
The shape of red blood cells is
(a)Disc
(b)Amoeboid
(c)Cuboid
(d)Spherical
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint The red blood cells in the human body have a particular shape for carrying out their primary functions of oxygen transport. The change in the shape is indicative of the maturity of the cell or a stress affecting the cells.
Complete answer:
- Human red blood cells (RBCs), or erythrocytes, are disc-shaped under physiological conditions. More specifically, they are biconcave in shape. The shape of these cells helps in efficient transport through narrow blood vessels.
- RBCs are the primary cellular component of blood, which is a connective tissue in the human body required for important functions such as oxygen and hormone transport.
- The typical human RBC is much smaller than other somatic cells. It has a diameter of 6 - 8 diameters and a thickness of 2 micrometers.
- A change in the shape of the RBC will make it inefficient in oxygen transport and gas exchange. This is observed in spherocytic anemia where the cells are spherical and sickle-cell anemia where the cells are sickle-shaped.
Additional Information:
- The RBCs contain hemoglobin molecules that carry out the oxygen transport. These molecules turn bright red on binding with oxygen.
- RBCs are considered as cells but do not contain a nucleus, nuclear DNA, and other organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. Due to this, the cells do not undergo fission or carry out aerobic respiration as they only carry the oxygen.
- Hemoglobin transports almost 98 % of oxygen through the body. The rest is transported as dissolved molecules in the plasma.
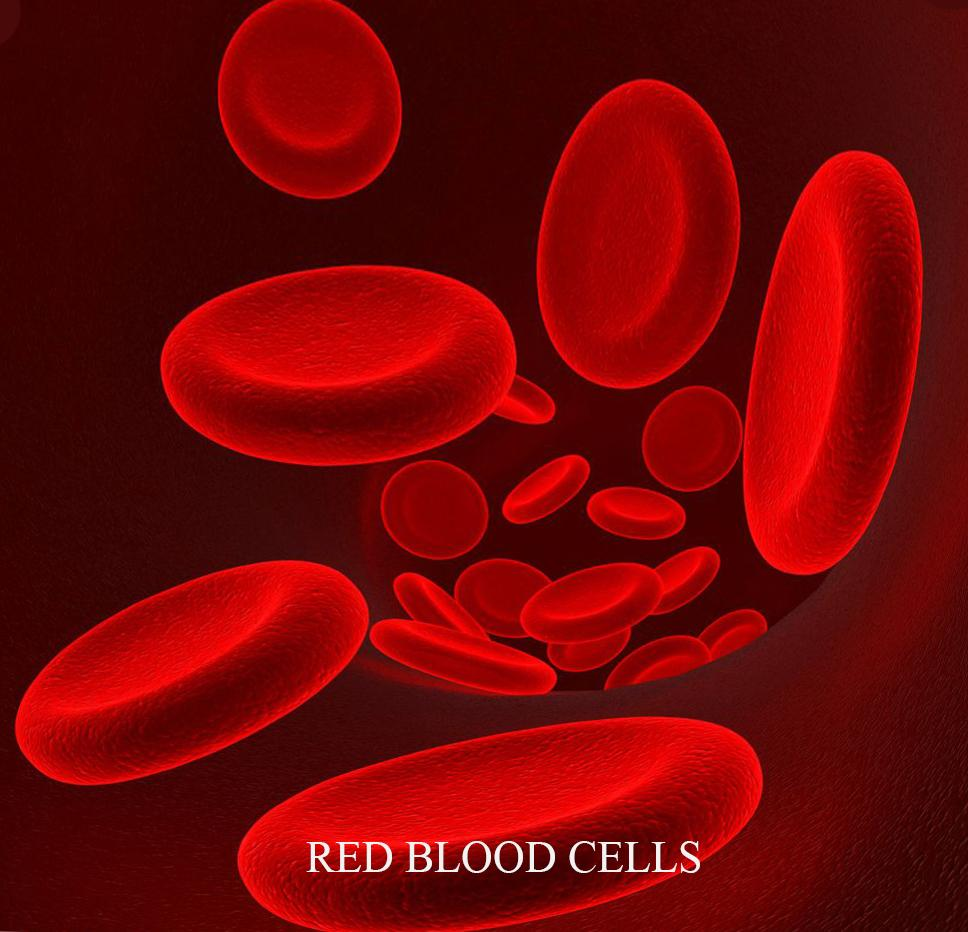
So, the correct answer is ‘disc’.
Note: - Adult healthy humans contain approximately 20-30 trillion RBCs at any given time.
- The shape of the RBC is also known as ‘discocyte’.
- RBCs are formed in the red bone marrow of bones and the old and damaged cells are eliminated or recycled by the spleen and the liver.
Complete answer:
- Human red blood cells (RBCs), or erythrocytes, are disc-shaped under physiological conditions. More specifically, they are biconcave in shape. The shape of these cells helps in efficient transport through narrow blood vessels.
- RBCs are the primary cellular component of blood, which is a connective tissue in the human body required for important functions such as oxygen and hormone transport.
- The typical human RBC is much smaller than other somatic cells. It has a diameter of 6 - 8 diameters and a thickness of 2 micrometers.
- A change in the shape of the RBC will make it inefficient in oxygen transport and gas exchange. This is observed in spherocytic anemia where the cells are spherical and sickle-cell anemia where the cells are sickle-shaped.
Additional Information:
- The RBCs contain hemoglobin molecules that carry out the oxygen transport. These molecules turn bright red on binding with oxygen.
- RBCs are considered as cells but do not contain a nucleus, nuclear DNA, and other organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. Due to this, the cells do not undergo fission or carry out aerobic respiration as they only carry the oxygen.
- Hemoglobin transports almost 98 % of oxygen through the body. The rest is transported as dissolved molecules in the plasma.

So, the correct answer is ‘disc’.
Note: - Adult healthy humans contain approximately 20-30 trillion RBCs at any given time.
- The shape of the RBC is also known as ‘discocyte’.
- RBCs are formed in the red bone marrow of bones and the old and damaged cells are eliminated or recycled by the spleen and the liver.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




