
The shape of carbonium ion is:
A) Planar
B) Linear
C) Pyramidal
D) Tetrahedral
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: Carbonium ion or carbocation is a member of a class of organic molecules with a positively charged pentavalent carbon atom. Carbon here is $s{p^2}$ hybridized. $s{p^2}$ hybridized is the mixture of one s-orbital and two p-orbitals.
Complete answer:
In chemistry, carbonium ion is a hydrocarbon ion with a positive charge on a carbon atom. It has a pentavalent carbon atom. In organic reactions, carbonium ions are one of the most common classes of intermediates. Some examples of carbonium ions are:
Methanium $C{H_5}^ + $
Ethenium ${C_2}{H_5}^ + $
In carbonium ion, a positively charged carbon atom is in $s{p^2}$ hybridization state. So, its shape is triangular planar. A $sp^2$ hybridized atom’s molecular geometry is trigonal as it has 3 sigma bonds. Carbonium ion has electron-deficient nature as there is a vacant p orbital which shows its nature. In valence shell carbon has 6 electrons. Thus, it is an electron deficient species.
The structure of carbonium ion is given below:
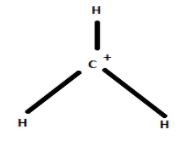
The carbonium ion or carbocation has a planar geometry.
Thus, the correct answer is option A. i.e., Planar.
Additional information: Carbonium ions react with the groups which can donate a pair of electrons. Thus, they are very reactive. The order of stability of carbonium ions are:
$C{H_3}^ + $(Methyl carbocation) < Primary carbocation < Secondary carbocation < Tertiary carbocation
The stability of carbocations depends on:
Resonance, Hyperconjugation and inductive effect, Electronegativity.
Carbonium ion’s nature depends upon the Carbon-atom bearing positive charge.
Note: Today Carbonium ion is also known as Carbenium. In the $s{p^2}$ hybridisation, the 1-s and 2 p-orbital are oriented in the trigonal planar geometry with the bond angle of ${120^ \circ }$. The positive charge present on the carbon atom with six electrons in the valence shell.
Complete answer:
In chemistry, carbonium ion is a hydrocarbon ion with a positive charge on a carbon atom. It has a pentavalent carbon atom. In organic reactions, carbonium ions are one of the most common classes of intermediates. Some examples of carbonium ions are:
Methanium $C{H_5}^ + $
Ethenium ${C_2}{H_5}^ + $
In carbonium ion, a positively charged carbon atom is in $s{p^2}$ hybridization state. So, its shape is triangular planar. A $sp^2$ hybridized atom’s molecular geometry is trigonal as it has 3 sigma bonds. Carbonium ion has electron-deficient nature as there is a vacant p orbital which shows its nature. In valence shell carbon has 6 electrons. Thus, it is an electron deficient species.
The structure of carbonium ion is given below:

The carbonium ion or carbocation has a planar geometry.
Thus, the correct answer is option A. i.e., Planar.
Additional information: Carbonium ions react with the groups which can donate a pair of electrons. Thus, they are very reactive. The order of stability of carbonium ions are:
$C{H_3}^ + $(Methyl carbocation) < Primary carbocation < Secondary carbocation < Tertiary carbocation
The stability of carbocations depends on:
Resonance, Hyperconjugation and inductive effect, Electronegativity.
Carbonium ion’s nature depends upon the Carbon-atom bearing positive charge.
Note: Today Carbonium ion is also known as Carbenium. In the $s{p^2}$ hybridisation, the 1-s and 2 p-orbital are oriented in the trigonal planar geometry with the bond angle of ${120^ \circ }$. The positive charge present on the carbon atom with six electrons in the valence shell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




