
The six carbon atoms of benzene are of:
(A) One type
(B) Two types
(C) Three types
(D) Four types
Answer
498k+ views
Hint: The different types of carbon in an organic compound can be present only if they differ in the type of hybridization or the type of substituents attached to them. If the bond lengths, hybridization and the neighboring groups of carbon atoms are the same, then they are considered to be of one type.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Benzene is an aromatic compound consisting of a six-membered ring in which the carbon atoms are alternatively double bonded. Each carbon atom is attached to two adjacent carbon atoms and a hydrogen atom. Thus, the neighboring group of each carbon atom is the same.
Though all carbon atoms in the six-membered ring are linked through double bonds, the bond distances are exactly the same for all carbon atoms. The resonance (delocalization of $ \pi $ electrons or bonds throughout the benzene ring) makes all the carbon atoms partially double bonded and equivalent in nature.
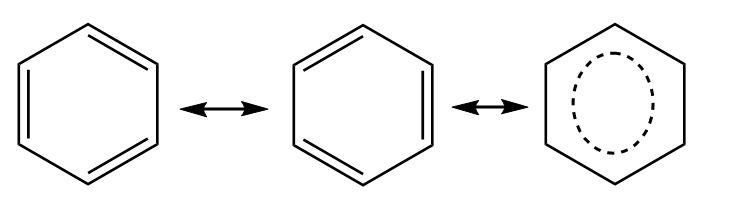
Each carbon atom in benzene is $ s{p^2} $ hybridized and contributes equally in the aromaticity of the structure resulting in a planar hexagonal ring.
$ \Rightarrow $ Thus, all six carbon atoms are of one type in a benzene ring due to equal bond distances and same hybridization and option (a) is correct.
Note:
Due to the delocalization, the bond distances change and are somewhere in between the regular double bond and single bond distances, which is why benzene is said to have partial double bonds. The double bonds in benzene therefore do not behave as normal double bonds found in alkenes.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Benzene is an aromatic compound consisting of a six-membered ring in which the carbon atoms are alternatively double bonded. Each carbon atom is attached to two adjacent carbon atoms and a hydrogen atom. Thus, the neighboring group of each carbon atom is the same.
Though all carbon atoms in the six-membered ring are linked through double bonds, the bond distances are exactly the same for all carbon atoms. The resonance (delocalization of $ \pi $ electrons or bonds throughout the benzene ring) makes all the carbon atoms partially double bonded and equivalent in nature.

Each carbon atom in benzene is $ s{p^2} $ hybridized and contributes equally in the aromaticity of the structure resulting in a planar hexagonal ring.
$ \Rightarrow $ Thus, all six carbon atoms are of one type in a benzene ring due to equal bond distances and same hybridization and option (a) is correct.
Note:
Due to the delocalization, the bond distances change and are somewhere in between the regular double bond and single bond distances, which is why benzene is said to have partial double bonds. The double bonds in benzene therefore do not behave as normal double bonds found in alkenes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




