
The type of overlap in the bridge bond existing in \[A{l_2}{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_6}\] is:
A.\[S{p^{3 - }}s{p^3}d - s{p^3}\]
B.\[S{p^3} - s{p^{2 - }}s{p^3}\]
C.\[S{p^3} - s - s{p^3}\]
D.\[S{p^3} - s{p^3} - s{p^3}\]
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint:An important compound of Boron is Diborane, \[{B_2}{H_6}\] . It is the hydride of Boron. Diborane is used as an important reagent in organic synthetic reactions. \[A{l_2}{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_6}\] is isostructural with Diborane \[\left( {{B_2}{H_6}} \right)\] .
Complete step by step answer:
Borane has a bridged structure. Each B atom is bonded to two Hydrogen atoms (terminal H atoms). By regular electron pair bonds. That is called two-center-two-electron \[\left( {2c - 2e} \right)\] bonds. The resulting \[B{H_2}\] fragments are in the same pane and are bridged by two Hydrogen atoms (bridging Hydrogen atoms). The two bridging Hydrogen atoms are positioned such that one lies above the plane containing \[B{H_2}\] fragments and the other lies below the plane.
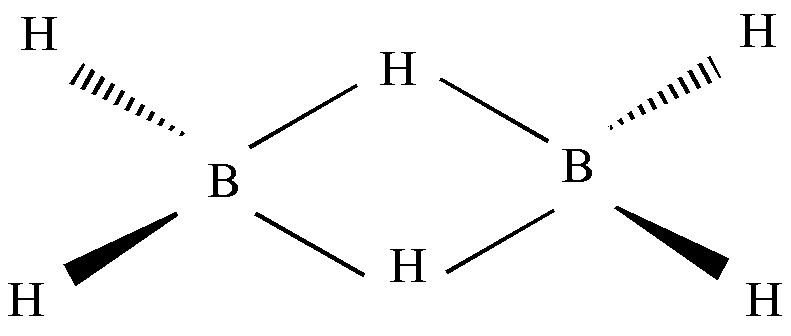
The two B-H-B bonds are not conventional bonds, these are known as three center-two electron bonds \[\left( {3c - 2e} \right)\] . In the bridge bonds 3 atoms are connected through only electrons, not through 4 electrons (two shared electron pairs). Consequently, these centers became electron deficient. Hence, Diborane is an electron deficient molecule.
We can explain the bonding in Borane.
B (Ground state)
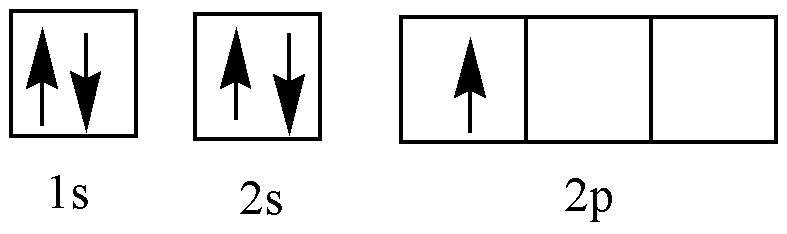
B (Excited state)
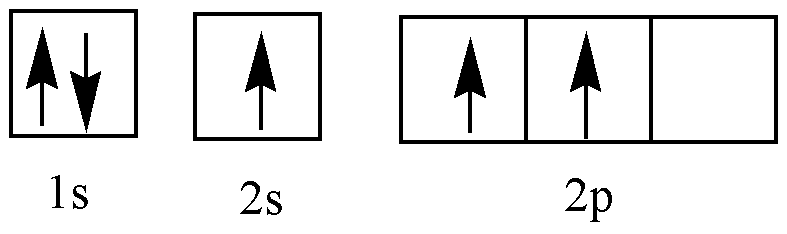
B (Hybridized state)
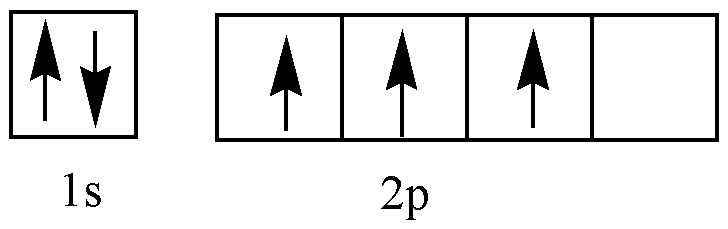
In Borane, the Boron atom is present in \[S{p^3}\] hybridized state. It has tetrahedral structure Among the four \[S{p^3}\] hybrid orbitals three of them have unpaired electrons. And one vacant \[S{p^3}\] orbital is present. The resulting geometry is that four terminal hydrogen atoms and the two Boron atoms lie in one plane. Four terminals \[B - H\] bonds are regular covalent bonds. \[\left( {2c - 2e} \right)\] . Above and below the plane two bridging Hydrogen atoms are present. Each B-H-B bridge results from the overlap of one half-filled \[S{p^3}\] orbital of one B, the unoccupied sp3 orbital of the other B and a half-filled 1s orbital of H atom. The two bridge bonds(B-H-B) are thus three center-two electron \[\left( {3c - 2e} \right)\] bonds. These bonds are referred to as Banana bonds.
Bonding in \[A{l_2}{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_6}\] is similar to bonding in Borane. Each Boron in the borane is \[S{p^3}\] hybridized. The type of overlap is \[s{p^3} - s{p^3} - s{p^3}\] . Similar overlap is present in \[A{l_2}{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_6}\].
Hence, the correct answer is option (D) i.e \[s{p^3} - s{p^3} - s{p^3}\] .
Note: Diborane is a colorless toxic gas. It is stable at ordinary temperatures. The three center-two electron bonds in a borane are known as Banana bonds. In Borane two banana bonds are present. Banana bonds are present in \[A{l_2}C{l_6}\] molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
Borane has a bridged structure. Each B atom is bonded to two Hydrogen atoms (terminal H atoms). By regular electron pair bonds. That is called two-center-two-electron \[\left( {2c - 2e} \right)\] bonds. The resulting \[B{H_2}\] fragments are in the same pane and are bridged by two Hydrogen atoms (bridging Hydrogen atoms). The two bridging Hydrogen atoms are positioned such that one lies above the plane containing \[B{H_2}\] fragments and the other lies below the plane.

