae having small receptacles called gemma cups. Sexual reproduction occurs through the male and the female sex organs known as antheridiophore and archegoniophore.
Additional Information:
- The gemmae are asexual buds that are multicellular and green. They help to develop receptacles known as gemma cups. These gemma cups are used for asexual reproduction and are located on the thalloid.
- When asexual reproduction occurs, mature gemmae germinate to grow up into a new individual after getting detached from their parent.
- The development of the zygote occurs after gametic fusion which results in the formation of the embryo. The embryo then gradually develops to become the sporophyte.
- The embryo, after developing into the sporophyte, gets differentiated in the structures known as the capsule, foot, and seta. Meiosis of the spore mother cells results in haploid spores. Free- living haploid gametophyte germinates on the liberation of spores.
So, the correct answer is ‘True’.
Note:
- In sexual reproduction, the archegonia and the antheridia are either on the same thalloid or it can be also in a different thalloid, You must take note of this fact.
- Rhizoids are a type of root- like structure that helps the bryophytes onto the rocks, soils, or the tree or any other such substrates.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
You may come across various names like Marchantia, Porella, who are non- vascular terrestrial plants of damp and moist habitats with a diploid sporophyte. They spend their lives like a parasite on haploid gametophytes. These are classified as bryophytes and the particular two examples which you saw above, belong to a further sub- classification of bryophytes known as liverworts. The liverworts have thalloid as their plant body which is seen in the case of Marchantia.

They grow in a moist habitat. They have two modes of reproduction, viz. Asexual, which usually occurs by fragmentation or they can also form special structures known as gemmae having small receptacles called gemma cups. Sexual reproduction occurs through the male and the female sex organs known as antheridiophore and archegoniophore.
Additional Information:
- The gemmae are asexual buds that are multicellular and green. They help to develop receptacles known as gemma cups. These gemma cups are used for asexual reproduction and are located on the thalloid.
- When asexual reproduction occurs, mature gemmae germinate to grow up into a new individual after getting detached from their parent.
- The development of the zygote occurs after gametic fusion which results in the formation of the embryo. The embryo then gradually develops to become the sporophyte.
- The embryo, after developing into the sporophyte, gets differentiated in the structures known as the capsule, foot, and seta. Meiosis of the spore mother cells results in haploid spores. Free- living haploid gametophyte germinates on the liberation of spores.
So, the correct answer is ‘True’.
Note:
- In sexual reproduction, the archegonia and the antheridia are either on the same thalloid or it can be also in a different thalloid, You must take note of this fact.
- Rhizoids are a type of root- like structure that helps the bryophytes onto the rocks, soils, or the tree or any other such substrates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




