
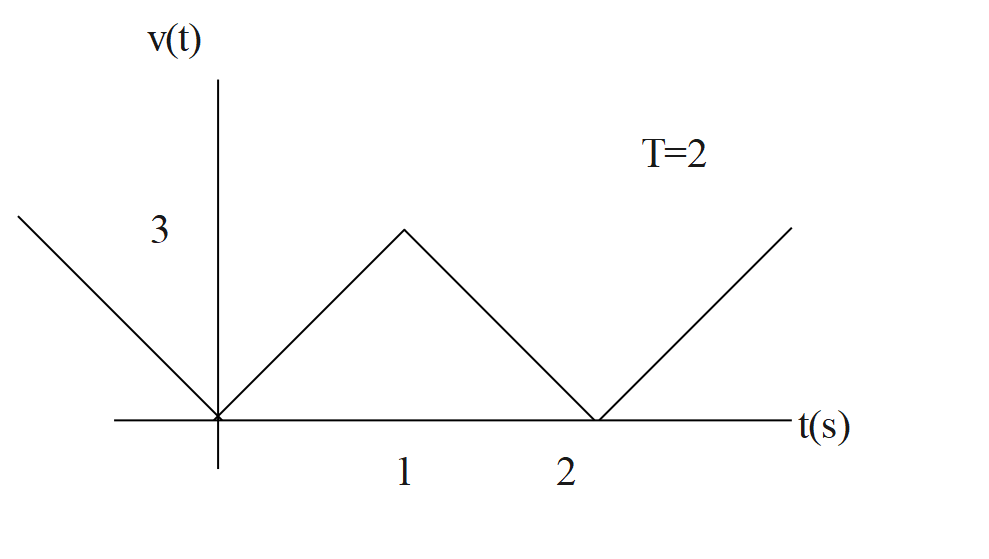
The voltage shown in the figure is known as a triangular waveform. Determine the rms value.

Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: Write the formula for the rms value of the wave form. The time taken for one complete cycle is given and the maximum voltages reached by the waveform will be taken from the graph. Also, the cycle is repeating, therefore, the rms value can be calculated for one cycle and it is the same and constant for all the other cycles.
Formula used:
${{V}_{rms}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{\int{{{v}^{2}}dt}}{\int{dt}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let us write down the given terms and quantities form the graph,
$\begin{align}
& {{V}_{\max }}=3V \\
& T=2\sec \\
\end{align}$
Now, the term in the formula $\int{{{v}^{2}}dt}$can be found by finding the area of one cycle
Therefore, let's find the area of one cycle in the waveform,
$\begin{align}
& \int{{{v}^{2}}dt}=2\times \dfrac{1}{2}\times 2\times 3 \\
& \Rightarrow \int{{{v}^{2}}dt}=9 \\
\end{align}$
The time period of the cycle can be obtained from the graph as t=2sec.
Therefore, substituting these into the formula we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{V}_{rms}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{9}{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{V}_{rms}}=\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we can find the rms value of the waveform in this way.
Additional information:
The term “rms” stands for “root-mean-squared”. Most books define this as the “amount of ac power that produces the same heating effect as an equivalent dc power”, or something similar along these lines, but an rms value is more than just that. The rms value is the square root of the mean (average) value of the squared function of the instantaneous values. The symbols used for defining an rms value are ${{V}_{rms}}$ or ${{I}_{rms}}$. Rms (root mean square) value is defined based on the heating effect of wave-forms. The value at which heat dissipated in the ac circuit is the same as the heat dissipated in the dc circuit is called rms value, provided both ac and dc circuits have equal value of resistance and operate for the same time.
Note:
The rms voltage which is also referred to as the effective value depends on the magnitude of the waveform and the rms voltage is not a function of either of the waveform’s frequency nor its phase angle.
Formula used:
${{V}_{rms}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{\int{{{v}^{2}}dt}}{\int{dt}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let us write down the given terms and quantities form the graph,
$\begin{align}
& {{V}_{\max }}=3V \\
& T=2\sec \\
\end{align}$
Now, the term in the formula $\int{{{v}^{2}}dt}$can be found by finding the area of one cycle
Therefore, let's find the area of one cycle in the waveform,
$\begin{align}
& \int{{{v}^{2}}dt}=2\times \dfrac{1}{2}\times 2\times 3 \\
& \Rightarrow \int{{{v}^{2}}dt}=9 \\
\end{align}$
The time period of the cycle can be obtained from the graph as t=2sec.
Therefore, substituting these into the formula we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{V}_{rms}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{9}{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{V}_{rms}}=\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we can find the rms value of the waveform in this way.
Additional information:
The term “rms” stands for “root-mean-squared”. Most books define this as the “amount of ac power that produces the same heating effect as an equivalent dc power”, or something similar along these lines, but an rms value is more than just that. The rms value is the square root of the mean (average) value of the squared function of the instantaneous values. The symbols used for defining an rms value are ${{V}_{rms}}$ or ${{I}_{rms}}$. Rms (root mean square) value is defined based on the heating effect of wave-forms. The value at which heat dissipated in the ac circuit is the same as the heat dissipated in the dc circuit is called rms value, provided both ac and dc circuits have equal value of resistance and operate for the same time.
Note:
The rms voltage which is also referred to as the effective value depends on the magnitude of the waveform and the rms voltage is not a function of either of the waveform’s frequency nor its phase angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




