
The product X will be:
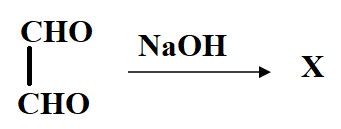
A.
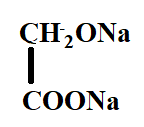
B.
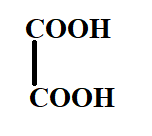
C.
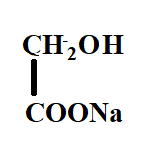
D.
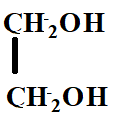
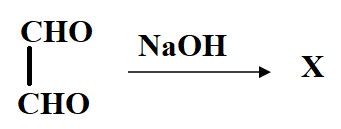
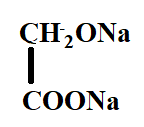
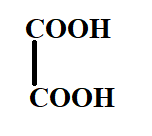
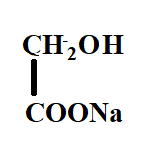
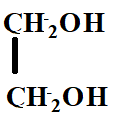
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you should recall the concept of Cannizzaro reaction. Cannizzaro reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the base-induced disproportionation of two molecules. It occurs when alpha hydrogen is missing in a carbonyl compound. It forms an alcohol and an acid.
Complete Step by step solution:
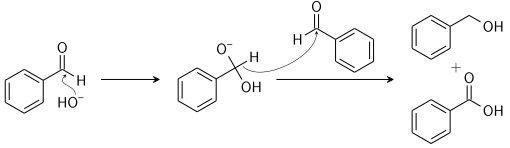
The reactants involved are non-enolizable aldehyde to yield a carboxylic acid and a primary alcohol. The reaction is initiated by a nucleophilic acyl substitution on a non-enolizable aldehyde where the leaving group attacks another aldehyde. This results in an intermediate which is tetrahedral in geometry from the attack of hydroxide on a carbonyl.
Now, a proton is exchanged by acid and alkoxide ions. With the introduction of a base of high concentration, the aldehyde forms an anion which has a charge of two. After this step a hydride ion is transferred to a second molecule of the aldehyde, forming carboxylate and alkoxide ions.
The overall mechanism can be summarised by the following mechanism:
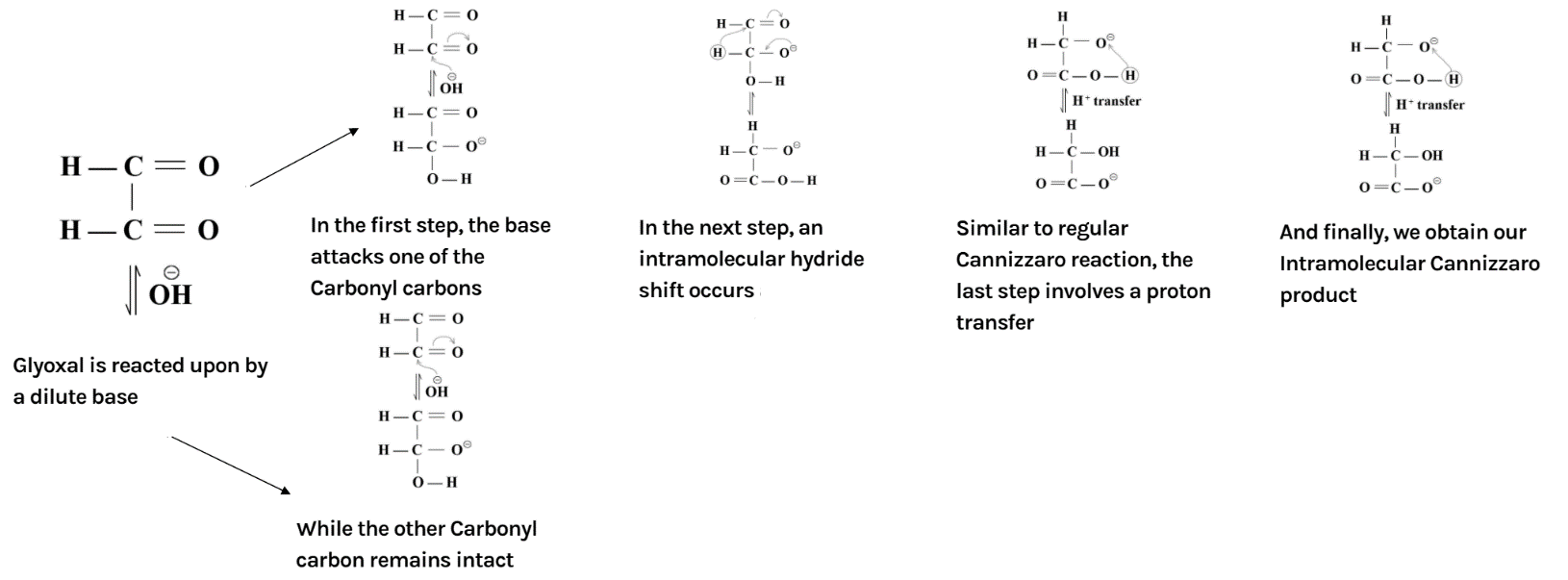
In the reaction, the reactant i.e. glyoxal does not have any alpha hydrogen so it will perform intramolecular Cannizzaro reaction. This means that one of the aldehydes will reduce and the other will oxidise.
Hence, the correct option is C.
The overall mechanism has been summarised as below:
Additional information: Another important reaction of aldehydes is aldol condensation. The reaction of aldehydes and ketones containing at least one $\alpha $ hydrogen is treated with dilute alkali; they form $\beta $ - hydroxy aldehydes or $\beta $ - hydroxy ketones (ketol) respectively. We know that in aldol condensation the hydroxide ion functions as a base moving the acidic hydrogen-producing the reactive enolate ion. Further, the aldehyde is attacked at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon by the nucleophilic enolate ion resulting in an alkoxide intermediate. The alkoxide ion now formed deprotonates the water molecule, ultimately resulting in hydroxide and the $\beta $ – hydroxy aldehyde.
