
What will be the Product A for the given reaction :
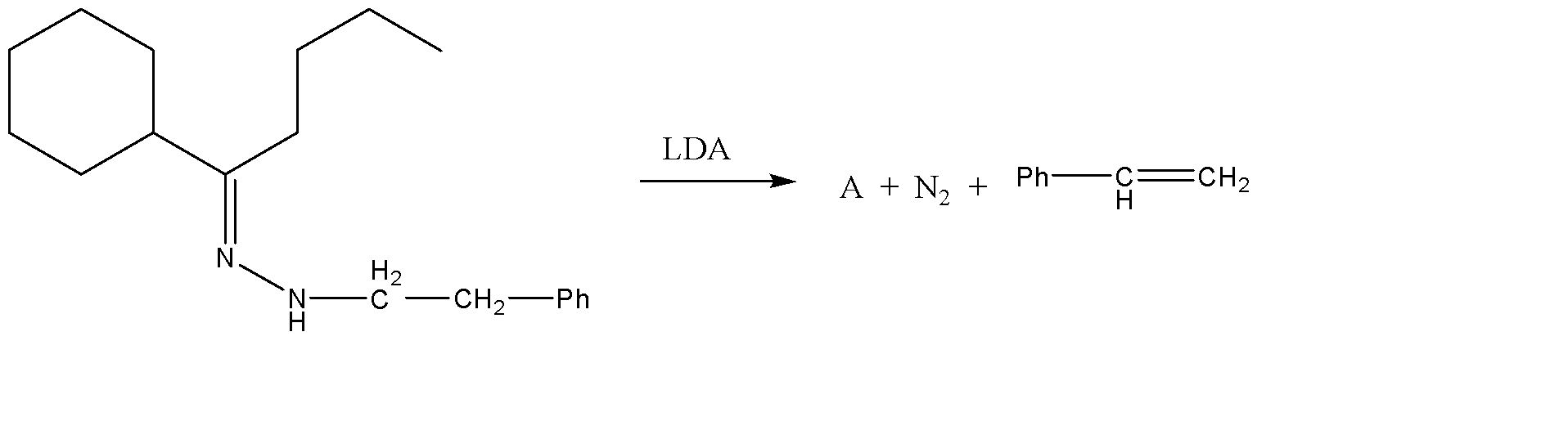
(LDA = Lithium di-isopropyl amide)
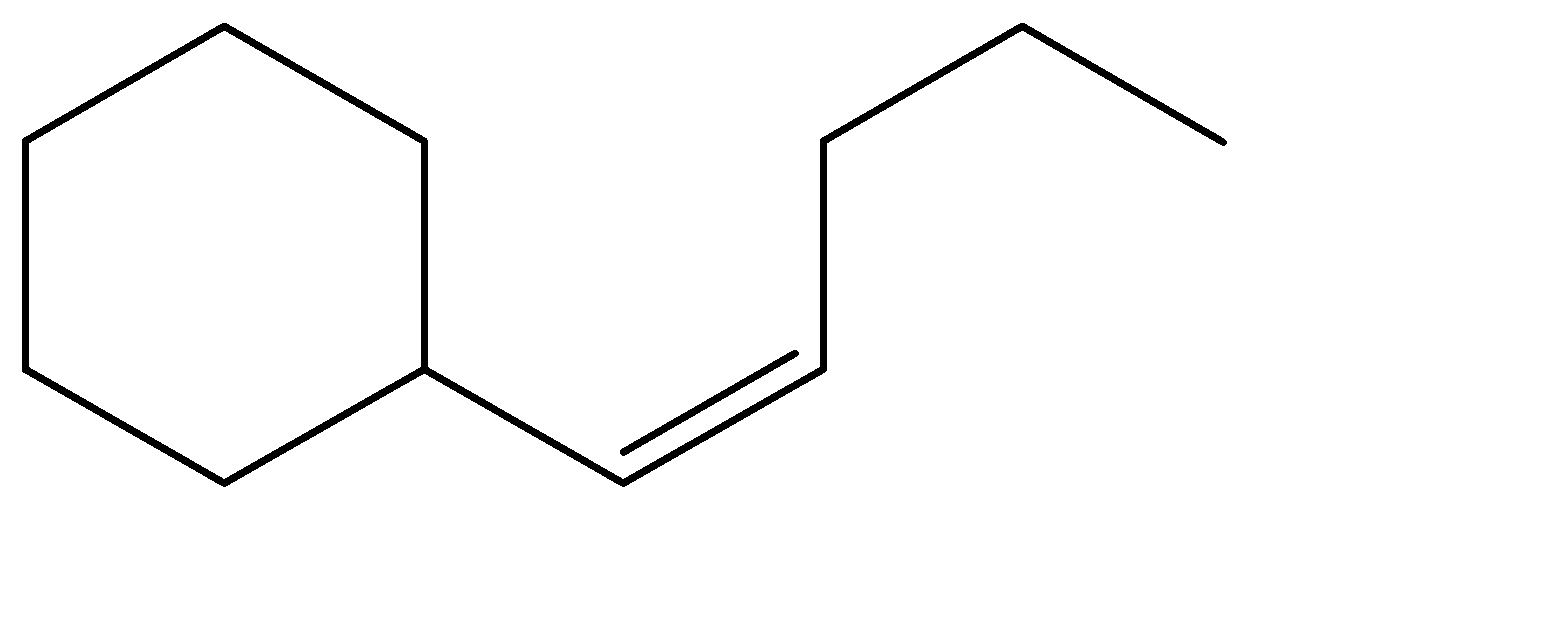
A.
