
The process used in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA is
A.Oxidative dehydration
B.Oxidative decarboxylation
C.Oxidative Phosphorylation
D.Oxidative dephosphorylation
E.None of the above
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: This reaction is very common to link between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. This is in the process used to convert pyruvate to acetyl CoA is oxidative decarboxylation.
Complete answer:
The correct answer is Oxidative decarboxylation. Decarboxylation or oxidative decarboxylation reaction is the biochemical reaction which uses pyruvate in order to form acetyl-CoA, by releasing NADH, which is a reducing equivalent, and carbon dioxide upon decarboxylation. We can observe such kinds of reactions in many organisms which are in between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
Additional Information: - Pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA in an intermediate process just before the citric acid cycle. Here, in oxidative decarboxylation, it reacts with coenzyme A. Here, it loses two of its oxygen and one of its carbons to form carbon dioxide. In addition, an NAD + molecule is reduced to form NADH. The resulting molecule is an acetyl-CoA molecule. The reaction in which a carboxylate group is removed and forms carbon dioxide is called Oxidative decarboxylation reactions. These reactions usually occur in biological systems and some of the examples are in the citric acid cycle. This type of reaction probably started early in the origin of life.
So, the correct answer is ‘oxidative Decarboxylation’.
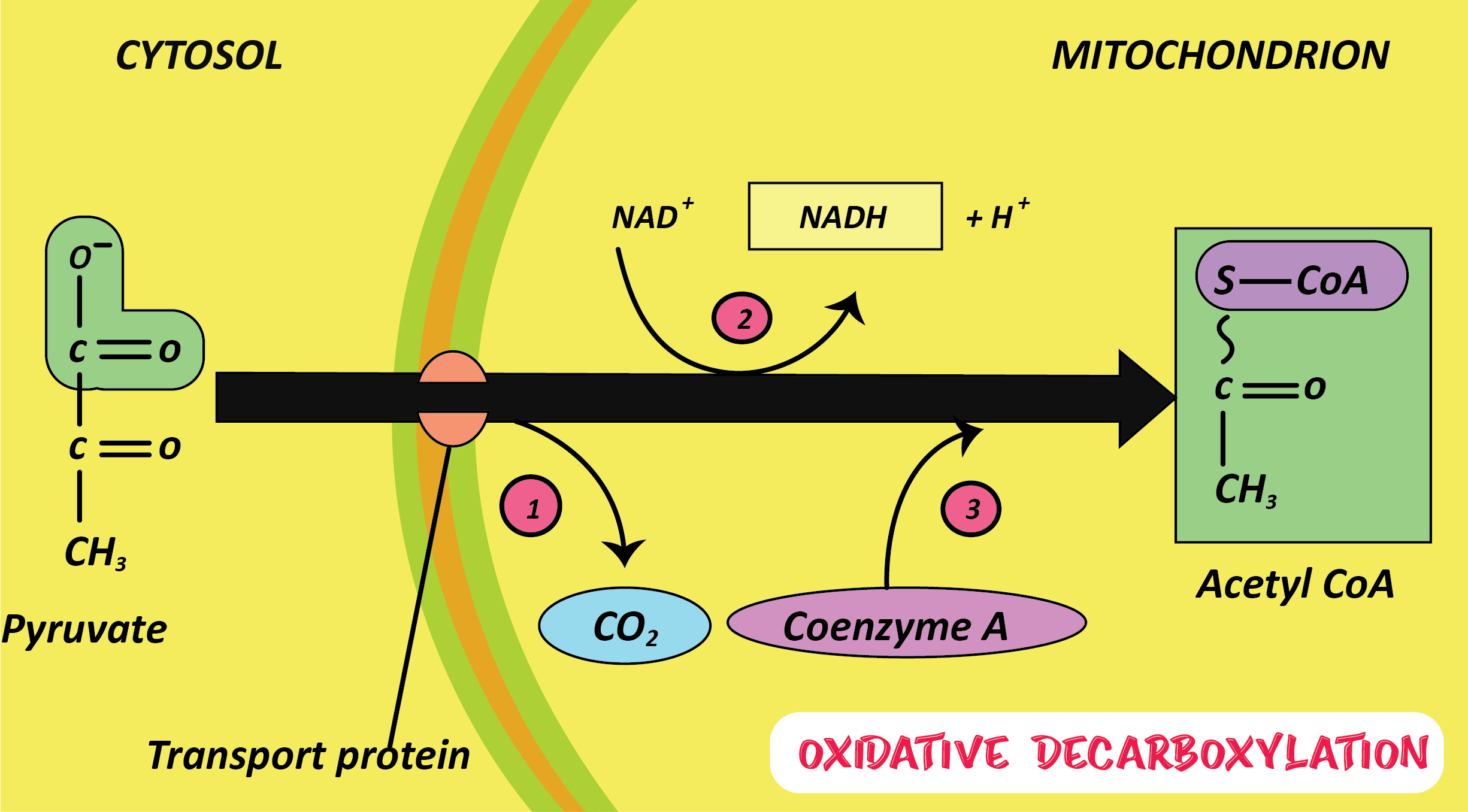
Note: Aerobic respiration starts after the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA. This conversion takes place in three steps: decarboxylation, reduction of NAD +, and binding of coenzyme A. This conversion begins with the decarboxylation (removal of $CO_2$) of pyruvate. Krebs cycle is also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle or the citric acid cycle.
- When glucose levels are low in the cell, CoA is acetylated using acetate by acetyl-CoA synthetase.
- Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.
Complete answer:
The correct answer is Oxidative decarboxylation. Decarboxylation or oxidative decarboxylation reaction is the biochemical reaction which uses pyruvate in order to form acetyl-CoA, by releasing NADH, which is a reducing equivalent, and carbon dioxide upon decarboxylation. We can observe such kinds of reactions in many organisms which are in between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
Additional Information: - Pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA in an intermediate process just before the citric acid cycle. Here, in oxidative decarboxylation, it reacts with coenzyme A. Here, it loses two of its oxygen and one of its carbons to form carbon dioxide. In addition, an NAD + molecule is reduced to form NADH. The resulting molecule is an acetyl-CoA molecule. The reaction in which a carboxylate group is removed and forms carbon dioxide is called Oxidative decarboxylation reactions. These reactions usually occur in biological systems and some of the examples are in the citric acid cycle. This type of reaction probably started early in the origin of life.
So, the correct answer is ‘oxidative Decarboxylation’.

Note: Aerobic respiration starts after the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA. This conversion takes place in three steps: decarboxylation, reduction of NAD +, and binding of coenzyme A. This conversion begins with the decarboxylation (removal of $CO_2$) of pyruvate. Krebs cycle is also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle or the citric acid cycle.
- When glucose levels are low in the cell, CoA is acetylated using acetate by acetyl-CoA synthetase.
- Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




