
The salts of ____ like sodium benzoate are used as food preservatives.
A.Acetic acid
B.Ethanoic acid
C.Benzoic acid
D.None of the above
Answer
594k+ views
Hint:
Sodium benzoate is produced by the neutralization of benzoic acid with sodium hydroxide.
Complete step by step answer:
Sodium benzoate has a melting point above 300 °C. Sodium Benzoate is extremely dissolvable or soluble in water (550–630 g/litre at 20 °C) and is hygroscopic at a comparative humidity of about above 50%. Its pH is around 7.5 at it has a concentration of 10 g/litre in water. It is soluble in various solvents like methanol, ethylene glycol, and methanol. In the dry state, sodium benzoate is capable of being electrically charged by frictional forces and forms an explosive mixture when the dust of sodium benzoate is dispersed in air. The molecular structure of Sodium Benzoate can be represented as:
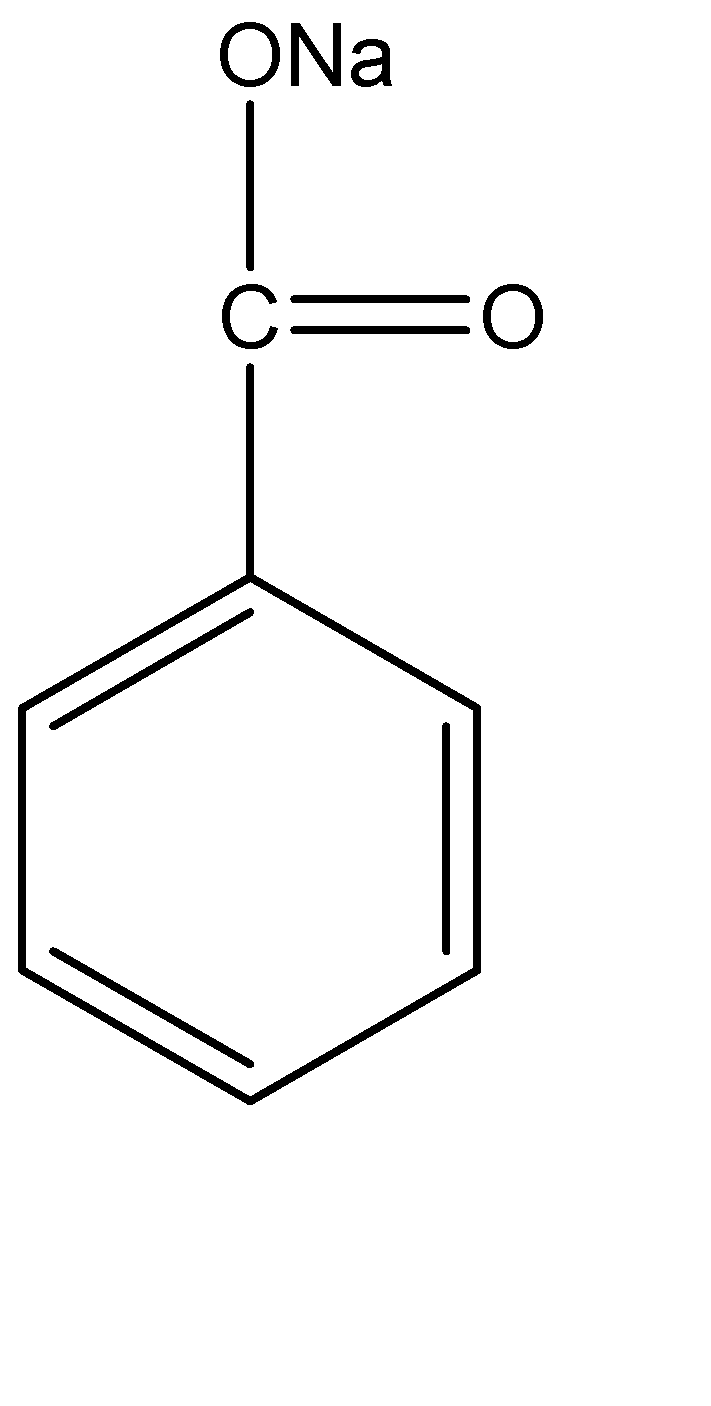
On the other hand, benzoic acid can be analytically determined using methods like spectrophotometric methods, which require extensive procedures for extraction and are not very specific. Another such methods are gas chromatographic (GC) methods, which are comparatively more sensitive for detection and specific, but they need lengthy sample preparation and derivatization in order to determine benzoic acid; also, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), is a method which has a relatively higher specificity and comparatively less amount of sample preparation and does not require derivatization.
Sodium benzoate is produced by the neutralization of benzoic acid with sodium hydroxide.
