
The skeletal structure of $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$ as shown above is correct but some of the bonds are shown incorrectly. Write the correct Lewis structure for acetic acid.
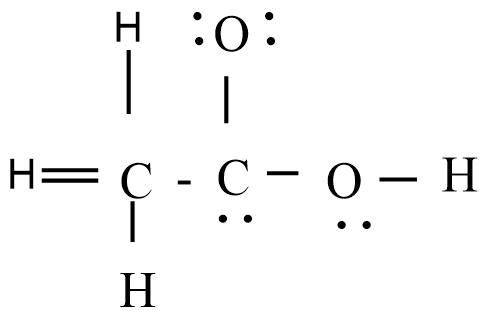
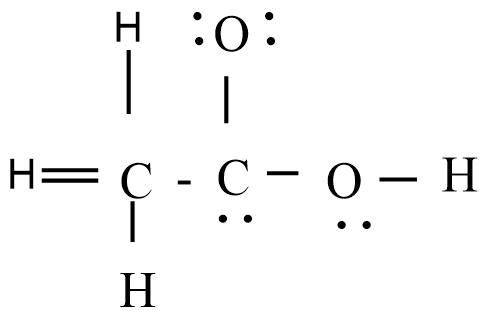
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: In order to explain the formation of chemical bonding in terms of electrons, Kossel-Lewis structure approach was first to provide some logical explanation of valence which was based on the inertness of noble gases. Lewis postulated that atoms achieve the stable octet when they are linked chemical bonds
Complete step by step answer:
Lewis structure and symbols:
In the formation of molecules, only outer shell electrons take part in chemical combination and known as valence electrons. Inner shell electrons and are protected and not involved in the combination process. G.N.lewis, an American scientist introduced simple notations to represent the valence electrons in an atom. These notations are called Lewis symbols. For example, Lewis notation for carbon, oxygen and hydrogen,
Octet rule: Kossel and Lewis developed a theory of chemical combination between atoms known as electron theory of chemical bonding. According to this, atoms can combine either transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another atom or by sharing of valence electrons in order to have an octet in their valence shells. This is known as the Octet rule.
The dots represent electrons, such structure referred to as Lewis dot structures. Let us apply Lewis dot structure to a given molecule $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$ in which combining atoms are different. The important condition follows that:
Each bond is formed as a result of sharing an electron pair between atoms.
Each combining atom contributes at least one electron to the shared pair.
The combining atoms attain the outer shell noble gas configuration as a result of the sharing of electrons.
Then the correct Lewis structure for acetic acid is:
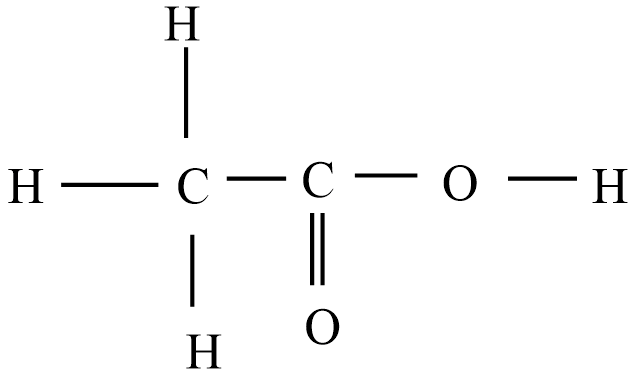
For acetic acid, O has 2 valence electrons forms two bonds
C has 4 valence electrons forms four bonds
H has one valence electron which forms one bond.
Note: The number of dots around the symbol represents the number of valence electrons. This number of valence electrons helps to calculate the common or group valence of the element. The bond formed, as a result of the electrostatic attraction between the positive and negative ions was termed as the electro covalent bond.
Complete step by step answer:
Lewis structure and symbols:
In the formation of molecules, only outer shell electrons take part in chemical combination and known as valence electrons. Inner shell electrons and are protected and not involved in the combination process. G.N.lewis, an American scientist introduced simple notations to represent the valence electrons in an atom. These notations are called Lewis symbols. For example, Lewis notation for carbon, oxygen and hydrogen,
Octet rule: Kossel and Lewis developed a theory of chemical combination between atoms known as electron theory of chemical bonding. According to this, atoms can combine either transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another atom or by sharing of valence electrons in order to have an octet in their valence shells. This is known as the Octet rule.
The dots represent electrons, such structure referred to as Lewis dot structures. Let us apply Lewis dot structure to a given molecule $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$ in which combining atoms are different. The important condition follows that:
Each bond is formed as a result of sharing an electron pair between atoms.
Each combining atom contributes at least one electron to the shared pair.
The combining atoms attain the outer shell noble gas configuration as a result of the sharing of electrons.
Then the correct Lewis structure for acetic acid is:
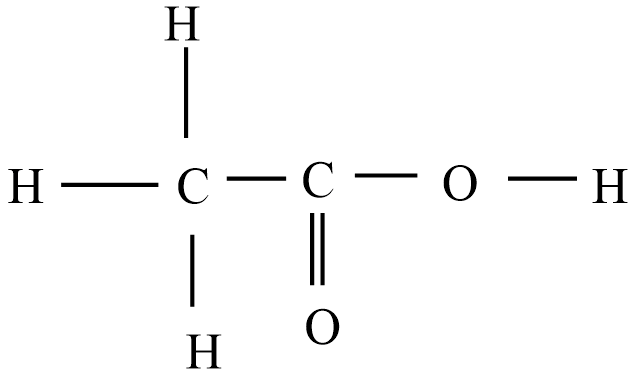
For acetic acid, O has 2 valence electrons forms two bonds
C has 4 valence electrons forms four bonds
H has one valence electron which forms one bond.
Note: The number of dots around the symbol represents the number of valence electrons. This number of valence electrons helps to calculate the common or group valence of the element. The bond formed, as a result of the electrostatic attraction between the positive and negative ions was termed as the electro covalent bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