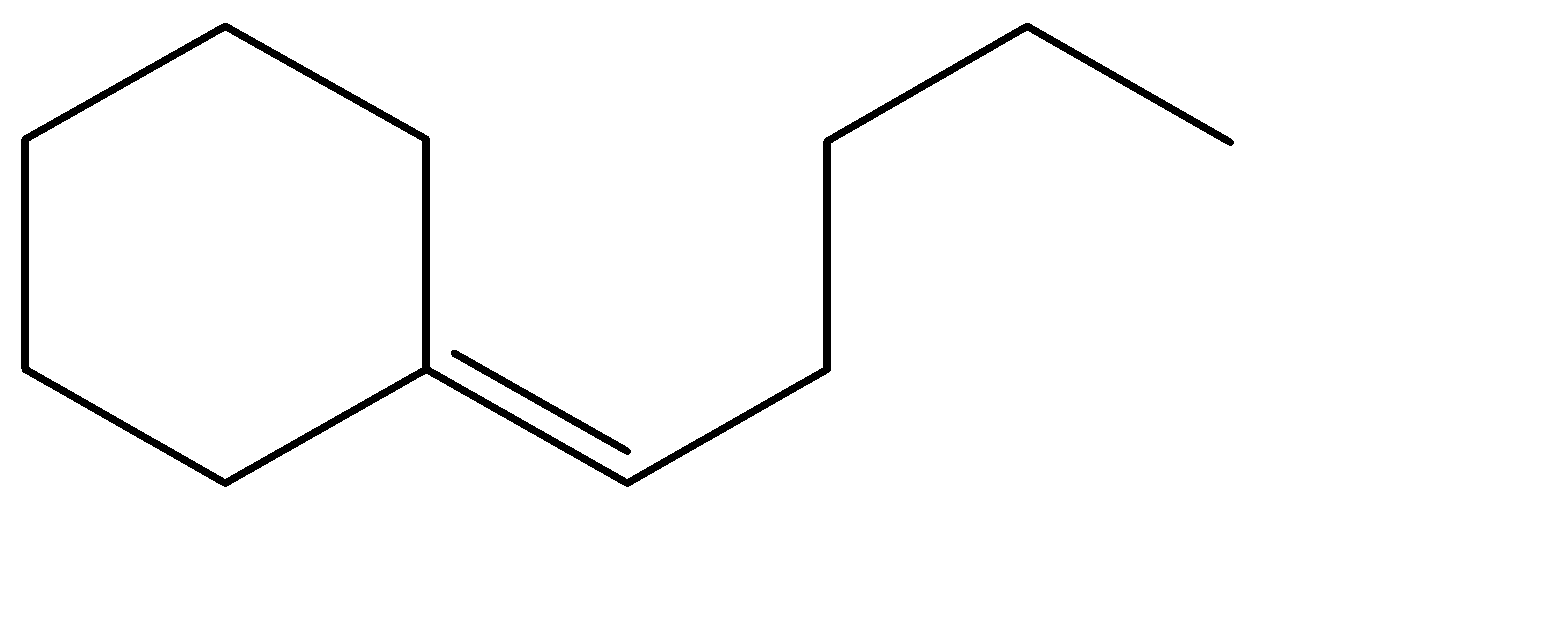
B.
