
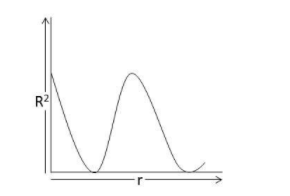
The probability distribution curve for 2s electron appears like:
A.
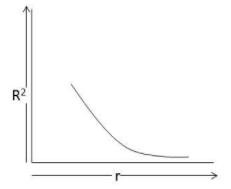
B.
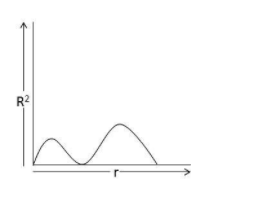
C.
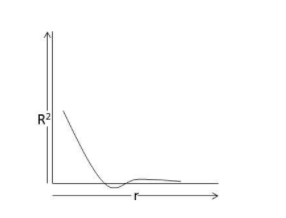
D.




Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: As we know an electron in an atom exhibits particle and wave-like behavior and the mathematical function describing this behavior is known as atomic orbital and also it is the area around the nucleus where the probability of finding an electron is maximum.
Complete step by step answer:
The probability of finding an electron around the nucleus at any point is calculated using the Schrodinger wave equation and orbital wave function (Ψ). The different orbitals are s,p,d, and f. The graph between the orbital wave function (Ψ) and the square of its absolute value ${\left| \Psi \right|^2}$ provides the probability distribution of the electron density. In the case of 2s electrons, the probability of finding an electron is maximum near the nucleus and on moving farther it decreases gradually to zero and starts increasing again and then decreases with the distance.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Additional Information:
The probability of finding the atom in the space around the nucleus helps determine the shape of the orbital. S orbital is spherical, whereas p-orbital is dumb-bell shaped and d-orbital has a doughnut shape.
Note: The point at which the probability of finding an electron is zero is known as Nodal surface or node and this can also be attributed as the point where the wave function ($\Psi $) changes sign from + to -. For any orbital, the number of nodes is calculated by the formula given by the below expression:
The number of nodes in any orbital = (n-l-1) where l is the azimuthal number.
Complete step by step answer:
The probability of finding an electron around the nucleus at any point is calculated using the Schrodinger wave equation and orbital wave function (Ψ). The different orbitals are s,p,d, and f. The graph between the orbital wave function (Ψ) and the square of its absolute value ${\left| \Psi \right|^2}$ provides the probability distribution of the electron density. In the case of 2s electrons, the probability of finding an electron is maximum near the nucleus and on moving farther it decreases gradually to zero and starts increasing again and then decreases with the distance.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Additional Information:
The probability of finding the atom in the space around the nucleus helps determine the shape of the orbital. S orbital is spherical, whereas p-orbital is dumb-bell shaped and d-orbital has a doughnut shape.
Note: The point at which the probability of finding an electron is zero is known as Nodal surface or node and this can also be attributed as the point where the wave function ($\Psi $) changes sign from + to -. For any orbital, the number of nodes is calculated by the formula given by the below expression:
The number of nodes in any orbital = (n-l-1) where l is the azimuthal number.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




