
When thiosulfate ion is oxidized by iodine, the new product X is formed. How many ${\text{S - S}}$ linkage is/are present in X?
Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint: Iodometric analysis is a quantitative analysis of a solution of an oxidizing agent by adding an iodide which reacts to form iodine. The released iodine is then titrated with another species. Usually, a standard thiosulfate solution is used for this.
Complete step by step solution:
The structure of sodium thiosulfate is given below:
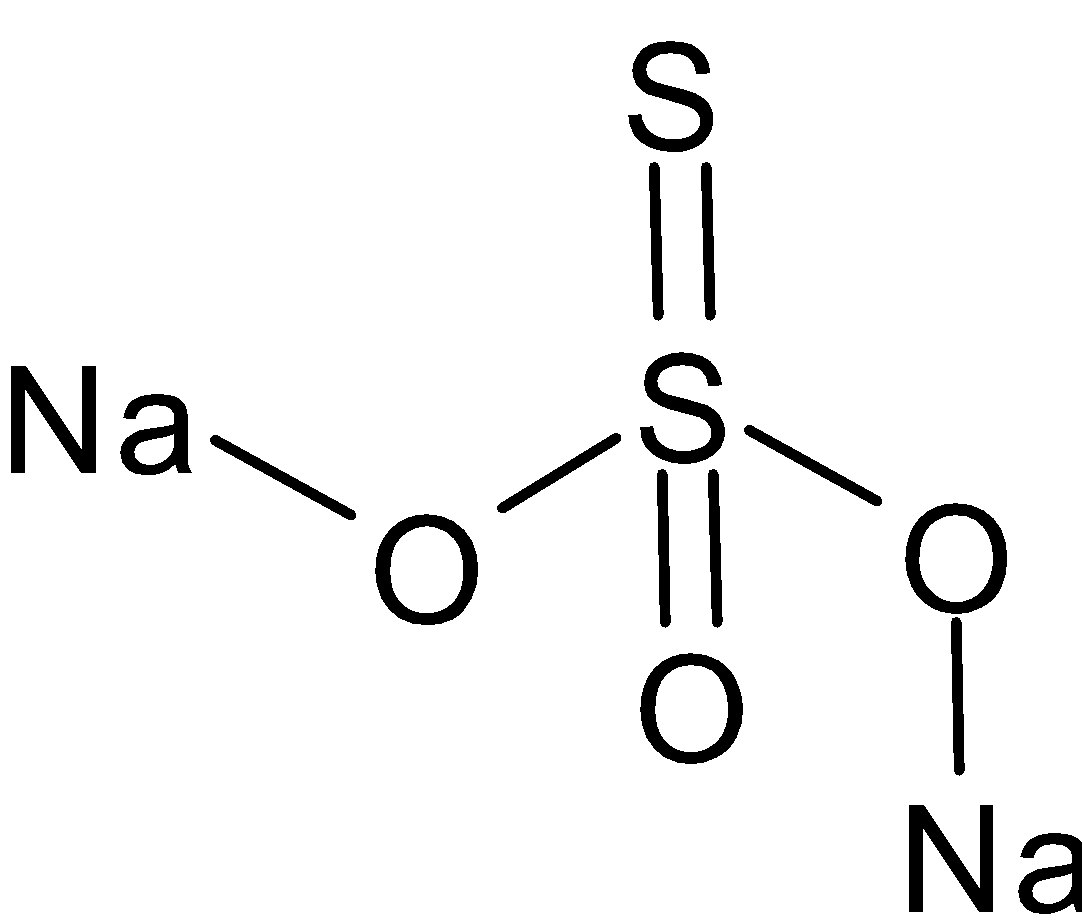
Sodium thiosulfate has one ${\text{S - S}}$ bond which is a double bond. Now let’s consider the thiosulfate ions reacting with iodine. The chemical equation is given below:
${{\text{S}}_2}{{\text{O}}_3}^{2 - } + {{\text{I}}_2} \to {{\text{S}}_4}{{\text{O}}_6}^{2 - } + 2{{\text{I}}^ - }$
Iodine is a weak oxidizing agent. In the above chemical equation, iodine is reduced to iodide anion, ${\text{I}}\left( { - 1} \right)$. The titration of thiosulfate with iodine is called iodometric titrations. The first step is the reaction of ${\text{KI}}$ and ${{\text{K}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{{\text{O}}_7}$. In this reaction, iodine is liberated. This iodine is titrated with thiosulfate ions in the presence of starch indicator. At the end point, the blue or violet color of the starch indicator disappears.
We can express the titration between the sodium thiosulfate and iodine as given below:
${\text{2N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{{\text{S}}_2}{{\text{O}}_3} + {{\text{I}}_2} \to {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{{\text{S}}_4}{{\text{O}}_6} + 2{\text{NaI}}$
In this reaction, sulfur changes its oxidation number from $ + 2$ to $ + 2.5$ . Thus oxidation number is increased, thereby it undergoes oxidation. While iodine changes its oxidation number from $0$ to $ - 1$. Thus oxidation number is reduced, thereby it undergoes reduction.