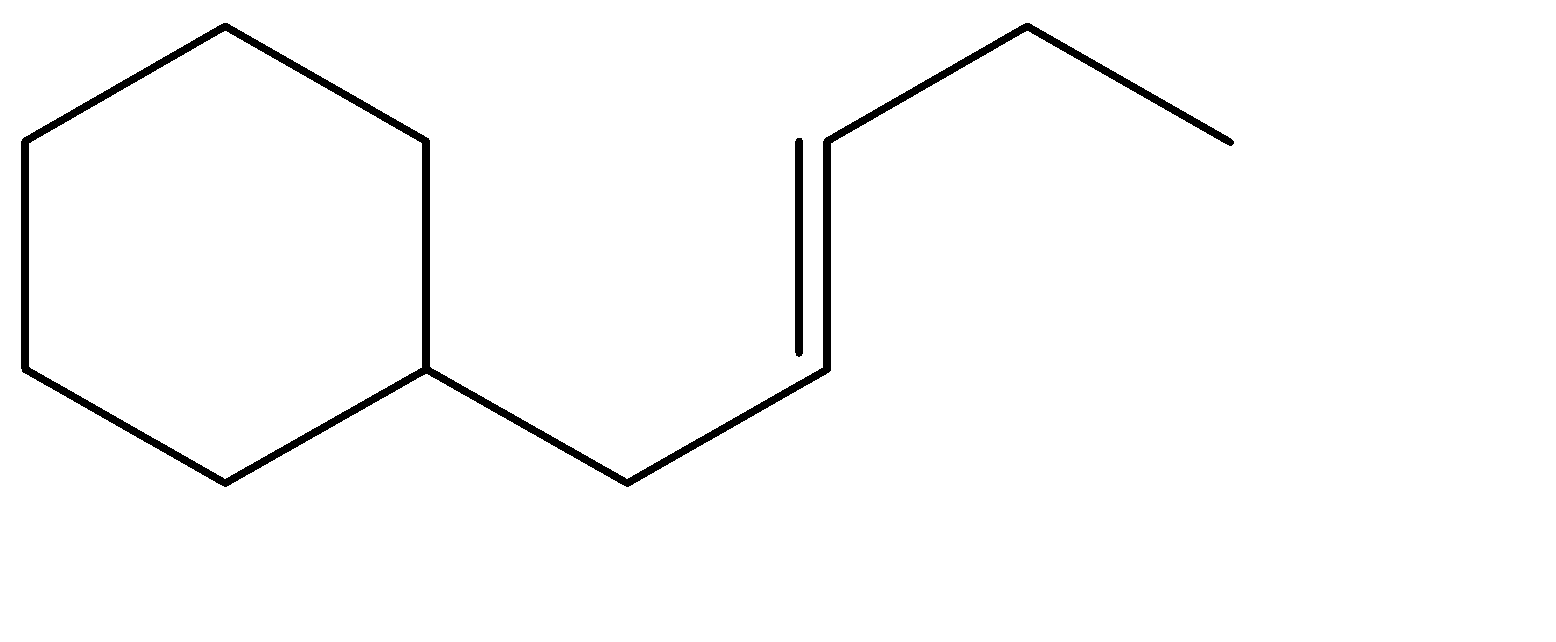
C.
D.






Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we need to first understand the nature of the compound that is being used as the reactant. Then we need to understand the nature of the catalyst being used, and its general effects on the compound. On the basis of this information, we can find the final solution.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
The compound given to us can be generally categorised as a hydrazone. A hydrazone can be represented by the general formula \[{R_1}{R_2}C = NN{H_2}\]. The structure of this molecule can be easily explained as hydrazine molecule which has substituted the oxygen atom in a carbonyl compound. Hydrazones generally form mixtures of geometrical isomers. If we apply the general formula for hydrazine to the given compound, then we can say that \[{R_1}\] is a cyclohexane and \[{R_2}\] is butane.