Note: Acetaldehyde does not participate in Cannizzaro reaction because the alpha-hydrogens are deprotonated due to the alkaline environment. Since acetaldehyde contains three alpha hydrogen, it readily enolate ions upon deprotonation and therefore cannot participate in the reaction.
Complete Step by step solution:
The reactants involved are non-enolizable aldehyde to yield a carboxylic acid and a primary alcohol. The reaction is initiated by a nucleophilic acyl substitution on a non-enolizable aldehyde where the leaving group attacks another aldehyde. This results in an intermediate which is tetrahedral in geometry from the attack of hydroxide on a carbonyl.
Now, a proton is exchanged by acid and alkoxide ions. With the introduction of a base of high concentration, the aldehyde forms an anion which has a charge of two. After this step a hydride ion is transferred to a second molecule of the aldehyde, forming carboxylate and alkoxide ions.
The overall mechanism can be summarised by the following mechanism:

In the reaction, the reactant i.e. glyoxal does not have any alpha hydrogen so it will perform intramolecular Cannizzaro reaction. This means that one of the aldehydes will reduce and the other will oxidise.
Hence, the correct option is C.
The overall mechanism has been summarised as below:

Additional information: Another important reaction of aldehydes is aldol condensation. The reaction of aldehydes and ketones containing at least one $\alpha $ hydrogen is treated with dilute alkali; they form $\beta $ - hydroxy aldehydes or $\beta $ - hydroxy ketones (ketol) respectively. We know that in aldol condensation the hydroxide ion functions as a base moving the acidic hydrogen-producing the reactive enolate ion. Further, the aldehyde is attacked at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon by the nucleophilic enolate ion resulting in an alkoxide intermediate. The alkoxide ion now formed deprotonates the water molecule, ultimately resulting in hydroxide and the $\beta $ – hydroxy aldehyde.
Note: Acetaldehyde does not participate in Cannizzaro reaction because the alpha-hydrogens are deprotonated due to the alkaline environment. Since acetaldehyde contains three alpha hydrogen, it readily enolate ions upon deprotonation and therefore cannot participate in the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




