
The total number of bones in the human skull is _______
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint:The axial skeleton is the upper part of the skeleton consisting of the skull, vertebrae, and trunk. It consists of a total of 86 bones. 25 out of 86 bones of the axial skeleton make up the trunk. 33 out of the 86 bones make up the vertebrae. The rest of the bones make up the skull with additional structures called ossicles of the middle ear, hyoid bone, and the sternum. The skull is the protective covering of the head.
Complete answer:The skull is the hard flat bone network that covers the head of the human body. It protects the sensitive brain from mechanical shocks. The skull is the major portion of the axial skeleton. Out of the 86 bones of the axial skeleton, 22 of them make up the skull. Thus, the total number of bones in the human skull is 22. 8 of these make cranial bones, 14 makes facial bones, 2 comprises temporal bones, 2 parietal bones, ethmoid, sphenoid, and the frontal bones.
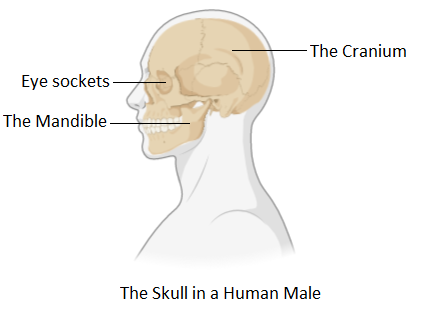
The flat bones of the skull house the brain and other sensitive and vital organs of the head. With an increase in age, the bones get weaker but the skull always remains strong. It functions to protect the brain from any injury. It further consists of the cranium and the mandible which makes the lower jaw or facial bones. The additional smaller spaces like cavities for the eyes, the internal ear, the nose, and the mouth are all made by 22 bones of the skull. The main functions of the skull are to protect the brain and other vital organs along with keeping the eyes and other structures of the face in their place. Also, it helps to keep the distance fixed between the eyes that allow stereoscopic vision.
Note: Any injury to the brain can be life-threatening. Thus, the skull is the most essential protective shield of the brain. Sometimes faulty growth patterns result in abnormal head shape. Various cranial defects can lead to visual impairment, eating difficulties, sleeping impairments, etc.
Complete answer:The skull is the hard flat bone network that covers the head of the human body. It protects the sensitive brain from mechanical shocks. The skull is the major portion of the axial skeleton. Out of the 86 bones of the axial skeleton, 22 of them make up the skull. Thus, the total number of bones in the human skull is 22. 8 of these make cranial bones, 14 makes facial bones, 2 comprises temporal bones, 2 parietal bones, ethmoid, sphenoid, and the frontal bones.

The flat bones of the skull house the brain and other sensitive and vital organs of the head. With an increase in age, the bones get weaker but the skull always remains strong. It functions to protect the brain from any injury. It further consists of the cranium and the mandible which makes the lower jaw or facial bones. The additional smaller spaces like cavities for the eyes, the internal ear, the nose, and the mouth are all made by 22 bones of the skull. The main functions of the skull are to protect the brain and other vital organs along with keeping the eyes and other structures of the face in their place. Also, it helps to keep the distance fixed between the eyes that allow stereoscopic vision.
Note: Any injury to the brain can be life-threatening. Thus, the skull is the most essential protective shield of the brain. Sometimes faulty growth patterns result in abnormal head shape. Various cranial defects can lead to visual impairment, eating difficulties, sleeping impairments, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




