
The trachea terminates into
A. Bronchi
B. Atrium
C. Bronchioles
D. Alveoli
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: The two lungs have a tube called bronchus which connects to the trachea. The trachea terminates in the lung and extends further in three broad categories, primary, secondary and tertiary tubes.
Complete answer:
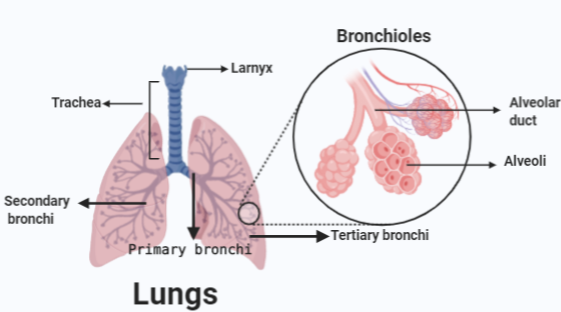
The lower respiratory tract of humans comprises of:
- Lungs
- Alveoli
- Bronchi
- Bronchioles
- Trachea
The lungs are the main organ for respiration in human beings. The lungs are located at the bottom of the trachea. The trachea is a tube that is responsible for the inlet and outlet of the air in the lungs. Each of the two lungs has a tube called bronchus which connects to the trachea. The trachea terminates and extends into bronchi. The bronchi and the trachea form an upside Y. The bronchi are of three types: primary, secondary, and tertiary. The bronchi further divide into smaller bronchi and further into very narrow tubes called bronchioles. Bronchioles cover most of the area of the lungs. Their structure is very similar to a tree and how a tree covers the area. The thinness of the bronchioles could be very similar to that of hair. Humans have 30,000 bronchioles in their lungs approximately, making 60,000 in total. The tubes of bronchioles are further divided into groups of small air sacs known as alveoli. Their physical appearances are very similar to that of a grape bunch. Each bronchiole has around 10,000 alveoli, making a total of about 600 million alveoli present in the human lungs. Each alveoli acts as a storage of oxygen. So, the humongous numbers of alveoli provide a huge amount of surface area to store oxygen.
Hence option A is correct.
Note: Activities like smoking harm lungs. While smoking, the tobacco present in the cigarettes travel down to the bronchioles and further down to the alveoli. Tobacco or other substances get collected there and reduce the surface area for oxygen aggregation and absorption in the alveoli. This reduces the oxygen supply to our body and so affects the proper functioning of the body.
Complete answer:

The lower respiratory tract of humans comprises of:
- Lungs
- Alveoli
- Bronchi
- Bronchioles
- Trachea
The lungs are the main organ for respiration in human beings. The lungs are located at the bottom of the trachea. The trachea is a tube that is responsible for the inlet and outlet of the air in the lungs. Each of the two lungs has a tube called bronchus which connects to the trachea. The trachea terminates and extends into bronchi. The bronchi and the trachea form an upside Y. The bronchi are of three types: primary, secondary, and tertiary. The bronchi further divide into smaller bronchi and further into very narrow tubes called bronchioles. Bronchioles cover most of the area of the lungs. Their structure is very similar to a tree and how a tree covers the area. The thinness of the bronchioles could be very similar to that of hair. Humans have 30,000 bronchioles in their lungs approximately, making 60,000 in total. The tubes of bronchioles are further divided into groups of small air sacs known as alveoli. Their physical appearances are very similar to that of a grape bunch. Each bronchiole has around 10,000 alveoli, making a total of about 600 million alveoli present in the human lungs. Each alveoli acts as a storage of oxygen. So, the humongous numbers of alveoli provide a huge amount of surface area to store oxygen.
Hence option A is correct.
Note: Activities like smoking harm lungs. While smoking, the tobacco present in the cigarettes travel down to the bronchioles and further down to the alveoli. Tobacco or other substances get collected there and reduce the surface area for oxygen aggregation and absorption in the alveoli. This reduces the oxygen supply to our body and so affects the proper functioning of the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




