
The total number of alkenes possible by debromination of 3 - Bromo - 3 - cyclopentylhexane using alcoholic KOH is:
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 6
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: For this problem, we have to write the complete reaction of the given reactant with potassium hydroxide in which the elimination of the bromine will take place and the formation of the double bond will occur at different positions.
Complete step by step solution:
- In the given question, we have to calculate the total number of alkenes which will form the elimination of the bromine from 3 - Bromo - 3 - cyclopentylhexane takes place with the help of alcoholic Potassium hydroxide.
- As we know that the alcoholic potassium hydroxide usually favours elimination reaction but if we will aqueous potassium hydroxide then it will favour substitution reaction due to which the formation of an alkene will not occur.
- That's why the alcoholic potassium hydroxide is used here for the formation of the alkene.
- Now, the structure of the given reactant that is 3 - Bromo - 3 - cyclo-pentyl hexane is:
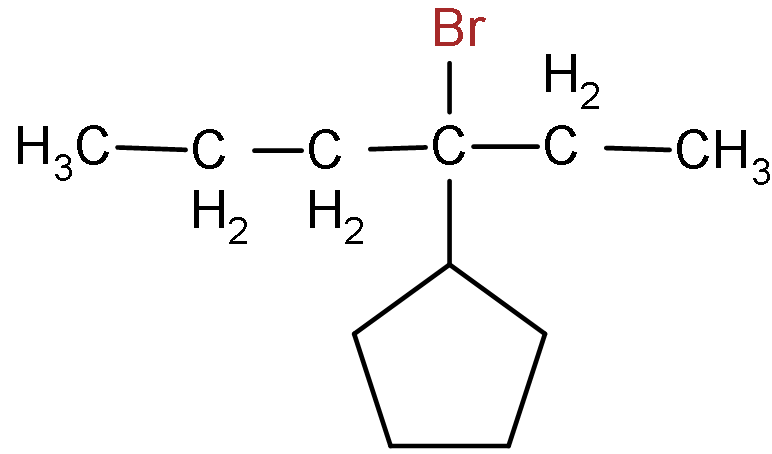
- Now, as we can see that there is only one bromine atom present in the reactant so when alcoholic potassium hydroxide reacts with it, then the removal of this bromine atom takes place.
- Now, there are three possibilities of the formation of the alkene.
- Firstly, the double bond can be formed between the third carbon and fourth carbon from the left side or between second carbon and third carbon from the right side.
- And at last double bonds can be formed between the third carbon and cyclopentyl.
- The balanced reaction will be:
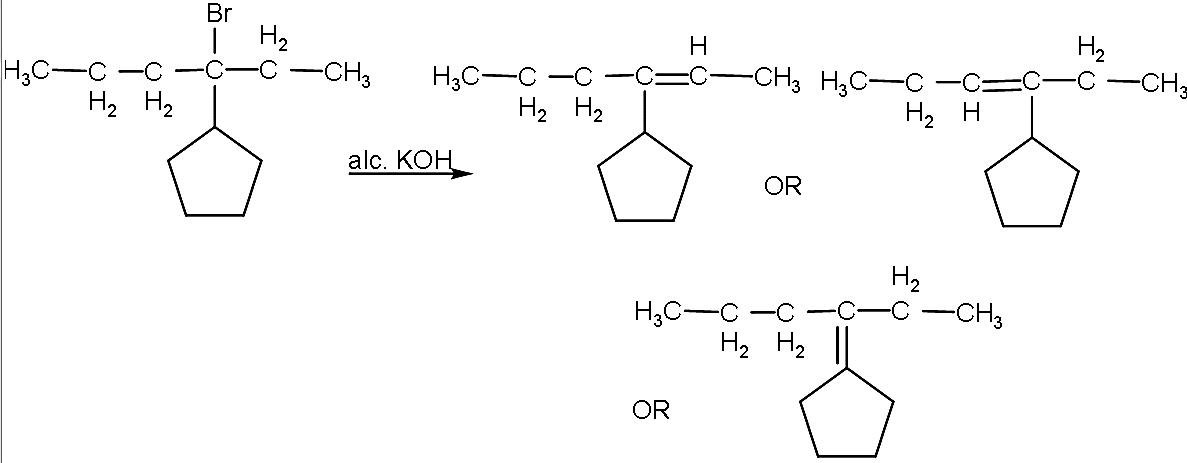
- Now, the first and second structure will show the geometrical isomerism due to which it will form the two non-superimposable mirror images.
- But the third structure will not show the geometrical isomerism and it will have only one structure.
- So, a total of 5 alkenes can be formed.
Therefore, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: Geometrical isomerism is the isomerism in which the mirror images do not superimpose on each other due to which it will form two types of structure which will be different from each other.
Complete step by step solution:
- In the given question, we have to calculate the total number of alkenes which will form the elimination of the bromine from 3 - Bromo - 3 - cyclopentylhexane takes place with the help of alcoholic Potassium hydroxide.
- As we know that the alcoholic potassium hydroxide usually favours elimination reaction but if we will aqueous potassium hydroxide then it will favour substitution reaction due to which the formation of an alkene will not occur.
- That's why the alcoholic potassium hydroxide is used here for the formation of the alkene.
- Now, the structure of the given reactant that is 3 - Bromo - 3 - cyclo-pentyl hexane is:

- Now, as we can see that there is only one bromine atom present in the reactant so when alcoholic potassium hydroxide reacts with it, then the removal of this bromine atom takes place.
- Now, there are three possibilities of the formation of the alkene.
- Firstly, the double bond can be formed between the third carbon and fourth carbon from the left side or between second carbon and third carbon from the right side.
- And at last double bonds can be formed between the third carbon and cyclopentyl.
- The balanced reaction will be:

- Now, the first and second structure will show the geometrical isomerism due to which it will form the two non-superimposable mirror images.
- But the third structure will not show the geometrical isomerism and it will have only one structure.
- So, a total of 5 alkenes can be formed.
Therefore, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: Geometrical isomerism is the isomerism in which the mirror images do not superimpose on each other due to which it will form two types of structure which will be different from each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




