
The water-conducting tissue generally present in gymnosperm is
(a)Vessels
(b)Sieve tube
(c)Tracheids
(d)Xylem fibers
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: These are elongated cells of vascular plants that serve in the transport of water and mineral salts. They do not have perforation plates (part of the cell wall with many holes).
Complete answer:
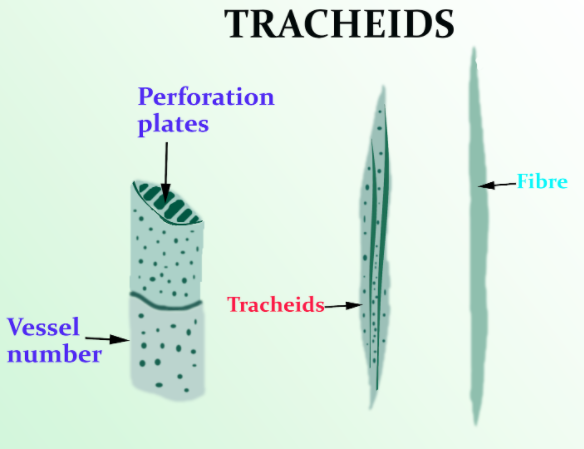
Water is transported with the help of these elongated cells longitudinally through endplates and laterally through pits. There are two types of tracheary elements, one vessel elements, and the other tracheids. Tracheids are used in gymnosperms as the major water-conducting tissue and mechanical supporting cells. The term was introduced by Carl Sanio in 1863. Tracheids are longer than individual vessels and do not have open ends like the vessels. Vessels primarily transport water in the angiosperm.
The tracheary elements develop before maturity a thick lignified cell wall and the presence of these tracheary elements is a characteristic of vascular plants. The secondary walls of tracheids have thickenings in various forms (like annular rings, continuous helices, a network, transverse nets, or as thickenings except in the region of pits). In softwoods, tracheids provide most of the mechanical support and are the major cell type. When transpiration is not occurring tracheids serve to hold water against gravity as they comparatively have a much higher surface to volume ratio to vessel elements which help the plant prevent air embolisms.
So, the correct answer is ‘Tracheids’.
Note: Gymnosperm plants are a vascular plant (have conducting tissue) that reproduce with an exposed seed (naked seeds) or ovules like evergreen trees such as pine, spruce, and fir. Angiosperms are a large number of flowering plant seeds enclosed by mature ovaries or fruits like lilies, orchids, agaves, and grasses.
Complete answer:
Water is transported with the help of these elongated cells longitudinally through endplates and laterally through pits. There are two types of tracheary elements, one vessel elements, and the other tracheids. Tracheids are used in gymnosperms as the major water-conducting tissue and mechanical supporting cells. The term was introduced by Carl Sanio in 1863. Tracheids are longer than individual vessels and do not have open ends like the vessels. Vessels primarily transport water in the angiosperm.
The tracheary elements develop before maturity a thick lignified cell wall and the presence of these tracheary elements is a characteristic of vascular plants. The secondary walls of tracheids have thickenings in various forms (like annular rings, continuous helices, a network, transverse nets, or as thickenings except in the region of pits). In softwoods, tracheids provide most of the mechanical support and are the major cell type. When transpiration is not occurring tracheids serve to hold water against gravity as they comparatively have a much higher surface to volume ratio to vessel elements which help the plant prevent air embolisms.
So, the correct answer is ‘Tracheids’.
Note: Gymnosperm plants are a vascular plant (have conducting tissue) that reproduce with an exposed seed (naked seeds) or ovules like evergreen trees such as pine, spruce, and fir. Angiosperms are a large number of flowering plant seeds enclosed by mature ovaries or fruits like lilies, orchids, agaves, and grasses.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




