
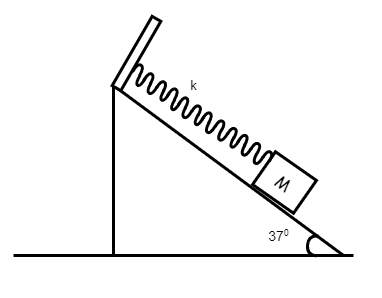
The system of the wedge and the block connected by a massless spring as shown in the figure is released with the spring in its natural length. Friction is absent. Maximum elongation in the spring will be
A) $\dfrac{{3Mg}}{{5k}}$.
B) $\dfrac{{6Mg}}{{5k}}$.
C) $\frac{{4Mg}}{{5k}}$.
D) $\dfrac{{8Mg}}{{5k}}$.

Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint:For this question, we have to calculate the displacement of the block given which will give us the maximum elongation of the spring. Here as the body is placed in an inclined plane, we have to place the displacement and divide it into its components, the vertical component, and the horizontal component.
Complete step by step answer:
Here we have a block of mass M that is connected by a massless spring to a wedge as shown in the figure.
Now to find the maximum elongation we have to calculate the displacement of the block first.
So, the amount of potential energy lost by the block is the energy stored by the spring.
The force acting on the block is $Mg$. Now, this can be divided into its vertical and horizontal components as $Mg\cos \theta $ and $Mg\sin \theta $. This gives us that the force acting on the block on the wedge will depend on $Mg\sin \theta $ as this is the component of force acting in that direction.
Let us consider the block is displaced by $x$, then we can write,
$Mg\sin \theta .x = \dfrac{1}{2}k.{x^2}$.
Now, equating we get,
$Mg\sin \theta = \dfrac{1}{2}k.x$.
This can be rewritten,
$x = \dfrac{{2Mg\sin \theta }}{k}$.
Now, $\theta = {37^0}$ this gives us,
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{3}{5}$.
Thus, $x = \dfrac{{2Mg}}{k} \cdot \dfrac{3}{5} = \dfrac{{6Mg}}{{5k}}$ .
So, the maximum elongation possible for the spring will be $\dfrac{{6Mg}}{{5k}}$.
Thus, the answer to this question is option (B).
Note:The most common mistake the students make in this problem is the use of force balance, i.e. they equate $kx = Mg\sin \theta $. This will give us displacement $x = \dfrac{{3Mg}}{{5k}}$. This will be giving us the mean position of displacement. This is not the maximum elongation but the mean elongation.
Complete step by step answer:
Here we have a block of mass M that is connected by a massless spring to a wedge as shown in the figure.
Now to find the maximum elongation we have to calculate the displacement of the block first.
So, the amount of potential energy lost by the block is the energy stored by the spring.
The force acting on the block is $Mg$. Now, this can be divided into its vertical and horizontal components as $Mg\cos \theta $ and $Mg\sin \theta $. This gives us that the force acting on the block on the wedge will depend on $Mg\sin \theta $ as this is the component of force acting in that direction.
Let us consider the block is displaced by $x$, then we can write,
$Mg\sin \theta .x = \dfrac{1}{2}k.{x^2}$.
Now, equating we get,
$Mg\sin \theta = \dfrac{1}{2}k.x$.
This can be rewritten,
$x = \dfrac{{2Mg\sin \theta }}{k}$.
Now, $\theta = {37^0}$ this gives us,
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{3}{5}$.
Thus, $x = \dfrac{{2Mg}}{k} \cdot \dfrac{3}{5} = \dfrac{{6Mg}}{{5k}}$ .
So, the maximum elongation possible for the spring will be $\dfrac{{6Mg}}{{5k}}$.
Thus, the answer to this question is option (B).
Note:The most common mistake the students make in this problem is the use of force balance, i.e. they equate $kx = Mg\sin \theta $. This will give us displacement $x = \dfrac{{3Mg}}{{5k}}$. This will be giving us the mean position of displacement. This is not the maximum elongation but the mean elongation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