Benzoic acid is a white solid that starts to sublime at 100 °C, with a melting point of 122 °C and a boiling point of 249 °C. Its solubility in water is low (2.9 g/litre at 20 °C), and its solution in water is weakly acid (dissociation constant at 25 °C = 6.335 × 10–5; pKa 4.19). It is soluble in ethanol and very slightly soluble in benzene and acetone. of 1.9. Its vapour pressure at 20 °C ranges from 0.11 to 0.53 Pa. The molecular structure of benzoic acid is
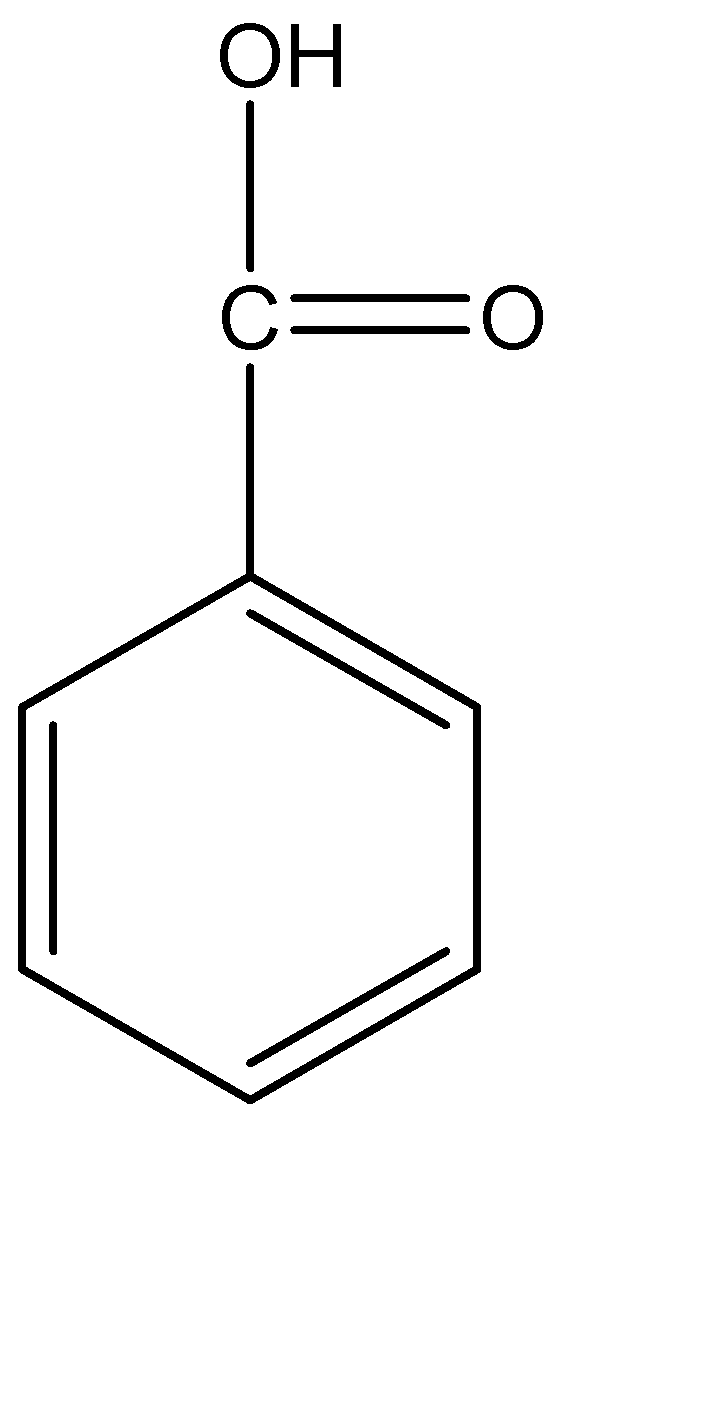
Sodium benzoate and benzoic acid both inhibit the growth of potentially harmful bacteria, mold, and other microbes in food, thus deterring spoilage. Both are particularly effective in acidic foods. Hence, they are commonly used in foods, such as soda, bottled lemon juice, pickles, jelly, salad dressing, soy sauce, and other condiments
Hence, Option C is the correct option.
Note:
In the food industry, acetic acid in lower concentrations is used as a food additive, flavouring and preservative. Acetic acid regulates food acidity.
Sodium benzoate is produced by the neutralization of benzoic acid with sodium hydroxide.
Complete step by step answer:
Sodium benzoate has a melting point above 300 °C. Sodium Benzoate is extremely dissolvable or soluble in water (550–630 g/litre at 20 °C) and is hygroscopic at a comparative humidity of about above 50%. Its pH is around 7.5 at it has a concentration of 10 g/litre in water. It is soluble in various solvents like methanol, ethylene glycol, and methanol. In the dry state, sodium benzoate is capable of being electrically charged by frictional forces and forms an explosive mixture when the dust of sodium benzoate is dispersed in air. The molecular structure of Sodium Benzoate can be represented as:

On the other hand, benzoic acid can be analytically determined using methods like spectrophotometric methods, which require extensive procedures for extraction and are not very specific. Another such methods are gas chromatographic (GC) methods, which are comparatively more sensitive for detection and specific, but they need lengthy sample preparation and derivatization in order to determine benzoic acid; also, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), is a method which has a relatively higher specificity and comparatively less amount of sample preparation and does not require derivatization.
Sodium benzoate is produced by the neutralization of benzoic acid with sodium hydroxide.
Benzoic acid is a white solid that starts to sublime at 100 °C, with a melting point of 122 °C and a boiling point of 249 °C. Its solubility in water is low (2.9 g/litre at 20 °C), and its solution in water is weakly acid (dissociation constant at 25 °C = 6.335 × 10–5; pKa 4.19). It is soluble in ethanol and very slightly soluble in benzene and acetone. of 1.9. Its vapour pressure at 20 °C ranges from 0.11 to 0.53 Pa. The molecular structure of benzoic acid is

Sodium benzoate and benzoic acid both inhibit the growth of potentially harmful bacteria, mold, and other microbes in food, thus deterring spoilage. Both are particularly effective in acidic foods. Hence, they are commonly used in foods, such as soda, bottled lemon juice, pickles, jelly, salad dressing, soy sauce, and other condiments
Hence, Option C is the correct option.
Note:
In the food industry, acetic acid in lower concentrations is used as a food additive, flavouring and preservative. Acetic acid regulates food acidity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




