
The principal functional group in aspirin is:
- A. Phenyl
B. -COOH
C. Ester
D. All

- A. Phenyl
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: Functional groups are the specific atoms bonded with certain arrangement due to which a compound gives certain chemical and physical properties. We know that the highest priority functional group is known as the principal functional group.
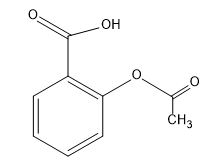
Complete step-by-step answer: From the structure of aspirin it is clear that it contains two functional groups one is
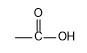 (carboxylic acid) and another is
(carboxylic acid) and another is
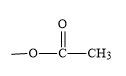 (ester). The common name of aspirin is acetylsalicylic acid and its IUPAC name is 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid. Between ester and carboxylic acid functional groups the highest priority functional group is carboxylic acid. Hence, in aspirin carboxylic acid is the principal functional group. Therefore, the correct option is B, -COOH.
(ester). The common name of aspirin is acetylsalicylic acid and its IUPAC name is 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid. Between ester and carboxylic acid functional groups the highest priority functional group is carboxylic acid. Hence, in aspirin carboxylic acid is the principal functional group. Therefore, the correct option is B, -COOH.
Additional Information: Aspirin is widely used to treat headaches, mild pains and fevers as a prescription medication. Instead, it helps reduce blood clotting, but it may trigger ulcers in the stomach and gastrointestinal tract at higher doses.
A functional group in organic chemistry is a particular group of atoms or bonds within a compound that is responsible for that compound's distinctive chemical reactions. Similarly, a certain functional group can perform similar reactions. In the naming of organic compounds, functional groups often play a significant role; the name of the functional groups combined with the names of the parental alkanes gives a way to differentiate compounds.
Note: A student gets confused between the common names and IUPAC names. In IUPAC nomenclature a compound's systematic naming, combining bonding and fundamental structural relations are given clearly. Hence, in case of Aspirin, as an ester group is joined at the second position of benzene ring with reference to the carboxylic acid group present at the first position, it will act as a substituent and then the whole compound is named accordingly to the rules of IUPAC as 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid.
Complete step-by-step answer: From the structure of aspirin it is clear that it contains two functional groups one is


Additional Information: Aspirin is widely used to treat headaches, mild pains and fevers as a prescription medication. Instead, it helps reduce blood clotting, but it may trigger ulcers in the stomach and gastrointestinal tract at higher doses.
A functional group in organic chemistry is a particular group of atoms or bonds within a compound that is responsible for that compound's distinctive chemical reactions. Similarly, a certain functional group can perform similar reactions. In the naming of organic compounds, functional groups often play a significant role; the name of the functional groups combined with the names of the parental alkanes gives a way to differentiate compounds.
Note: A student gets confused between the common names and IUPAC names. In IUPAC nomenclature a compound's systematic naming, combining bonding and fundamental structural relations are given clearly. Hence, in case of Aspirin, as an ester group is joined at the second position of benzene ring with reference to the carboxylic acid group present at the first position, it will act as a substituent and then the whole compound is named accordingly to the rules of IUPAC as 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




