
The prothallus of the fern has -
(a)Antheridia and archegonia on the lower surface
(b)Antheridia and archegonia on the upper surface
(c)Antheridia on the upper surface and archegonia on the lower surface
(d)Antheridia on the lower surface and archegonia on the upper surface
Answer
567.9k+ views
Hint The prothallus holds the reproductive organs of the fern. The antheridia and archegonia are the male and female reproductive organs, respectively. Their location differs in different plants, such as mosses or ferns. In ferns, the antheridia are above the rhizoids and the archegonia are below the apical notch.
Complete answer: - The fern is a pteridophyte. It has a sexual phase (gametophyte) and an asexual phase (sporophyte) phase of reproduction in its life cycle.
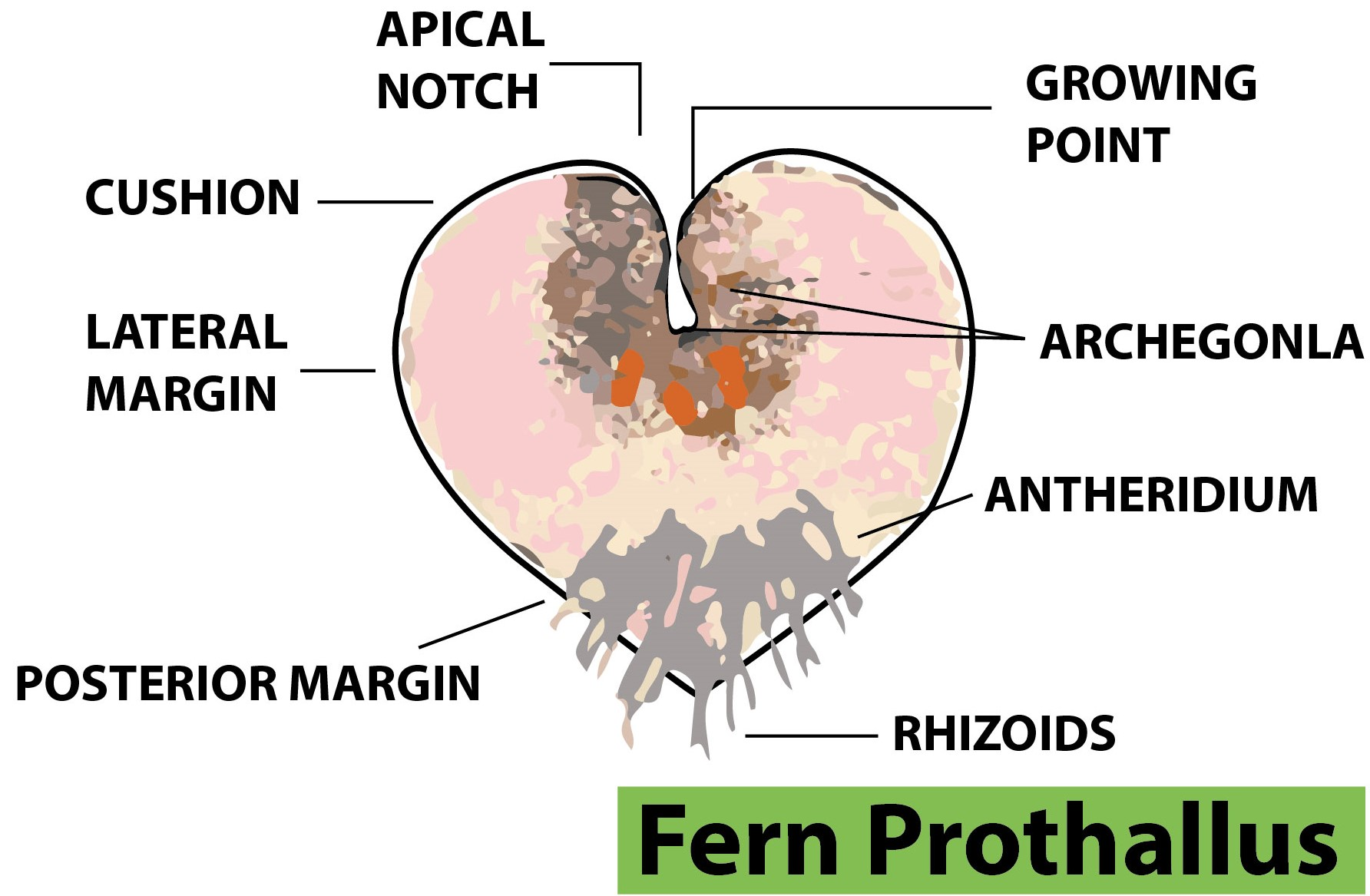
- The site of sexual reproduction occurs at the prothallus, a small heart-shaped structure. The antheridium is the male reproductive organ and the archegonium is the female reproductive organ.
- The antheridia are located in the posterior margin, above the rhizoids, while the archegonia are located in the lower side of the anterior margin, below the apical notch. Hence, both of these organs are located on the lower surface of the prothallus.
Additional information: - Rhizoids grow at the bottom of the prothallus which are root-like structures that anchor the prothallus and also function as roots to provide water and nutrients to the prothallus.
- The antheridium consists of a jacket of sterile cells with sperm-producing cells inside. The archegonium is divided into the upper neck and the lower center part. It contains one gamete which is always located in the venter, the lower, more, or less dilated portion.
- The antheridia contains antherozoid mother cells that produce antherozoids.
- Fertilization occurs when the sperm swim through free water toward simple organic acids like malic acid released at the opening of the archegonium. The neck of the archegonium spreads apart at the apex, permitting the neck cells to be extruded and the sperm to swim in and penetrate the egg, starting the formation of a diploid embryo.
So, the correct answer is ‘Antheridia and archegonia on the lower surface’.
Note: - The prothallus has a photosynthetic capacity that provides energy for the growth of the gametes.
- Antherozoids have flagella that help in motility during fertilization.
Complete answer: - The fern is a pteridophyte. It has a sexual phase (gametophyte) and an asexual phase (sporophyte) phase of reproduction in its life cycle.
- The site of sexual reproduction occurs at the prothallus, a small heart-shaped structure. The antheridium is the male reproductive organ and the archegonium is the female reproductive organ.
- The antheridia are located in the posterior margin, above the rhizoids, while the archegonia are located in the lower side of the anterior margin, below the apical notch. Hence, both of these organs are located on the lower surface of the prothallus.
Additional information: - Rhizoids grow at the bottom of the prothallus which are root-like structures that anchor the prothallus and also function as roots to provide water and nutrients to the prothallus.
- The antheridium consists of a jacket of sterile cells with sperm-producing cells inside. The archegonium is divided into the upper neck and the lower center part. It contains one gamete which is always located in the venter, the lower, more, or less dilated portion.
- The antheridia contains antherozoid mother cells that produce antherozoids.
- Fertilization occurs when the sperm swim through free water toward simple organic acids like malic acid released at the opening of the archegonium. The neck of the archegonium spreads apart at the apex, permitting the neck cells to be extruded and the sperm to swim in and penetrate the egg, starting the formation of a diploid embryo.
So, the correct answer is ‘Antheridia and archegonia on the lower surface’.

Note: - The prothallus has a photosynthetic capacity that provides energy for the growth of the gametes.
- Antherozoids have flagella that help in motility during fertilization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




