
The skull of the frog is
(a) Tricondylic
(b) Monocondylic
(c) Dicondylic
(d) Noncondylic
(e) Polycondylic
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: It is a skull that is attached to the body by two articulatory condyles. Beneath the foramen magnum (the hole in the base of the skull) of the frog, there are two occipital condyles (round knob at the base of the skull).
Complete answer:
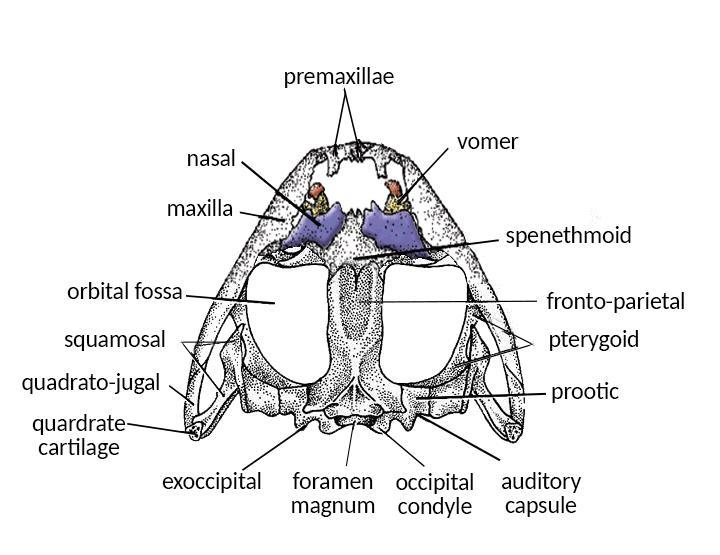
The skull of the frog is dicondylic. On either side of the foramen magnum, dorsolateral (upper and side) exoccipital bones are present.
Additional information:
- As a frog has no ribs, the dicondylic skull is connected to the first vertebral bone of the spine.
- The skull of a frog is broad and flat and consists of a narrow cranium or brain box, paired sense capsules, large orbits, the jaws, hyoid, and cartilages of the larynx.
- In the front part of the cranium of frog, the sphenethmoid (front end bone) encloses the forebrain and olfactory sacs.
- A monocondylic skull contains a single occipital condyle, such as the skull of reptiles.
- The skull of human beings is a dicondylic skull. It has two occipital condyles, with the help of these two condyles skull is connected by the first vertebral column that is the atlas bone.
- In humans, the condyles are oval or reformed (kidney-shaped) . The articular (forming a joint) surfaces of the condyles in humans are convex from before the backward and from side to side and look downward and lateral.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Dicondylic.’
Note: The skull of a frog is divided by a transverse partition into an anterior ethmoidal (separating the nasal cavity from the brain) region and a posterior sphenoidal (middle part of the base) region which encloses the forebrain. The ethmoidal region encloses the olfactory sacs.
Complete answer:
The skull of the frog is dicondylic. On either side of the foramen magnum, dorsolateral (upper and side) exoccipital bones are present.
Additional information:
- As a frog has no ribs, the dicondylic skull is connected to the first vertebral bone of the spine.
- The skull of a frog is broad and flat and consists of a narrow cranium or brain box, paired sense capsules, large orbits, the jaws, hyoid, and cartilages of the larynx.
- In the front part of the cranium of frog, the sphenethmoid (front end bone) encloses the forebrain and olfactory sacs.
- A monocondylic skull contains a single occipital condyle, such as the skull of reptiles.
- The skull of human beings is a dicondylic skull. It has two occipital condyles, with the help of these two condyles skull is connected by the first vertebral column that is the atlas bone.
- In humans, the condyles are oval or reformed (kidney-shaped) . The articular (forming a joint) surfaces of the condyles in humans are convex from before the backward and from side to side and look downward and lateral.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Dicondylic.’
Note: The skull of a frog is divided by a transverse partition into an anterior ethmoidal (separating the nasal cavity from the brain) region and a posterior sphenoidal (middle part of the base) region which encloses the forebrain. The ethmoidal region encloses the olfactory sacs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




