
The reaction in which $ \text{NaCN/ }{{\text{C}}_{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\text{OH/ HOH} $ is used is :
A) perkin reaction
B) benzoin condensation
C) reimer tiemann reaction
D) rosenmunds reduction
Answer
479.1k+ views
Hint: The chemical molecule benzaldehyde ( $ {{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\text{CHO} $ ) is made up of a benzene ring with a formyl substituent. It is the most basic aromatic aldehyde and one of the most valuable in industry. It's a colourless liquid with a distinctive almond scent. Benzaldehyde, the main component of bitter almond oil, may be derived from a variety of other natural sources.
Complete answer:
The benzoin addition is a process in which two aldehydes are added together. Aromatic aldehydes or glyoxals are commonly involved in this reaction. An acyloin is formed as a result of the reaction. Benzaldehyde is transformed to benzoin in the traditional use. Benzaldehyde is heated with ethanolic NaCN or KCN to create the self-condensing product benzoin in benzoin condensation.
Nucleophiles such as cyanide or an N-heterocyclic carbene catalyse the process. The cyanide anion (as sodium cyanide) interacts with the aldehyde in a nucleophilic addition in the first stage of this reaction. The carbonyl group's polarity is reversed as a result of the intermediate's rearrangement, and it then adds to the second carbonyl group in a second nucleophilic addition. The result of proton transfer and cyanide ion removal is benzoin. This is a reversible reaction, which implies that the distribution of products is governed by the products' and starting material's respective thermodynamic stability.
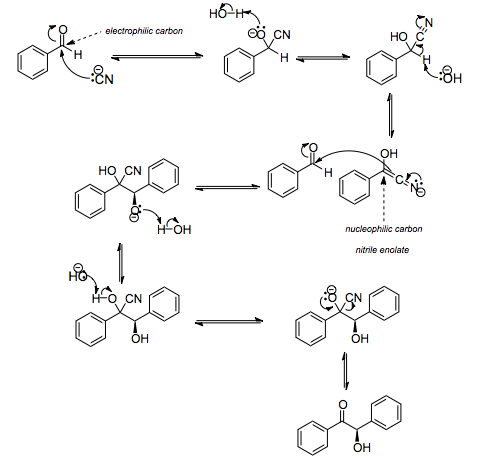
One aldehyde provides a proton and the other receives a proton in this reaction. Some aldehydes, such as 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, can only contribute protons, whereas benzaldehyde can receive and donate protons. Mixed benzoins, i.e. goods having different groups on either side of the product, can be synthesised this way. To avoid unwanted homo-dimerization, care should be exercised when matching a proton giving aldehyde with a proton accepting aldehyde.
Note:
With base catalysis in the presence of thiazolium salts, the reaction may be expanded to aliphatic aldehydes; the reaction mechanism is basically the same... The synthesis of heterocyclic compounds relies on these molecules. The Stetter reaction is the similar 1,4-addition of an aldehyde to an enone. The coenzyme thiamine is responsible for the production of acyloin-like compounds via the benzoin addition in biochemistry. A thiazolium moiety is also present in this coenzyme, which deprotonates to a nucleophilic carbene.
Complete answer:
The benzoin addition is a process in which two aldehydes are added together. Aromatic aldehydes or glyoxals are commonly involved in this reaction. An acyloin is formed as a result of the reaction. Benzaldehyde is transformed to benzoin in the traditional use. Benzaldehyde is heated with ethanolic NaCN or KCN to create the self-condensing product benzoin in benzoin condensation.
Nucleophiles such as cyanide or an N-heterocyclic carbene catalyse the process. The cyanide anion (as sodium cyanide) interacts with the aldehyde in a nucleophilic addition in the first stage of this reaction. The carbonyl group's polarity is reversed as a result of the intermediate's rearrangement, and it then adds to the second carbonyl group in a second nucleophilic addition. The result of proton transfer and cyanide ion removal is benzoin. This is a reversible reaction, which implies that the distribution of products is governed by the products' and starting material's respective thermodynamic stability.

One aldehyde provides a proton and the other receives a proton in this reaction. Some aldehydes, such as 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, can only contribute protons, whereas benzaldehyde can receive and donate protons. Mixed benzoins, i.e. goods having different groups on either side of the product, can be synthesised this way. To avoid unwanted homo-dimerization, care should be exercised when matching a proton giving aldehyde with a proton accepting aldehyde.
Note:
With base catalysis in the presence of thiazolium salts, the reaction may be expanded to aliphatic aldehydes; the reaction mechanism is basically the same... The synthesis of heterocyclic compounds relies on these molecules. The Stetter reaction is the similar 1,4-addition of an aldehyde to an enone. The coenzyme thiamine is responsible for the production of acyloin-like compounds via the benzoin addition in biochemistry. A thiazolium moiety is also present in this coenzyme, which deprotonates to a nucleophilic carbene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