The treatment of the given hydrazone with a catalytic amount of LDA results in the formation of an enolate. An enolate can be understood as an organic anion which is formed as a result of the deprotonation of the given carbonyl compound. Hence, this deprotonation takes place from the butane alkyl group of the substituted carbonyl compound. This results in the formation of a pi bond on the adjacent carbon atom. This enolate is unstable and hence splits into different compounds. The complete reaction can be given as follows:
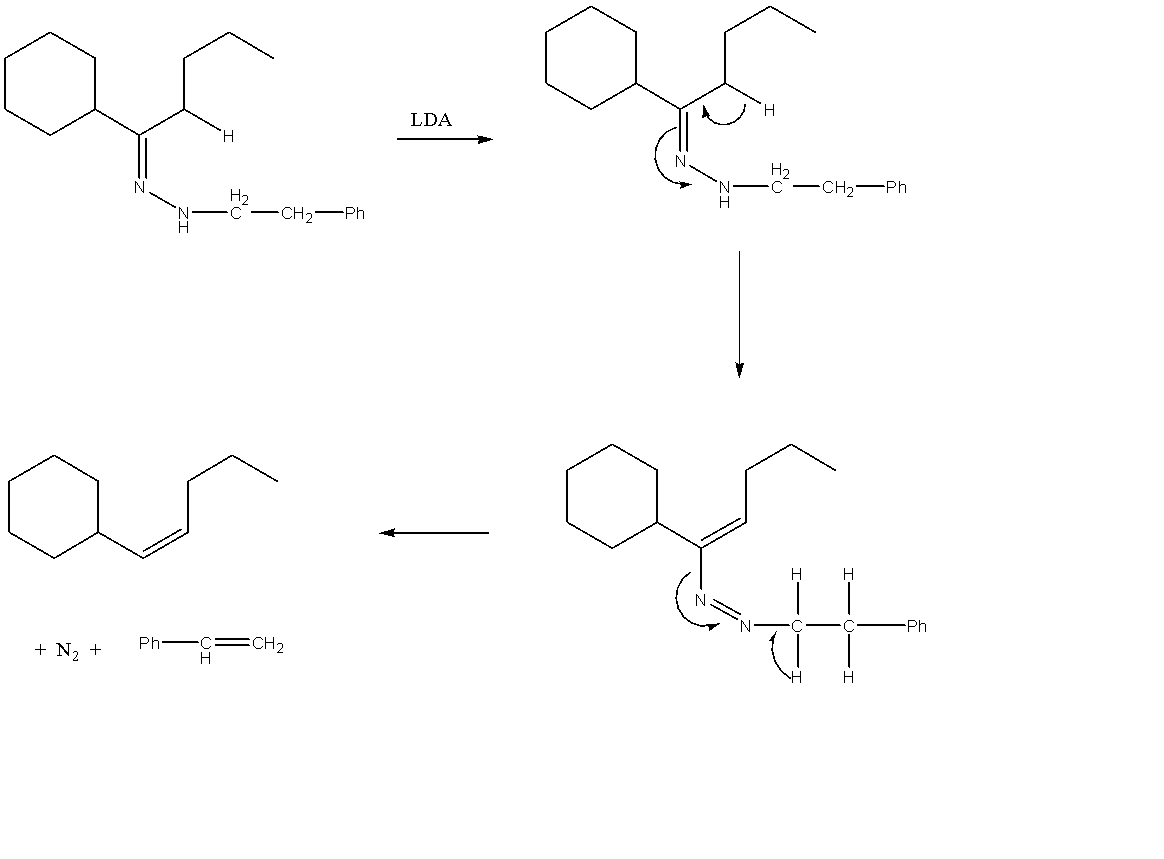
Hence, Option A is the correct option
Note: LDA stands for Lithium di-isopropyl amide. The general chemical formula for LDA can be given as \[{[{(C{H_3})_2}CH]_2}NLi\]. This compound is a strong base and can hence cause reactions like deprotonation in reacting compounds.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
The compound given to us can be generally categorised as a hydrazone. A hydrazone can be represented by the general formula \[{R_1}{R_2}C = NN{H_2}\]. The structure of this molecule can be easily explained as hydrazine molecule which has substituted the oxygen atom in a carbonyl compound. Hydrazones generally form mixtures of geometrical isomers. If we apply the general formula for hydrazine to the given compound, then we can say that \[{R_1}\] is a cyclohexane and \[{R_2}\] is butane.
The treatment of the given hydrazone with a catalytic amount of LDA results in the formation of an enolate. An enolate can be understood as an organic anion which is formed as a result of the deprotonation of the given carbonyl compound. Hence, this deprotonation takes place from the butane alkyl group of the substituted carbonyl compound. This results in the formation of a pi bond on the adjacent carbon atom. This enolate is unstable and hence splits into different compounds. The complete reaction can be given as follows:

Hence, Option A is the correct option
Note: LDA stands for Lithium di-isopropyl amide. The general chemical formula for LDA can be given as \[{[{(C{H_3})_2}CH]_2}NLi\]. This compound is a strong base and can hence cause reactions like deprotonation in reacting compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




