
There are seven types of crystal system and 14 types of Bravais lattices.
Reason: Rhombohedral, triclinic and hexagonal crystal systems have only primitive unit cells.
A. Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
B. Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
C. Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
D. Assertion is incorrect but Reason is correct.
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: In a crystalline solid, the constituent units (atoms, ions, or molecules) are arranged in a regular repeating pattern. The positions of the constituent units in a crystal relative to one another are generally shown by points. The arrangement of an infinite set of points is known as space lattice. Thus, the regular arrangements of constituent particles at different points in three-dimensional space are called crystal lattice or space lattice.
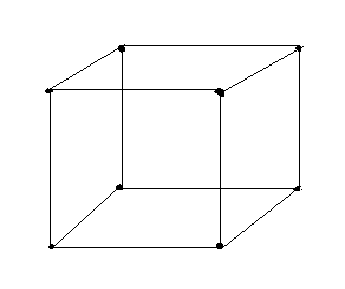
Space lattice and unit cell
Complete step by step answer:
1.There are 14 possible three-dimensional lattices, called Bravais lattice.
2.Some characteristics of crystal lattices are:
Each point in a crystal lattice can be called the lattice point or lattice site.
Each point is a crystal lattice represents one constituent particle (atom, molecule, or ion)
Lattice points are joined by straight lines to give the geometry of the crystal lattice.
A unit cell is known by its cell dimensions a, b, and c and also the axial angles $\alpha $, $\beta $ and $\gamma $. Depending on these parameters, it is found that there are seven types of primitive unit cells. These are also called a seven crystal system.
In the table given below we will discuss the seven crystal system in details:
After seeing the table we can say that rhombohedral, hexagonal, and triclinic have only primitive unit cells.
So we can say that both assertion and reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: A unit cell is the smallest three-dimensional portion which repeats itself in different directions to produce a complete space lattice with characteristics of a unit cell. A unit cell is characterized by:Its dimension along the three edges a, b and c. These edges may or may not be mutually perpendicular. Angles between the edges $\left( {\alpha ,\beta ,\gamma } \right)$ .

Space lattice and unit cell
Complete step by step answer:
1.There are 14 possible three-dimensional lattices, called Bravais lattice.
2.Some characteristics of crystal lattices are:
Each point in a crystal lattice can be called the lattice point or lattice site.
Each point is a crystal lattice represents one constituent particle (atom, molecule, or ion)
Lattice points are joined by straight lines to give the geometry of the crystal lattice.
A unit cell is known by its cell dimensions a, b, and c and also the axial angles $\alpha $, $\beta $ and $\gamma $. Depending on these parameters, it is found that there are seven types of primitive unit cells. These are also called a seven crystal system.
In the table given below we will discuss the seven crystal system in details:
| Central System | Possible Variation | Edge length | Axial angles | Examples |
| Cubic | Primitive, Face centered, Body centered | $a = b = c$ | $\alpha = \beta = \gamma = {90^ \circ }$ | $NaCl$ |
| Tetragonal | Primitive, Body centered | $a = b \ne c$ | $\alpha = \beta = \gamma = {90^ \circ }$ | $KN{O_3}$ |
| Orthorhombic | Primitive, Body centered, Face centered, End centered | $a \ne b \ne c$ | $\alpha = \beta = \gamma = {90^ \circ }$ | $CaC{O_3}$ |
| Hexagonal | Primitive | $a = b \ne c$ | $\alpha = \beta = {90^ \circ } \gamma = {120^ \circ }$ | $ZnO$ |
| Rhombohedral | Primitive | $a = b = c$ | $\alpha = \beta = \gamma = {90^ \circ }$ | $HgS$ |
| Monoclinic | Primitive, End centered | $a \ne b \ne c$ | $ \alpha = \gamma = {90^ \circ } \beta \ne {120^ \circ } $$z | $N{a_2}S{O_{_4}}.10{H_2}O$ |
| Triclinic | Primitive | $a \ne b \ne c$ | $\alpha \ne \beta \ne \gamma \ne {90^ \circ }$ | ${K_2}C{r_2}{O_7}$ |
After seeing the table we can say that rhombohedral, hexagonal, and triclinic have only primitive unit cells.
So we can say that both assertion and reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: A unit cell is the smallest three-dimensional portion which repeats itself in different directions to produce a complete space lattice with characteristics of a unit cell. A unit cell is characterized by:Its dimension along the three edges a, b and c. These edges may or may not be mutually perpendicular. Angles between the edges $\left( {\alpha ,\beta ,\gamma } \right)$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