The structure of ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{{\text{S}}_4}{{\text{O}}_6}$ is given below:
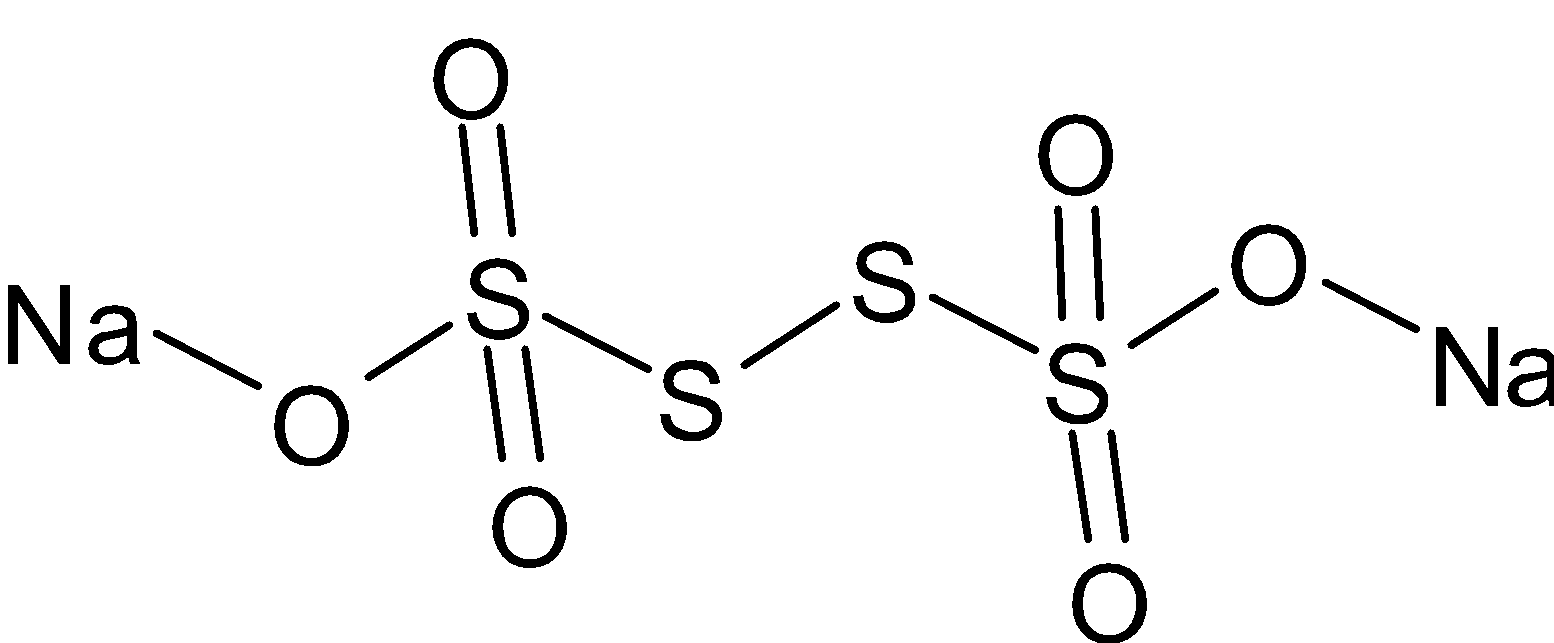
The number of ${\text{S - S}}$ linkages in ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{{\text{S}}_4}{{\text{O}}_6}$ is three. They form only single bonds. They form double bonds with only oxygen. But in ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{{\text{S}}_2}{{\text{O}}_3}$, it forms double bonds with both sulfur and oxygen.
Note: Iodine is very useful in titration method. This method helps us to determine the amount of thiosulfate ions in the solution. Iodine is not soluble in water, so iodine solution is prepared by dissolving potassium iodide in water.
Complete step by step solution:
The structure of sodium thiosulfate is given below:

Sodium thiosulfate has one ${\text{S - S}}$ bond which is a double bond. Now let’s consider the thiosulfate ions reacting with iodine. The chemical equation is given below:
${{\text{S}}_2}{{\text{O}}_3}^{2 - } + {{\text{I}}_2} \to {{\text{S}}_4}{{\text{O}}_6}^{2 - } + 2{{\text{I}}^ - }$
Iodine is a weak oxidizing agent. In the above chemical equation, iodine is reduced to iodide anion, ${\text{I}}\left( { - 1} \right)$. The titration of thiosulfate with iodine is called iodometric titrations. The first step is the reaction of ${\text{KI}}$ and ${{\text{K}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{{\text{O}}_7}$. In this reaction, iodine is liberated. This iodine is titrated with thiosulfate ions in the presence of starch indicator. At the end point, the blue or violet color of the starch indicator disappears.
We can express the titration between the sodium thiosulfate and iodine as given below:
${\text{2N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{{\text{S}}_2}{{\text{O}}_3} + {{\text{I}}_2} \to {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{{\text{S}}_4}{{\text{O}}_6} + 2{\text{NaI}}$
In this reaction, sulfur changes its oxidation number from $ + 2$ to $ + 2.5$ . Thus oxidation number is increased, thereby it undergoes oxidation. While iodine changes its oxidation number from $0$ to $ - 1$. Thus oxidation number is reduced, thereby it undergoes reduction.
The structure of ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{{\text{S}}_4}{{\text{O}}_6}$ is given below:

The number of ${\text{S - S}}$ linkages in ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{{\text{S}}_4}{{\text{O}}_6}$ is three. They form only single bonds. They form double bonds with only oxygen. But in ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{{\text{S}}_2}{{\text{O}}_3}$, it forms double bonds with both sulfur and oxygen.
Note: Iodine is very useful in titration method. This method helps us to determine the amount of thiosulfate ions in the solution. Iodine is not soluble in water, so iodine solution is prepared by dissolving potassium iodide in water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




