
The structure of diborane (${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$) contains:
(A)Four 2c - 2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds and two 3c - 2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds
(B)Two 2c - 2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds and four 3C - 2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds
(C)Two 2c - 2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds and two 3c - 2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds
(D)Four 2c - 2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds and four 3c - 2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds
Answer
563.7k+ views
Hint: In the structure of diborane, there are two boron atoms and six hydrogen atoms and four hydrogens are terminal hydrogens while the other two are bridged hydrogens between the two boron centres. It is a highly unstable molecule.
Complete Solution :
- In the question we are asked to comment about the structure of diborane. It is a factual type question, in which we have to say about the structure of a diborane molecule.
So let’s brief discuss about diborane and its structure:
-Diborane is a chemical compound which consists of two borons and six hydrogens with the molecular formula ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$.
-It is a colourless, pyrophoric gas which has a repulsively sweet odour.
-Diborane is highly unstable at the room temperature.
-And the compounds which consist of boron and hydrogen as the constituent atoms are called boranes.
-Diborane is one of the simplest boron hydrides.
- Diborane is a major boron compound which possesses a wide variety of applications. It finds a wide range of attention for its electronic structure. Its derivatives are useful reagents.
Now let’s discuss the structure of diborane.
- In diborane, as we know there are two born and six hydrogen atoms in which the four hydrogens are terminal hydrogens while the other two are bridged hydrogens, between the two boron centres. The four hydrogens are covalently bonded with the Boron atoms and hence there are two electrons present in the bond between the atoms. Therefore B - H bonds are 2c-2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds and there is 2c-2${{e}^{-}}$ bond.
- But the other two hydrogen atoms are bridged between the B-H-B bonds are 3c-2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds and there is two 3c-2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds.
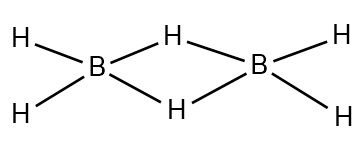
- Hence, diborane has four 2c - 2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds and two 3c - 2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds. The length of the B – H bridge bond is 1.33$\mathop A\limits^ \circ $ and the length of B – H terminal bond is 1.19 $\mathop A\limits^ \circ $. This difference in bond lengths gives the answer for the difference in strengths of the bond. The B – H bridge bond is relatively weaker than the B – H terminal bond.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Remember that both the boron atoms in diborane are $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised. Also, the bridge bonds are relatively weaker than the terminal ones. ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ is a molecule species which is isoelectronic with ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}^{2+}$.
Complete Solution :
- In the question we are asked to comment about the structure of diborane. It is a factual type question, in which we have to say about the structure of a diborane molecule.
So let’s brief discuss about diborane and its structure:
-Diborane is a chemical compound which consists of two borons and six hydrogens with the molecular formula ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$.
-It is a colourless, pyrophoric gas which has a repulsively sweet odour.
-Diborane is highly unstable at the room temperature.
-And the compounds which consist of boron and hydrogen as the constituent atoms are called boranes.
-Diborane is one of the simplest boron hydrides.
- Diborane is a major boron compound which possesses a wide variety of applications. It finds a wide range of attention for its electronic structure. Its derivatives are useful reagents.
Now let’s discuss the structure of diborane.
- In diborane, as we know there are two born and six hydrogen atoms in which the four hydrogens are terminal hydrogens while the other two are bridged hydrogens, between the two boron centres. The four hydrogens are covalently bonded with the Boron atoms and hence there are two electrons present in the bond between the atoms. Therefore B - H bonds are 2c-2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds and there is 2c-2${{e}^{-}}$ bond.
- But the other two hydrogen atoms are bridged between the B-H-B bonds are 3c-2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds and there is two 3c-2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds.

- Hence, diborane has four 2c - 2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds and two 3c - 2${{e}^{-}}$ bonds. The length of the B – H bridge bond is 1.33$\mathop A\limits^ \circ $ and the length of B – H terminal bond is 1.19 $\mathop A\limits^ \circ $. This difference in bond lengths gives the answer for the difference in strengths of the bond. The B – H bridge bond is relatively weaker than the B – H terminal bond.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Remember that both the boron atoms in diborane are $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised. Also, the bridge bonds are relatively weaker than the terminal ones. ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ is a molecule species which is isoelectronic with ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}^{2+}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




