
The potential energy associated with an electron in the orbit
a) Increases with the increase in the radii of the orbit
b) Decreases with the increase in the radii of the orbit
c) Remains the same with change in the radii of the orbit
d) None of these
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: The electrons revolve in the orbits with the nucleus of the atom as its centre. The nucleus has a positive charge and the electrons have a negative charge. This results in an electrostatic force of attraction between them. The electrons cannot exist in any orbit of radius r i.e. they exist in permitted orbits according to Bohr’s theory. From the definition of energy it becomes clear that whether potential energy increases or decreases with the radius due to electrostatic force.
Complete step by step answer:
The electrostatic force due a positive charge is given by $F=\dfrac{kQq}{{{r}^{2}}}$ where Q and q are the charges between which force exists, r is the distance of their separation and k is the permittivity of free space. Let us denote the atomic number by Z. Hence the charge on the nucleus is equal to eZ, where e is the magnitude of charge and Z is the number of protons in the atom. If an electron is at a distance r from the centre of the nucleus than electrostatic force of attraction between them is given by $F=\dfrac{kZe(-e)}{{{r}^{2}}}$. Hence we can write the potential energy of the electron as force times the displacement i.e. the distance r, as a result of this potential energy of an electron is $\text{P}\text{.E}=\dfrac{kZe(-e)}{{{r}^{2}}}\times r=\dfrac{kZe(-e)}{r}J$.
Hence the expression for potential energy is $\text{P}\text{.E}=-\dfrac{kZ{{e}^{2}}}{r}J$. From this equation we can observe that the value of potential energy becomes less negative as it moves from an orbit of lesser radius to an orbit of greater radius.
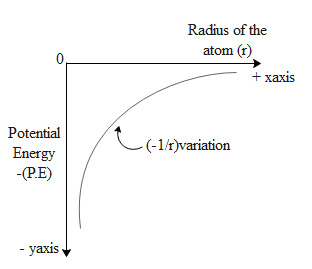
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note:
One may conclude that the potential energy varies or is inversely proportional to the radius of the orbit . Hence the potential energy decreases with the increase in the radius. But this is not true because the negative value of potential energy increases as we decrease the radius of the orbit.
Complete step by step answer:
The electrostatic force due a positive charge is given by $F=\dfrac{kQq}{{{r}^{2}}}$ where Q and q are the charges between which force exists, r is the distance of their separation and k is the permittivity of free space. Let us denote the atomic number by Z. Hence the charge on the nucleus is equal to eZ, where e is the magnitude of charge and Z is the number of protons in the atom. If an electron is at a distance r from the centre of the nucleus than electrostatic force of attraction between them is given by $F=\dfrac{kZe(-e)}{{{r}^{2}}}$. Hence we can write the potential energy of the electron as force times the displacement i.e. the distance r, as a result of this potential energy of an electron is $\text{P}\text{.E}=\dfrac{kZe(-e)}{{{r}^{2}}}\times r=\dfrac{kZe(-e)}{r}J$.
Hence the expression for potential energy is $\text{P}\text{.E}=-\dfrac{kZ{{e}^{2}}}{r}J$. From this equation we can observe that the value of potential energy becomes less negative as it moves from an orbit of lesser radius to an orbit of greater radius.

Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note:
One may conclude that the potential energy varies or is inversely proportional to the radius of the orbit . Hence the potential energy decreases with the increase in the radius. But this is not true because the negative value of potential energy increases as we decrease the radius of the orbit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




