
The reaction of cyclohexanone with dimethylamine in the presence of the catalytic amount of an acid forms a compound. During the reaction if the water is continuously removed the compound formed is generally known as:
(A) An amine
(B) An imine
(C) An enamine
(D) A Schiff’s base
Answer
547.5k+ views
Hint: A substance used to speed up the reaction by changing the mechanism of reaction or reducing the activation energy is known as catalyst. Amines directly attack ketones and form amino hydroxyl compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Catalyst: Catalyst is a substance which is added to reactants to increase the reaction rate. The catalyst used is not consumed in the reaction, it is extracted back after completion of reaction, its only work is to increase the rate of the reaction.
Catalysts usually change the reaction mechanisms or speed up the reaction rate. Catalysts lower the activation energy (minimum amount of energy required to proceed the reaction) and hence the reaction occurs speedily.
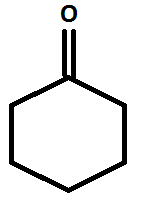
Structure of cyclohexanone:
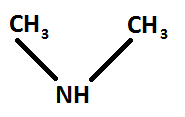
Structure of dimethylamine:
The reaction is as follows:
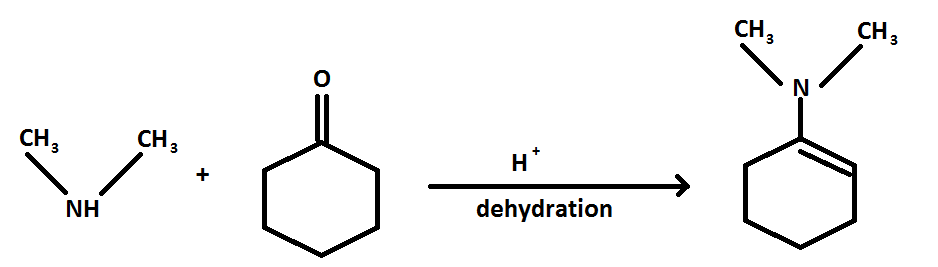
The reaction of cyclohexanone with dimethylamine in the presence of a catalyst is a sequential reaction.
When cyclohexanone reacts with dimethylamine in presence of acid a hydroxyl amine is formed, further when water is removed an enamine is formed as a product.
Hence option (C) is correct.
Note:
When cyclohexanone reacts with dimethylamine in the presence of a catalyst enamine is formed as a product by the reduction of water molecules as an intermediate step. Due to hindrance, the water molecule leaves the compound.
Complete step by step answer:
Catalyst: Catalyst is a substance which is added to reactants to increase the reaction rate. The catalyst used is not consumed in the reaction, it is extracted back after completion of reaction, its only work is to increase the rate of the reaction.
Catalysts usually change the reaction mechanisms or speed up the reaction rate. Catalysts lower the activation energy (minimum amount of energy required to proceed the reaction) and hence the reaction occurs speedily.
Structure of cyclohexanone:

Structure of dimethylamine:

The reaction is as follows:

The reaction of cyclohexanone with dimethylamine in the presence of a catalyst is a sequential reaction.
When cyclohexanone reacts with dimethylamine in presence of acid a hydroxyl amine is formed, further when water is removed an enamine is formed as a product.
Hence option (C) is correct.
Note:
When cyclohexanone reacts with dimethylamine in the presence of a catalyst enamine is formed as a product by the reduction of water molecules as an intermediate step. Due to hindrance, the water molecule leaves the compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




