
The R and S configuration for each stereogenic centre in this from top to bottom is:
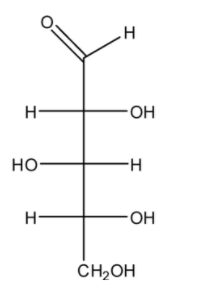
A.R, R, R
B.R, S, S
C.R, S, R
D.S, S, R

Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: From the CIP rules, one can easily figure out whether the configuration is S or R. On the count of 1,2,3 if it rotates in an anti-clockwise direction, it is S configuration and if clockwise, then it is R configuration. But the position of hydrogen must be away from the viewer.
Complete answer:
R.S. Cahn, C. Ingold, and V. Prelog and, as such, is also often called the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules. (CIP). Stereoisomers can be defined as compounds that have the same molecular formula and same connectivity of atoms but they differ in their three-dimensional orientation.
The right hand and left hand is a nomenclature used for the enantiomers of a chiral compound. Stereoisomers are compounds having the same molecular formula and same connectivity of atoms but differ in their 3D orientation. A stereocenter or stereogenic center is any point in a molecule, bearing different substituents, such that interchanging any two substituents leads to a stereoisomer. The stereocenters are labelled as R or S. For this, the substituents must be prioritized as stated in the rules below:
Rule 1- Firstly, atoms of higher atomic number should get priority. If there are four atoms then according to their atomic number, atom of higher priority is assigned number one while atom of least priority is assigned number four.
Rule 2- Let’s consider that the first atom in the two groups have the same atomic number, in such a case, relative priority of the group is decided by comparing the atomic number of the next atom in the two groups.
Rule 3- Lastly, all the multiple bonds should be treated as separate single bonds.
Rule 4- when lowest priority is at horizontal line, opposite configuration is considered.
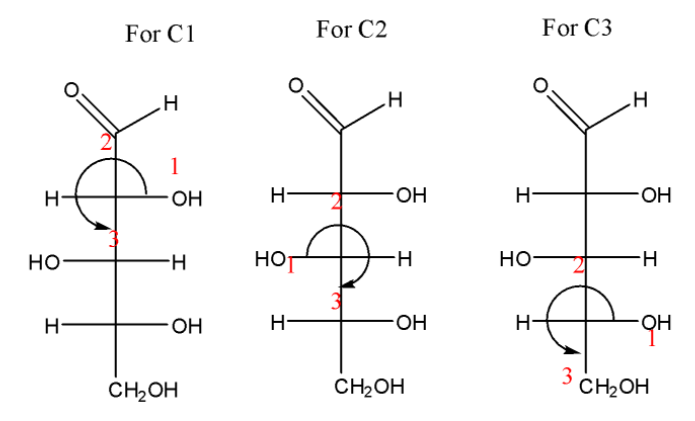
Now, look at the compound, it has three stereogenic centres at C1, C2 and C3 as they have all different substituents. Using CIP rules, let us check the configuration at C1. First priority is given to OH due to its high atomic number. Second to the long carbon chain, third to the CHO and fourth to the H. As H is on horizontal, on rotating it from $1 \to 2 \to 3$, we get S configuration changed to R. Similarly, in case of C2 and C3, we will get S and R respectively.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
Keep in mind that the lowest priority does not affect the direction of the arrow. However, this is very important as it is a requirement when assigning the R and S configuration. The lowest priority must point away from the viewer. As we saw, it shouldn’t be on the horizontal line, but if it is, then change the configuration to the opposite one.
Complete answer:
R.S. Cahn, C. Ingold, and V. Prelog and, as such, is also often called the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules. (CIP). Stereoisomers can be defined as compounds that have the same molecular formula and same connectivity of atoms but they differ in their three-dimensional orientation.
The right hand and left hand is a nomenclature used for the enantiomers of a chiral compound. Stereoisomers are compounds having the same molecular formula and same connectivity of atoms but differ in their 3D orientation. A stereocenter or stereogenic center is any point in a molecule, bearing different substituents, such that interchanging any two substituents leads to a stereoisomer. The stereocenters are labelled as R or S. For this, the substituents must be prioritized as stated in the rules below:
Rule 1- Firstly, atoms of higher atomic number should get priority. If there are four atoms then according to their atomic number, atom of higher priority is assigned number one while atom of least priority is assigned number four.
Rule 2- Let’s consider that the first atom in the two groups have the same atomic number, in such a case, relative priority of the group is decided by comparing the atomic number of the next atom in the two groups.
Rule 3- Lastly, all the multiple bonds should be treated as separate single bonds.
Rule 4- when lowest priority is at horizontal line, opposite configuration is considered.
Now, look at the compound, it has three stereogenic centres at C1, C2 and C3 as they have all different substituents. Using CIP rules, let us check the configuration at C1. First priority is given to OH due to its high atomic number. Second to the long carbon chain, third to the CHO and fourth to the H. As H is on horizontal, on rotating it from $1 \to 2 \to 3$, we get S configuration changed to R. Similarly, in case of C2 and C3, we will get S and R respectively.

Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
Keep in mind that the lowest priority does not affect the direction of the arrow. However, this is very important as it is a requirement when assigning the R and S configuration. The lowest priority must point away from the viewer. As we saw, it shouldn’t be on the horizontal line, but if it is, then change the configuration to the opposite one.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