The two B-H-B bonds are not conventional bonds, these are known as three center-two electron bonds \[\left( {3c - 2e} \right)\] . In the bridge bonds 3 atoms are connected through only electrons, not through 4 electrons (two shared electron pairs). Consequently, these centers became electron deficient. Hence, Diborane is an electron deficient molecule.
We can explain the bonding in Borane.
B (Ground state)

B (Excited state)

B (Hybridized state)

In Borane, the Boron atom is present in \[S{p^3}\] hybridized state. It has tetrahedral structure Among the four \[S{p^3}\] hybrid orbitals three of them have unpaired electrons. And one vacant \[S{p^3}\] orbital is present. The resulting geometry is that four terminal hydrogen atoms and the two Boron atoms lie in one plane. Four terminals \[B - H\] bonds are regular covalent bonds. \[\left( {2c - 2e} \right)\] . Above and below the plane two bridging Hydrogen atoms are present. Each B-H-B bridge results from the overlap of one half-filled \[S{p^3}\] orbital of one B, the unoccupied sp3 orbital of the other B and a half-filled 1s orbital of H atom. The two bridge bonds(B-H-B) are thus three center-two electron \[\left( {3c - 2e} \right)\] bonds. These bonds are referred to as Banana bonds.
Bonding in \[A{l_2}{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_6}\] is similar to bonding in Borane. Each Boron in the borane is \[S{p^3}\] hybridized. The type of overlap is \[s{p^3} - s{p^3} - s{p^3}\] . Similar overlap is present in \[A{l_2}{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_6}\].
Hence, the correct answer is option (D) i.e \[s{p^3} - s{p^3} - s{p^3}\] .
Note: Diborane is a colorless toxic gas. It is stable at ordinary temperatures. The three center-two electron bonds in a borane are known as Banana bonds. In Borane two banana bonds are present. Banana bonds are present in \[A{l_2}C{l_6}\] molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




