
The structural and functional unit of nerve tissue is
(a)Nephron
(b)Neuron
(c)Axon
(d)Cyton
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Nervous tissue is responsible for coordinating and controlling many body activities and is found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. The tissue has three principal parts and they are dendrites, cell body, and axon.
Complete step-by-step answer:
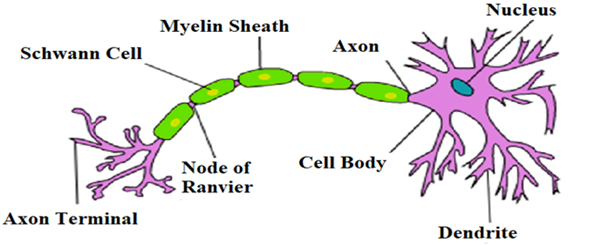
The structural and functional units of the nervous system are neurons. Nervous tissue is complex but mainly consists of just two basic types of nerve cells: neurons and glial cells. They transmit electrical signals, called nerve impulses (specialized to carry messages through an electrochemical process). The dendrites (extend from the cell body and receive nerve impulses from other neurons), the cell body (contains the nucleus and other cell organelles), and one axon (is a long slender extension of the cell body that transmits nerve impulses to other cells) are the parts of the tissue.
Additional Information: -Nephron – the structural and functional unit of the kidney and is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule it regulates water and soluble substances in the blood by filtering the blood, reabsorbing, and excreting the rest as urine.
- Axon- known as a nerve fiber which connects with other neurons or with muscle or gland cells. It conducts nerve impulses away from the neuron's cell body or soma. Axons are in effect the primary transmission lines and as bundles, they help make up nerves.
-Cyton- the central or cell body of a neuron containing the nucleus and is the main part of the neuron and carries impulse from dendrites to the axon.
So, the correct answer is option ‘Neuron’.
Note: The non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses are known as glial cells or neuroglia. Glial cells provide support for neurons (they provide neurons with nutrients and other materials).
Complete step-by-step answer:
The structural and functional units of the nervous system are neurons. Nervous tissue is complex but mainly consists of just two basic types of nerve cells: neurons and glial cells. They transmit electrical signals, called nerve impulses (specialized to carry messages through an electrochemical process). The dendrites (extend from the cell body and receive nerve impulses from other neurons), the cell body (contains the nucleus and other cell organelles), and one axon (is a long slender extension of the cell body that transmits nerve impulses to other cells) are the parts of the tissue.

Additional Information: -Nephron – the structural and functional unit of the kidney and is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule it regulates water and soluble substances in the blood by filtering the blood, reabsorbing, and excreting the rest as urine.
- Axon- known as a nerve fiber which connects with other neurons or with muscle or gland cells. It conducts nerve impulses away from the neuron's cell body or soma. Axons are in effect the primary transmission lines and as bundles, they help make up nerves.
-Cyton- the central or cell body of a neuron containing the nucleus and is the main part of the neuron and carries impulse from dendrites to the axon.
So, the correct answer is option ‘Neuron’.
Note: The non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses are known as glial cells or neuroglia. Glial cells provide support for neurons (they provide neurons with nutrients and other materials).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




