
The two strands of DNA are held together by bonds of
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Oxygen
(c) Hydrogen
(d) Carbon
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: The structure of DNA is a double stranded molecule and is like a spiral staircase. The nucleotides are the railings of the staircase and nucleotides are like the steps of the staircase.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The stability of the DNA helix is provided by weak covalent bonds.
There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA, i.e Guanine, Cytosine, Adenine, and Thymine. The complementary base pairs of guanine with cytosine and adenine with thymine connect to one another by hydrogen bonds. The hydrogen bonds between complementary nucleotides keep the two strands of DNA helix together.
Additional Information:
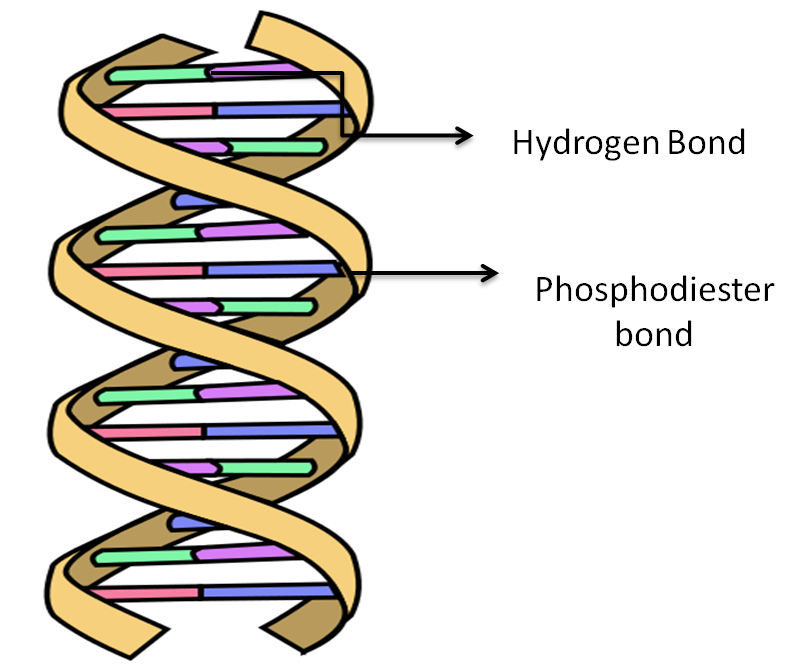
- The nucleotide monomers in DNA are connected by a strong electromagnetic attraction called phosphodiester bonds. The phosphodiester bonds that join one DNA nucleotide to another always link the 3’ carbon of the first nucleotide to the 5' carbon of the second nucleotide.
- Hydrogen bonds exist between the two strands and form a base between the two strands of DNA. Each base can also form hydrogen bonds with water also. These hydrogen bonds are individually weak but collectively make strong.
- The A nucleotides are always hydrogen-bonded to T nucleotides with 2 hydrogen bonds.
- The G nucleotides are always hydrogen-bonded to C nucleotides with 3 hydrogen bonds.
- The hydrogen between the two DNA strands is a breakdown during DNA replication by the enzyme helicase or during denaturation at high temperature.
So, the correct answer is ‘hydrogen bonds’.
Note: -DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material in mainly all organisms.
-DNA is located in the cell nucleus where it is called nuclear DNA, but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria and chloroplast in plants.
-The information in DNA is stored as a code made up of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T).
-There are three types of DNA- A-DNA, B-DNA, Z-DNA.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The stability of the DNA helix is provided by weak covalent bonds.
There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA, i.e Guanine, Cytosine, Adenine, and Thymine. The complementary base pairs of guanine with cytosine and adenine with thymine connect to one another by hydrogen bonds. The hydrogen bonds between complementary nucleotides keep the two strands of DNA helix together.
Additional Information:

- The nucleotide monomers in DNA are connected by a strong electromagnetic attraction called phosphodiester bonds. The phosphodiester bonds that join one DNA nucleotide to another always link the 3’ carbon of the first nucleotide to the 5' carbon of the second nucleotide.
- Hydrogen bonds exist between the two strands and form a base between the two strands of DNA. Each base can also form hydrogen bonds with water also. These hydrogen bonds are individually weak but collectively make strong.
- The A nucleotides are always hydrogen-bonded to T nucleotides with 2 hydrogen bonds.
- The G nucleotides are always hydrogen-bonded to C nucleotides with 3 hydrogen bonds.
- The hydrogen between the two DNA strands is a breakdown during DNA replication by the enzyme helicase or during denaturation at high temperature.
So, the correct answer is ‘hydrogen bonds’.
Note: -DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material in mainly all organisms.
-DNA is located in the cell nucleus where it is called nuclear DNA, but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria and chloroplast in plants.
-The information in DNA is stored as a code made up of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T).
-There are three types of DNA- A-DNA, B-DNA, Z-DNA.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




