
The S.I unit of magnetic moment is ________.
Answer
524k+ views
Hint: The magnetic moment of a bar magnet is defined as the product of one of the pole strengths with the distance between the poles (magnetic length). It’s a vector quantity and conventionally its direction taken from S- pole to N- pole.
Formulas used:
The magnetic dipole moment of a magnet having pole strength ${{q}_{m}}$and the distance between the poles $2\overrightarrow{l}$(directed from S-pole to N-pole) is given by
$\overrightarrow{m}={{q}_{m}}\times 2\overrightarrow{l}$
Torque on a magnetic dipole in a magnetic field with strength $\overrightarrow{B}$is given by
$\tau =\text{ Force }\times \text{ perpendicular distance}$
$\tau =mB\sin \theta \ \text{ or }\overrightarrow{\tau }=\overrightarrow{m}\times \overrightarrow{B}$
Complete step by step answer:
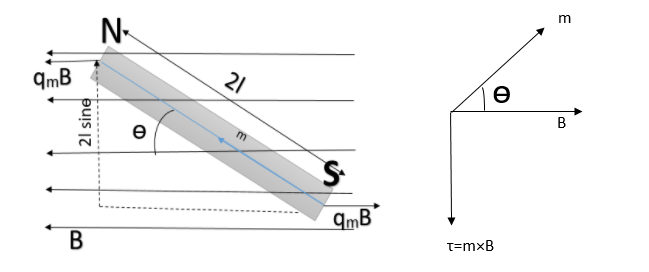
Consider a bar magnet of length $2l$ placed in an uniform magnetic field $\overrightarrow{B}$. Let ${{q}_{m}}$be the pole strength of each pole. Let the magnetic axis make an angle $\theta $ with the field.
Force on North-pole is ${{F}_{N}}={{q}_{m}}B$ along $\overrightarrow{B}$
Force on South-pole is ${{F}_{S}}={{q}_{m}}B$ opposite to $\overrightarrow{B}$
The force on the two poles are equal and opposite, they form a couple, moment of couple or torque is given by
$\begin{align}
& \tau =\text{ Force }\times \text{ perpendicular distance} \\
& \Rightarrow \tau \text{=}{{\text{q}}_{m}}B\times 2l\sin \theta \\
& \Rightarrow \tau =mB\sin \theta \\
\end{align}$
Where $m={{q}_{m}}\times 2l$ is a magnetic dipole moment or simply magnetic moment of the magnet.
In vector form the torque is written as $=\overrightarrow{m}\times \overrightarrow{B}$
Unit of magnetic moment:
$m=\dfrac{\tau }{B\sin \theta }$
The S.I unit of $\tau $ is \[\text{Newton}\times \text{meter or }Nm\] and the unit of $B$is Tesla.
So S.I unit of magnetic moment is $\dfrac{1Nm}{1T.1}=Nm{{T}^{-1}}\text{ or }J{{T}^{-1}}\text{ or Ampere}\times {{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Additional Information:
The direction of torque is perpendicular to the plane containing both the magnet and the magnetic field. The effect of the torque is to make the magnet align itself parallel to the external magnetic field. Due to this a freely suspended magnet aligns itself in the north south direction.
Note:
When the angle between the magnetic axis and the external field is zero i.e. $\theta =0$ then $\tau =0$. So the torque is minimum when the magnet aligns itself in the direction of the applied field.
When the magnet lies perpendicular to the field then \[\theta =90{}^\circ \] so $\tau =mB$. So the maximum torque is experienced when the dipole lies perpendicular to the Magnetic field.
Formulas used:
The magnetic dipole moment of a magnet having pole strength ${{q}_{m}}$and the distance between the poles $2\overrightarrow{l}$(directed from S-pole to N-pole) is given by
$\overrightarrow{m}={{q}_{m}}\times 2\overrightarrow{l}$
Torque on a magnetic dipole in a magnetic field with strength $\overrightarrow{B}$is given by
$\tau =\text{ Force }\times \text{ perpendicular distance}$
$\tau =mB\sin \theta \ \text{ or }\overrightarrow{\tau }=\overrightarrow{m}\times \overrightarrow{B}$
Complete step by step answer:

Consider a bar magnet of length $2l$ placed in an uniform magnetic field $\overrightarrow{B}$. Let ${{q}_{m}}$be the pole strength of each pole. Let the magnetic axis make an angle $\theta $ with the field.
Force on North-pole is ${{F}_{N}}={{q}_{m}}B$ along $\overrightarrow{B}$
Force on South-pole is ${{F}_{S}}={{q}_{m}}B$ opposite to $\overrightarrow{B}$
The force on the two poles are equal and opposite, they form a couple, moment of couple or torque is given by
$\begin{align}
& \tau =\text{ Force }\times \text{ perpendicular distance} \\
& \Rightarrow \tau \text{=}{{\text{q}}_{m}}B\times 2l\sin \theta \\
& \Rightarrow \tau =mB\sin \theta \\
\end{align}$
Where $m={{q}_{m}}\times 2l$ is a magnetic dipole moment or simply magnetic moment of the magnet.
In vector form the torque is written as $=\overrightarrow{m}\times \overrightarrow{B}$
Unit of magnetic moment:
$m=\dfrac{\tau }{B\sin \theta }$
The S.I unit of $\tau $ is \[\text{Newton}\times \text{meter or }Nm\] and the unit of $B$is Tesla.
So S.I unit of magnetic moment is $\dfrac{1Nm}{1T.1}=Nm{{T}^{-1}}\text{ or }J{{T}^{-1}}\text{ or Ampere}\times {{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Additional Information:
The direction of torque is perpendicular to the plane containing both the magnet and the magnetic field. The effect of the torque is to make the magnet align itself parallel to the external magnetic field. Due to this a freely suspended magnet aligns itself in the north south direction.
Note:
When the angle between the magnetic axis and the external field is zero i.e. $\theta =0$ then $\tau =0$. So the torque is minimum when the magnet aligns itself in the direction of the applied field.
When the magnet lies perpendicular to the field then \[\theta =90{}^\circ \] so $\tau =mB$. So the maximum torque is experienced when the dipole lies perpendicular to the Magnetic field.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




