
The site of glycolysis/EMP is
(a)Chloroplast
(b)Chromosome
(c)Cytoplasm
(d)Nucleus
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: This is a thick solution that fills each cell and is enclosed by the cell membrane. It is mainly made up of water, salts, and proteins. In eukaryotic cells, they include all of the material inside the cell and outside of the nucleus.
Complete answer:
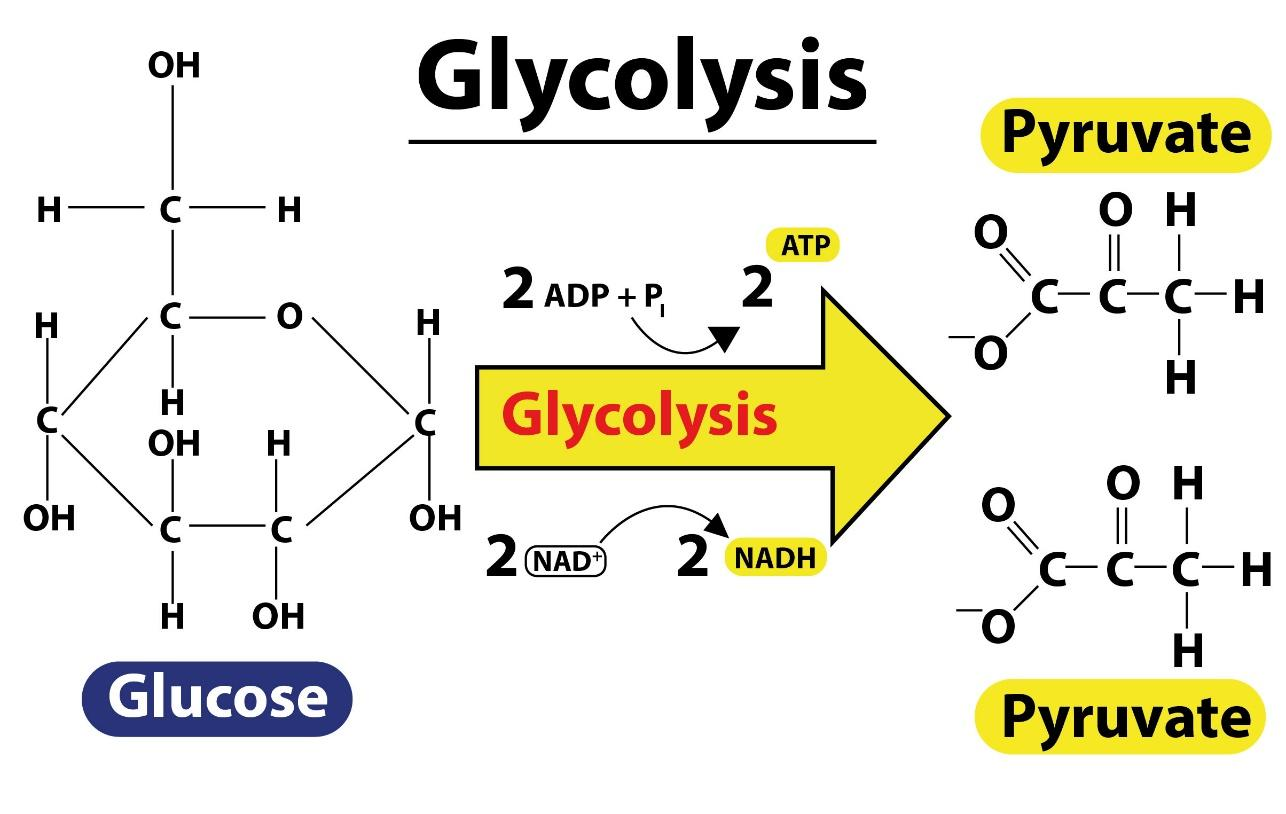
Glycolysis is the process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy. It produces two molecules of pyruvate, ATP, NADH, and water. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell, in the presence or absence of oxygen.
Additional Information: Steps involved in the glycolysis are-
-A phosphate group is added to glucose in the cytoplasm of the cell, by the action of enzyme hexokinase. In this, a phosphate group is transferred from ATP to glucose forming glucose,6-phosphate.
-Glucose-6-phosphate is isomerized into fructose,6-phosphate by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase.
-The other ATP molecule transfers a phosphate group to fructose 6-phosphate and converts it into fructose 1,6-bisphosphate by the action of enzyme phosphofructokinase.
-The enzyme aldolase converts fructose 1,6-bisphosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate, which are isomers of each other.
-Triose-phosphate isomerase converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate which is the substrate in the successive step of glycolysis.
-The enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase transfers 1 hydrogen molecule from glyceraldehyde phosphate to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide to form NADH along with hydrogen ion. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase adds a phosphate to the oxidized glyceraldehyde phosphate to form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
-Phosphate is transferred from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP to form ATP with the help of phosphoglycerokinase. Thus two molecules of phosphoglycerate and ATP are obtained at the end of this reaction.
-The phosphate of both the phosphoglycerate molecules is relocated from the third to the second carbon to yield two molecules of 2-phosphoglycerate by the enzyme phosphoglyceromutase.
-The enzyme enolase removes a water molecule from 2-phosphoglycerate to form phosphoenolpyruvate.
-A phosphate from phosphoenolpyruvate is transferred to ADP to form pyruvate and ATP by the action of pyruvate kinase. Two molecules of pyruvate and ATP are obtained as the end products.
So, the correct answer is ‘Cytoplasm’.
Note: This metabolic pathway was discovered by three German biochemists- Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas in the early 19th century and are known as the EMP pathway (Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas).
Complete answer:
Glycolysis is the process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy. It produces two molecules of pyruvate, ATP, NADH, and water. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell, in the presence or absence of oxygen.
Additional Information: Steps involved in the glycolysis are-
-A phosphate group is added to glucose in the cytoplasm of the cell, by the action of enzyme hexokinase. In this, a phosphate group is transferred from ATP to glucose forming glucose,6-phosphate.
-Glucose-6-phosphate is isomerized into fructose,6-phosphate by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase.
-The other ATP molecule transfers a phosphate group to fructose 6-phosphate and converts it into fructose 1,6-bisphosphate by the action of enzyme phosphofructokinase.
-The enzyme aldolase converts fructose 1,6-bisphosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate, which are isomers of each other.
-Triose-phosphate isomerase converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate which is the substrate in the successive step of glycolysis.
-The enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase transfers 1 hydrogen molecule from glyceraldehyde phosphate to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide to form NADH along with hydrogen ion. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase adds a phosphate to the oxidized glyceraldehyde phosphate to form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
-Phosphate is transferred from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP to form ATP with the help of phosphoglycerokinase. Thus two molecules of phosphoglycerate and ATP are obtained at the end of this reaction.
-The phosphate of both the phosphoglycerate molecules is relocated from the third to the second carbon to yield two molecules of 2-phosphoglycerate by the enzyme phosphoglyceromutase.
-The enzyme enolase removes a water molecule from 2-phosphoglycerate to form phosphoenolpyruvate.
-A phosphate from phosphoenolpyruvate is transferred to ADP to form pyruvate and ATP by the action of pyruvate kinase. Two molecules of pyruvate and ATP are obtained as the end products.

So, the correct answer is ‘Cytoplasm’.
Note: This metabolic pathway was discovered by three German biochemists- Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas in the early 19th century and are known as the EMP pathway (Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




