
The tissue which has dead cells in the functional state is
(a) Collenchyma
(b) Sclerenchyma
(c) Parenchyma
(d) Phloem
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: These cells provide rigidity, mechanical support, support transportation of water, and nutrients to the plants.
Complete step-by-step answer:
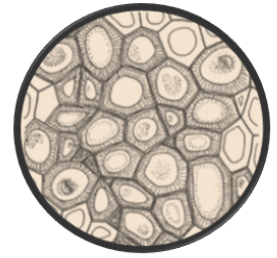
Sclerenchyma has a very thick cell wall due to the deposition of lignin and cells are dead cells at maturity. They are located in the leaf veins, hard coverings of the seeds, and also found surrounding the vascular bundle. They are present in the form of fibers or sclereids (stone cells) and other functions include plant stiffness and hardness.
Additional Information:
-Parenchyma- these are living tissues with a thin cell wall (made of cellulose) with dense cytoplasm and central vacuole. They are located in the parts such as the pith and cortex where the parts are soft. These cells store food, exchange gas, and help in photosynthesis. The parenchyma cells are diametric in shape.
-Collenchyma- these are living tissues having an elongated shape and thick cell wall (made of cellulose, pectin, and hemicellulose) in the corner. The cell walls are uneven in shape. They can be located in the leaf veins, stem, and below the epidermis, etc. collenchyma cells provide mechanical support and elasticity to the plant allowing for easy bending without breakage.
-Phloem- it transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis to sink tissues (ex. non-photosynthetic root cells or developing flowers) and the process is known as photosynthates and is a living tissue in vascular plants.
So, the correct answer is 'Sclerenchyma'.
Note: A class of complex organic polymers that form structural materials in the support tissues of vascular plants and some algae is known as lignin. It is abundant in cell walls of some specific cells and its functions are water transport, mechanical support, and resistance to various stresses.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Figure: Structure of sclerenchyma
Sclerenchyma has a very thick cell wall due to the deposition of lignin and cells are dead cells at maturity. They are located in the leaf veins, hard coverings of the seeds, and also found surrounding the vascular bundle. They are present in the form of fibers or sclereids (stone cells) and other functions include plant stiffness and hardness.
Additional Information:
-Parenchyma- these are living tissues with a thin cell wall (made of cellulose) with dense cytoplasm and central vacuole. They are located in the parts such as the pith and cortex where the parts are soft. These cells store food, exchange gas, and help in photosynthesis. The parenchyma cells are diametric in shape.
-Collenchyma- these are living tissues having an elongated shape and thick cell wall (made of cellulose, pectin, and hemicellulose) in the corner. The cell walls are uneven in shape. They can be located in the leaf veins, stem, and below the epidermis, etc. collenchyma cells provide mechanical support and elasticity to the plant allowing for easy bending without breakage.
-Phloem- it transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis to sink tissues (ex. non-photosynthetic root cells or developing flowers) and the process is known as photosynthates and is a living tissue in vascular plants.
So, the correct answer is 'Sclerenchyma'.
Note: A class of complex organic polymers that form structural materials in the support tissues of vascular plants and some algae is known as lignin. It is abundant in cell walls of some specific cells and its functions are water transport, mechanical support, and resistance to various stresses.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




