
The value of horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at a point is \[0.5\times {{10}^{-4}}\text{tesla}\] and the angle of dip is \[\text{45}{}^\circ \]. Find the value of vertical components.
Answer
602.4k+ views
Hint: The total magnetic field is always the magnitude of the horizontal and vertical component of the magnetic field vector. So we can find out any component of the magnetic field from other magnetic field vector components and the angle of declination or inclination.
Formula used: \[\tan \phi =\dfrac{{{B}_{v}}}{{{B}_{H}}}\], \[{{B}_{v}}\] is the vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field, \[{{B}_{H}}\] is the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field and \[\phi \] is the dip angle.
Complete step by step answer:
We can simply consider the earth magnetic field as a permanent large bar magnet located at the centre of the earth. The south pole of this magnet is along the direction of the geographic north pole. That’s why the north pole of the magnetic needle points towards the geographic north pole. The earth magnetic field’s magnitude is varying with places in the earth. The dip angle or magnetic inclination is the angle between the horizontal component of the magnetic field and the total magnetic field vector.
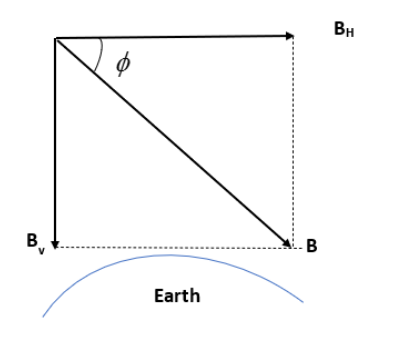
As you can see in the figure, the value of the vertical component can find out from the horizontal component of the magnetic field and the dip angle. Here, the value of the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at a point is \[0.5\times {{10}^{-4}}\text{tesla}\] and the angle of dip is \[\text{45}{}^\circ \].
The vertical component can be written as,
\[\tan \phi =\dfrac{{{B}_{v}}}{{{B}_{H}}}\], \[{{B}_{v}}\] is the vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field, \[{{B}_{H}}\] is the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field and \[\phi \] is the dip angle.
\[{{B}_{v}}={{B}_{H}}\tan \phi \]
We can assign the given values into the equation.
\[{{B}_{v}}=0.5\times {{10}^{-4}}\text{tesla}\times \tan 45{}^\circ \]
\[{{B}_{v}}=0.5\times {{10}^{-4}}\times 1\]
Since the angle of dip is \[\text{45}{}^\circ \], the vertical component and horizontal component will be the same.
\[{{B}_{v}}=0.5\times {{10}^{-4}}\text{Tesla}\]
Note: If we have to find the total magnetic field from the horizontal component of the magnetic field, we can use the following equation.
\[\cos \phi =\dfrac{{{B}_{H}}}{B}\], where B is the total magnetic field. Unlike the earth’s geographic equator, the magnetic equator of earth is not fixed. It will vary with time. Studies show that the earth’s magnetic field becomes weaker day by day.
Formula used: \[\tan \phi =\dfrac{{{B}_{v}}}{{{B}_{H}}}\], \[{{B}_{v}}\] is the vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field, \[{{B}_{H}}\] is the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field and \[\phi \] is the dip angle.
Complete step by step answer:
We can simply consider the earth magnetic field as a permanent large bar magnet located at the centre of the earth. The south pole of this magnet is along the direction of the geographic north pole. That’s why the north pole of the magnetic needle points towards the geographic north pole. The earth magnetic field’s magnitude is varying with places in the earth. The dip angle or magnetic inclination is the angle between the horizontal component of the magnetic field and the total magnetic field vector.

As you can see in the figure, the value of the vertical component can find out from the horizontal component of the magnetic field and the dip angle. Here, the value of the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at a point is \[0.5\times {{10}^{-4}}\text{tesla}\] and the angle of dip is \[\text{45}{}^\circ \].
The vertical component can be written as,
\[\tan \phi =\dfrac{{{B}_{v}}}{{{B}_{H}}}\], \[{{B}_{v}}\] is the vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field, \[{{B}_{H}}\] is the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field and \[\phi \] is the dip angle.
\[{{B}_{v}}={{B}_{H}}\tan \phi \]
We can assign the given values into the equation.
\[{{B}_{v}}=0.5\times {{10}^{-4}}\text{tesla}\times \tan 45{}^\circ \]
\[{{B}_{v}}=0.5\times {{10}^{-4}}\times 1\]
Since the angle of dip is \[\text{45}{}^\circ \], the vertical component and horizontal component will be the same.
\[{{B}_{v}}=0.5\times {{10}^{-4}}\text{Tesla}\]
Note: If we have to find the total magnetic field from the horizontal component of the magnetic field, we can use the following equation.
\[\cos \phi =\dfrac{{{B}_{H}}}{B}\], where B is the total magnetic field. Unlike the earth’s geographic equator, the magnetic equator of earth is not fixed. It will vary with time. Studies show that the earth’s magnetic field becomes weaker day by day.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




