
The points at which crossing over has taken place between homologous chromosomes are called
A. Protein axis
B. Synaptonemal complexes
C. Chiasmata
D. Centromeres
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint:A couple of homologous chromosomes, or homologs, are a set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside a cell during fertilization. Homologs have the same genes in the same loci where they provide points along each chromosome which enable a pair of chromosomes to align correctly with each other before separating during meiosis.
Complete answer:Chromosomes are linear arrangements of condensed deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and histone proteins, which form a complex called chromatin. Homologous chromosomes are made up of chromosome pairs of approximately the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern, for genes with the same corresponding loci. In diploid (2n) organisms, the genome is composed of one set of each homologous chromosome pair, as compared to tetraploid organisms which may have two sets of each homologous chromosome pair. The alleles on the homologous chromosomes may be different, resulting in different phenotypes of the same genes. Homologous chromosomes are important in the processes of meiosis and mitosis. They allow for the recombination and random segregation of genetic material from the mother and father into new cells.
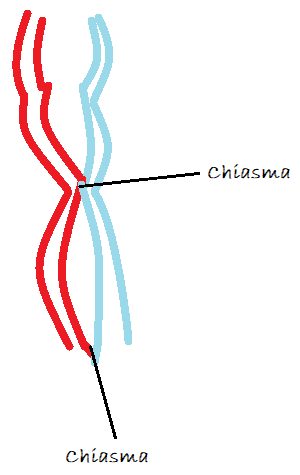
In the process of crossing-over, genes are exchanged by the breaking and union of homologous portions of the chromosomes’ lengths. Structures called chiasmata are the site of the exchange. Chiasmata physically link the homologous chromosomes once crossing over occurs and throughout the process of chromosomal segregation during meiosis. Both the non-crossover and crossover types of recombination function as processes for repairing DNA damage, particularly double-strand breaks. At the diplotene stage of prophase I the synaptonemal complex disassembles before which will allow the homologous chromosomes to separate, while the sister chromatids stay associated with their centromeres.
Hence, the correct option is (C) Chiasmata.
Note: Homologous chromosomes are chromosomes that contain the same genes in the same order along their chromosomal arms. There are two main properties of homologous chromosomes: the length of chromosomal arms and the placement of the centromere. Centromere placement can be characterized by four main arrangements, consisting of being either metacentric, submetacentric, acrocentric, or telocentric. Since homologous chromosomes are not identical and do not originate from the same organism, they are different from sister chromatids.
Complete answer:Chromosomes are linear arrangements of condensed deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and histone proteins, which form a complex called chromatin. Homologous chromosomes are made up of chromosome pairs of approximately the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern, for genes with the same corresponding loci. In diploid (2n) organisms, the genome is composed of one set of each homologous chromosome pair, as compared to tetraploid organisms which may have two sets of each homologous chromosome pair. The alleles on the homologous chromosomes may be different, resulting in different phenotypes of the same genes. Homologous chromosomes are important in the processes of meiosis and mitosis. They allow for the recombination and random segregation of genetic material from the mother and father into new cells.
In the process of crossing-over, genes are exchanged by the breaking and union of homologous portions of the chromosomes’ lengths. Structures called chiasmata are the site of the exchange. Chiasmata physically link the homologous chromosomes once crossing over occurs and throughout the process of chromosomal segregation during meiosis. Both the non-crossover and crossover types of recombination function as processes for repairing DNA damage, particularly double-strand breaks. At the diplotene stage of prophase I the synaptonemal complex disassembles before which will allow the homologous chromosomes to separate, while the sister chromatids stay associated with their centromeres.
Hence, the correct option is (C) Chiasmata.

Note: Homologous chromosomes are chromosomes that contain the same genes in the same order along their chromosomal arms. There are two main properties of homologous chromosomes: the length of chromosomal arms and the placement of the centromere. Centromere placement can be characterized by four main arrangements, consisting of being either metacentric, submetacentric, acrocentric, or telocentric. Since homologous chromosomes are not identical and do not originate from the same organism, they are different from sister chromatids.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




