
The waves in which the particles of the medium vibrate in a direction perpendicular to direction of wave motion is known as:
A. Transverse wave
B. Propagated wave
C. Longitudinal waves
D. Stationary waves.
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: A wave is a disturbance that travels through a medium from one point to another without transporting any matter. A mechanical wave is a disturbance travelling through a medium like solid, liquid gas etc. We have two types of waves; longitudinal wave and transverse wave. To solve this question we see what are transverse waves and longitudinal waves.
Complete step by step answer:
In longitudinal waves, the particles of the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of the motion of the wave.
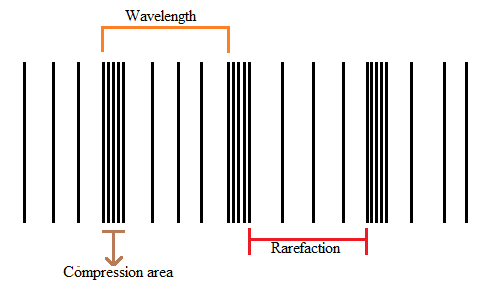
In a transverse wave when the wave moves forward, the particles of the medium vibrate perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave.
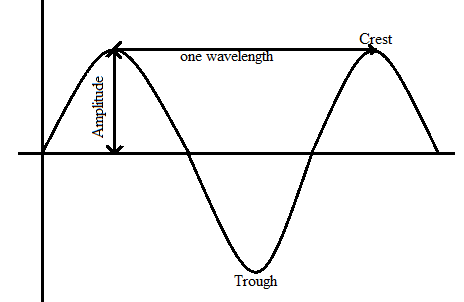
Hence here we have a transverse wave.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
A transverse wave is generated by any kind of vibration.
The highest point above the surface is the crest of a wave and the lowest point below the surface is the trough.
The amplitude of the wave is the maximum height the wave has. It can measure from the top of the crest to the equilibrium line or from the bottom of the trough to the equilibrium line.
The distance from one crest to the other crest or the distance from one trough to the next nearest trough is called the wavelength of the wave.
The time taken to one complete vibration is the time period.
The rate of vibration, i.e. the total number of cycles per second is called the frequency.
When frequency increases wavelength decreases and frequency decreases wavelength increases. I.e. We can say that wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency.
Velocity of the wave is independent of the frequency of the wave. I.e. a change in frequency does not affect the velocity of the wave, it remains the same.
Wave equation gives the relation between velocity, frequency and wavelength of the wave.
$v=f\lambda $ , Where ‘v’ is the velocity of the wave, ‘f’ is its frequency and $'\lambda '$ is the wavelength.
Examples of transverse waves are light waves, radio waves, etc.
Note: We have one more type of wave; longitudinal wave.
As said before, in this type of waves the wave motion is in one direction and the motion of the particles is the same as that of the wave, i.e. they are parallel to each other.
Longitudinal waves have compression and rarefaction areas.
Sound waves are examples of longitudinal waves.
Complete step by step answer:
In longitudinal waves, the particles of the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of the motion of the wave.

In a transverse wave when the wave moves forward, the particles of the medium vibrate perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave.

Hence here we have a transverse wave.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
A transverse wave is generated by any kind of vibration.
The highest point above the surface is the crest of a wave and the lowest point below the surface is the trough.
The amplitude of the wave is the maximum height the wave has. It can measure from the top of the crest to the equilibrium line or from the bottom of the trough to the equilibrium line.
The distance from one crest to the other crest or the distance from one trough to the next nearest trough is called the wavelength of the wave.
The time taken to one complete vibration is the time period.
The rate of vibration, i.e. the total number of cycles per second is called the frequency.
When frequency increases wavelength decreases and frequency decreases wavelength increases. I.e. We can say that wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency.
Velocity of the wave is independent of the frequency of the wave. I.e. a change in frequency does not affect the velocity of the wave, it remains the same.
Wave equation gives the relation between velocity, frequency and wavelength of the wave.
$v=f\lambda $ , Where ‘v’ is the velocity of the wave, ‘f’ is its frequency and $'\lambda '$ is the wavelength.
Examples of transverse waves are light waves, radio waves, etc.
Note: We have one more type of wave; longitudinal wave.
As said before, in this type of waves the wave motion is in one direction and the motion of the particles is the same as that of the wave, i.e. they are parallel to each other.
Longitudinal waves have compression and rarefaction areas.
Sound waves are examples of longitudinal waves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




