
The replication of DNA in meiosis occur during
A. S phase
B. S phase and leptotene
C. S phase and zygotene
D. All of the above
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Meiosis is a process where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the original amount of genetic information.
These cells are the sex cells – sperm in males, eggs in females.
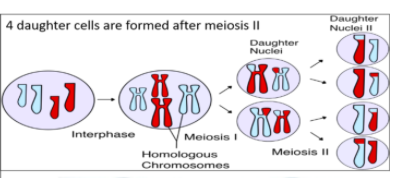
During meiosis, one cell divides twice to form four daughter cells.
Complete answer: In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells.
Each daughter cell has half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell.
The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II.
Before meiosis begins, during the S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids, which remain held together through sister chromatid cohesion. This S-phase can be referred to as "premeiotic S-phase" or "meiotic S-phase".
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
The cell cycle has four stages – G1, G2, S and M phase.
1. The M phase or mitotic phase has 4 phases - Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase.
2. The G1, G2, and S phase together are known as interphase.
3. Cytokinesis begins in anaphase and ends in telophase, reaching completion as the next interphase begins. Meiosis is divided into meiosis I and meiosis II.
4. Meiosis I is divided into Karyokinesis I and Cytokinesis I and Meiosis II is divided into Karyokinesis II and Cytokinesis II.
5. Meiosis includes the stages of meiosis I (prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I) and meiosis II (prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II).
Note: Interphase is followed by meiosis I and then meiosis II.
1. Meiosis I separate replicated homologous chromosomes, each still made up of two sister chromatids, into two daughter cells, thus reducing the chromosome number by half.
2. During meiosis II, sister chromatids decouple and the resultant daughter chromosomes are segregated into four daughter cells. For diploid organisms, the daughter cells resulting from meiosis are haploid and contain only one copy of each chromosome.
3. In some species, cells enter a resting phase known as interkinesis between meiosis I and meiosis II.
These cells are the sex cells – sperm in males, eggs in females.
During meiosis, one cell divides twice to form four daughter cells.
Complete answer: In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells.
Each daughter cell has half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell.
The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II.
Before meiosis begins, during the S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids, which remain held together through sister chromatid cohesion. This S-phase can be referred to as "premeiotic S-phase" or "meiotic S-phase".

So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
The cell cycle has four stages – G1, G2, S and M phase.
1. The M phase or mitotic phase has 4 phases - Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase.
2. The G1, G2, and S phase together are known as interphase.
3. Cytokinesis begins in anaphase and ends in telophase, reaching completion as the next interphase begins. Meiosis is divided into meiosis I and meiosis II.
4. Meiosis I is divided into Karyokinesis I and Cytokinesis I and Meiosis II is divided into Karyokinesis II and Cytokinesis II.
5. Meiosis includes the stages of meiosis I (prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I) and meiosis II (prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II).
Note: Interphase is followed by meiosis I and then meiosis II.
1. Meiosis I separate replicated homologous chromosomes, each still made up of two sister chromatids, into two daughter cells, thus reducing the chromosome number by half.
2. During meiosis II, sister chromatids decouple and the resultant daughter chromosomes are segregated into four daughter cells. For diploid organisms, the daughter cells resulting from meiosis are haploid and contain only one copy of each chromosome.
3. In some species, cells enter a resting phase known as interkinesis between meiosis I and meiosis II.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




