
The shape of \[Xe{{F}_{4}}\] is: -
(a)- tetrahedral
(b)- octahedral
(c)- square planar
(d)- pyramidal
Answer
520.8k+ views
Hint: The shape of \[Xe{{F}_{4}}\] is based on the number of atoms joined to the central atom. Not only atoms, but lone pairs are also considered for the shape. For finding the shape of a compound the number of total number of electron pairs and number of lone pairs should be calculated with the help of valence electrons, number of bonds etc.
Complete step by step answer:
Both the VSEPR theory and the concept of hybridization are applied to predict the molecular geometries of xenon compounds.
According to the VSEPR theory, the shape of the molecule is predicted by the total number of electron pairs (lone pairs + bond pairs) in the valence shell of the central Xe atom.
To calculate the total number of electron pairs:
\[\dfrac{\text{valence electrons of central atom + number of bonded atoms}}{\text{2}}\]
With the above formula: \[\dfrac{8+4}{2}=6\]
Hence, there are 6 electron pairs.
Since there are 4 fluorine atoms joined to xenon. So, there will be a 4bond pair of electrons.
Now for calculating the number of lone pairs in the compound: -
total number of electron pairs –number of bond pairs.
Lone pairs=\[6-4=2\].
Hence, in the compound, there are 2 lone pairs.
Depending on the number of \[Xe-F\] covalent bonds to be formed, the requisite number of electrons of the of the\[5p-orbital\] valence shell of Xe get unpaired and promoted to the vacant \[5d-orbitals\] followed by hybridization.
Since, there are 6 electron pairs, the hybridization of the compound will be \[s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}\].
So, the hybridization is \[s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}\] and it has 2 lone pairs, the shape of \[Xe{{F}_{4}}\] is square planar.
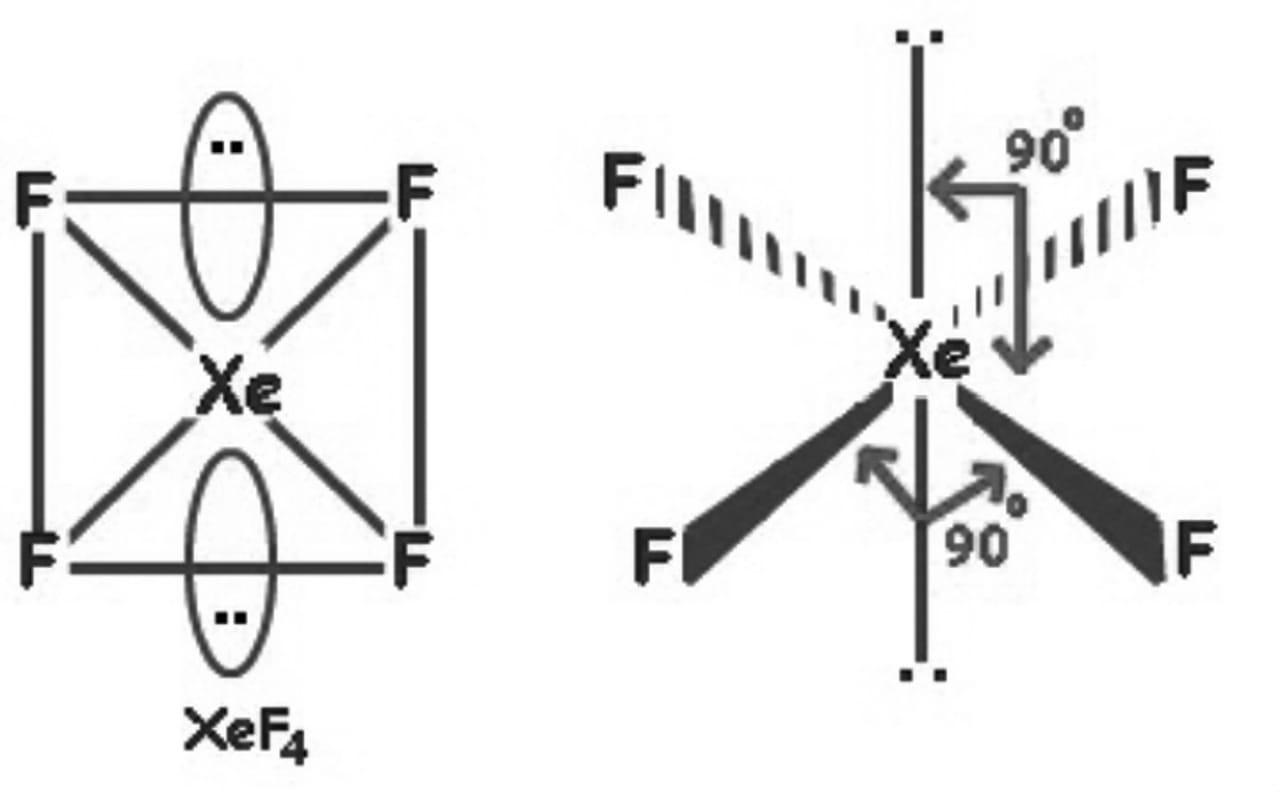
Hence, the correct answer is an option (c)- square planar.
Note: Whenever you are drawing the compound structure the number of lone pairs should also be considered. In this example also there are 4 fluorine atoms with xenon, so you could get confused between tetrahedral and square planar shape.
Complete step by step answer:
Both the VSEPR theory and the concept of hybridization are applied to predict the molecular geometries of xenon compounds.
According to the VSEPR theory, the shape of the molecule is predicted by the total number of electron pairs (lone pairs + bond pairs) in the valence shell of the central Xe atom.
To calculate the total number of electron pairs:
\[\dfrac{\text{valence electrons of central atom + number of bonded atoms}}{\text{2}}\]
With the above formula: \[\dfrac{8+4}{2}=6\]
Hence, there are 6 electron pairs.
Since there are 4 fluorine atoms joined to xenon. So, there will be a 4bond pair of electrons.
Now for calculating the number of lone pairs in the compound: -
total number of electron pairs –number of bond pairs.
Lone pairs=\[6-4=2\].
Hence, in the compound, there are 2 lone pairs.
Depending on the number of \[Xe-F\] covalent bonds to be formed, the requisite number of electrons of the of the\[5p-orbital\] valence shell of Xe get unpaired and promoted to the vacant \[5d-orbitals\] followed by hybridization.
Since, there are 6 electron pairs, the hybridization of the compound will be \[s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}\].
So, the hybridization is \[s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}\] and it has 2 lone pairs, the shape of \[Xe{{F}_{4}}\] is square planar.

Hence, the correct answer is an option (c)- square planar.
Note: Whenever you are drawing the compound structure the number of lone pairs should also be considered. In this example also there are 4 fluorine atoms with xenon, so you could get confused between tetrahedral and square planar shape.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




