
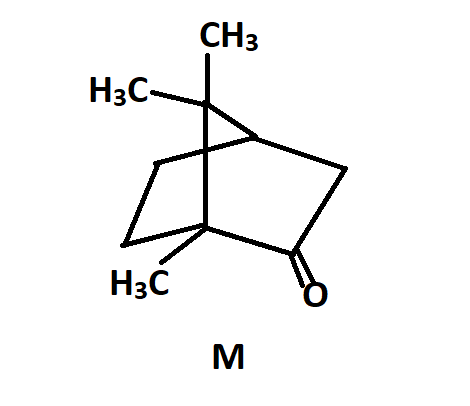
The total number of stereoIsomers that can exist for the give M are:

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: Isomers are compounds that possess the same molecular formula but differ from each other in physical and chemical properties. Since isomers have the same molecular formula the difference in their properties might be due to different modes of combination of arrangement of atoms within the molecule
Complete Step by step answer: The isomers which differ only in the orientation of atoms in space are known as stereoisomers and this phenomenon is known as stereoisomerism. One of the types is geometrical isomerism, isomers which possess the same molecular and structural formula but differ in arrangement of atoms or groups in space around the double bonds are known as geometrical isomers and the phenomenon is known as geometrical isomerism.
Since the above given compound has a lot of steric repulsion and strain due to reorientation its bond might break therefore it cannot show geometrical isomerism.
The only other stereoisomer that can exist for this compound will be its mirror image. Since the two stereoisomers for this compound are each other’s mirror image, it will be superimposable. That is if you try to put one compound over another they will completely cover each other and no discrepancy will be observed.
In other words, stereoisomerism is exhibited by such compounds which have identical molecular structure but different configurations. The other isomers are structural isomers. If the above compound would have been a geometrical isomer, it would be non-imposable.
Hence from the above we can conclude that the total number of stereoisomers for the compound is 2.
Note: The compounds showing geometrical isomerism are alkenes that contain unsaturated double bonds between C-C atoms. Since the above compound does not contain C-C double bonds, it does not show geometrical isomerism.
Complete Step by step answer: The isomers which differ only in the orientation of atoms in space are known as stereoisomers and this phenomenon is known as stereoisomerism. One of the types is geometrical isomerism, isomers which possess the same molecular and structural formula but differ in arrangement of atoms or groups in space around the double bonds are known as geometrical isomers and the phenomenon is known as geometrical isomerism.
Since the above given compound has a lot of steric repulsion and strain due to reorientation its bond might break therefore it cannot show geometrical isomerism.
The only other stereoisomer that can exist for this compound will be its mirror image. Since the two stereoisomers for this compound are each other’s mirror image, it will be superimposable. That is if you try to put one compound over another they will completely cover each other and no discrepancy will be observed.
In other words, stereoisomerism is exhibited by such compounds which have identical molecular structure but different configurations. The other isomers are structural isomers. If the above compound would have been a geometrical isomer, it would be non-imposable.
Hence from the above we can conclude that the total number of stereoisomers for the compound is 2.
Note: The compounds showing geometrical isomerism are alkenes that contain unsaturated double bonds between C-C atoms. Since the above compound does not contain C-C double bonds, it does not show geometrical isomerism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




