
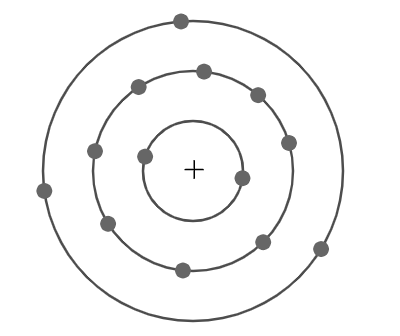
The symbol of the aluminium atom is $ {}_{13}^{27}A $ Bohr model of the atom is given in figure. Analyse these and complete the table:
Atomic number
Mass number
Number of protons
Number of electrons
Number of neutrons
Electronic configuration

Answer
506.4k+ views
Hint : In order to solve this question, we should know about the basics of the Bohr atomic model, Bohr suggested that electrons of an atom revolve in circular orbit around the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus contains protons and neutrons and electrons are distributed in a quantized manner in different orbits of an atom. We will use this concept and from the diagram we will find all the parameters asked in the question.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
When an atom is represented as $ {}_X^YZ $ where Z represents the symbol of atom and X is known as the atomic number of an atom, Y is known as the mass number of an atom.
Since, we also know the number of protons in an atom is equal to the number of electrons and this number is known as atomic number.
Mass number is the sum of the number of protons and number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
Electronic configuration represents how the electrons of an atom are distributed in successive orbits of an atom.
So, from the given symbol of aluminium $ {}_{13}^{27}A $ we can see that,
Atomic number is given as $ 13 $
This atomic number will equal the number of protons and the number of electrons.
Mass number is given as $ 27 $
Now, since mass number is the sum of number of proton which is $ 13 $ in aluminium and number of neutrons so we can write,
$ {M_{number}} = {n_{proton}} + {n_{neutron}} $
Or
$ 27 = 13 + {n_{neutron}} $
$ {n_{neutron}} = 14 $
Hence, number of neutrons are $ {n_{neutron}} = 14 $
Now, from the given figure we can see that, two electrons are distributed in the first orbit around the nucleus of an aluminium atom and then eight electrons are distributed in the next orbit and later three electrons are distributed in the last orbit.
So, electronic configuration can simply be written in the form of the number of electrons in successive orbits. $ 2,8,3 $
Hence,
Atomic number $ 13 $
Mass number $ 27 $
Number of protons $ 13 $
Number of electrons $ 13 $
Number of neutrons \[14\]
Electronic configuration \[2,8,3\].
Note :
It should be remembered that, maximum number of electrons an orbit can have according to Bohr’s atomic model can be calculated using formula $ 2{n^2} $ where n represents the number of orbit and remember electron shave a negative charge, proton have a positive charge whereas neutron has no charge on it.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
When an atom is represented as $ {}_X^YZ $ where Z represents the symbol of atom and X is known as the atomic number of an atom, Y is known as the mass number of an atom.
Since, we also know the number of protons in an atom is equal to the number of electrons and this number is known as atomic number.
Mass number is the sum of the number of protons and number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
Electronic configuration represents how the electrons of an atom are distributed in successive orbits of an atom.
So, from the given symbol of aluminium $ {}_{13}^{27}A $ we can see that,
Atomic number is given as $ 13 $
This atomic number will equal the number of protons and the number of electrons.
Mass number is given as $ 27 $
Now, since mass number is the sum of number of proton which is $ 13 $ in aluminium and number of neutrons so we can write,
$ {M_{number}} = {n_{proton}} + {n_{neutron}} $
Or
$ 27 = 13 + {n_{neutron}} $
$ {n_{neutron}} = 14 $
Hence, number of neutrons are $ {n_{neutron}} = 14 $
Now, from the given figure we can see that, two electrons are distributed in the first orbit around the nucleus of an aluminium atom and then eight electrons are distributed in the next orbit and later three electrons are distributed in the last orbit.
So, electronic configuration can simply be written in the form of the number of electrons in successive orbits. $ 2,8,3 $
Hence,
Atomic number $ 13 $
Mass number $ 27 $
Number of protons $ 13 $
Number of electrons $ 13 $
Number of neutrons \[14\]
Electronic configuration \[2,8,3\].
Note :
It should be remembered that, maximum number of electrons an orbit can have according to Bohr’s atomic model can be calculated using formula $ 2{n^2} $ where n represents the number of orbit and remember electron shave a negative charge, proton have a positive charge whereas neutron has no charge on it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




