
The repeating components of each DNA strand lengthwise is called?
Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: As we know DNA is a cluster of molecules that are responsible for carrying and transmitting hereditary materials or genetic information from parents to offsprings. They are also present in viruses as most of these entities have either RNA or DNA as their genetic material. Apart from the inheritance of genetic information, DNA also plays a crucial role in the production of proteins.
Complete answer:
The full form of DNA is Deoxyribonucleic Acid which is an organic compound that has a unique molecular structure. It is present in all prokaryotic cells as well as eukaryotic cells.
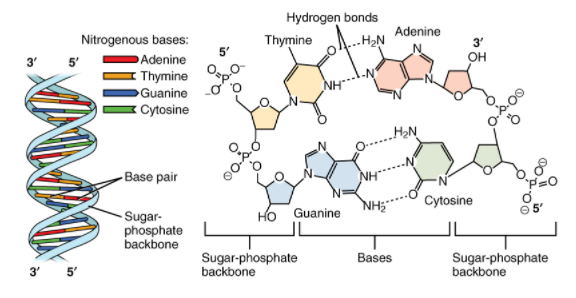
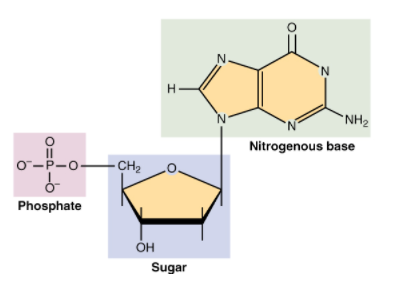
Each DNA strand comprises repeating nucleotides. Each nucleotide has phosphate and also sugar that is a pentose group attached lengthwise and a nitrogenous base (Adenine, Guanine, cytosine and thymine) attached to the sugar.
A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids. RNA and DNA are polymers that are made up of long chains of nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule which is either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA that is attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base.
There are three different types of DNA which are:
i) A-DNA: Dehydrated DNA takes an A form which protects the DNA during extreme condition such as desiccation.
ii) B-DNA: This is the most common DNA conformation, and it is a right-handed helix.
iii) Z-DNA: Z-DNA is a left-handed DNA where the double-helical structure is winded to the left in a zig-zag pattern.
So the repeating units of DNA strand are known as nucleotides.
Note: DNA was first recognized and identified by the Swiss biologist, Johannes Friedrich Miescher during his research on white blood cells. The double-helical structure of a DNA molecule was later discovered through the experimental data by James Watson and Francis Crick. Finally, it was proved that DNA is responsible for storing genetic information in human beings.
Complete answer:
The full form of DNA is Deoxyribonucleic Acid which is an organic compound that has a unique molecular structure. It is present in all prokaryotic cells as well as eukaryotic cells.
Each DNA strand comprises repeating nucleotides. Each nucleotide has phosphate and also sugar that is a pentose group attached lengthwise and a nitrogenous base (Adenine, Guanine, cytosine and thymine) attached to the sugar.
A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids. RNA and DNA are polymers that are made up of long chains of nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule which is either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA that is attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base.


There are three different types of DNA which are:
i) A-DNA: Dehydrated DNA takes an A form which protects the DNA during extreme condition such as desiccation.
ii) B-DNA: This is the most common DNA conformation, and it is a right-handed helix.
iii) Z-DNA: Z-DNA is a left-handed DNA where the double-helical structure is winded to the left in a zig-zag pattern.
So the repeating units of DNA strand are known as nucleotides.
Note: DNA was first recognized and identified by the Swiss biologist, Johannes Friedrich Miescher during his research on white blood cells. The double-helical structure of a DNA molecule was later discovered through the experimental data by James Watson and Francis Crick. Finally, it was proved that DNA is responsible for storing genetic information in human beings.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




