
This is the floral formula of
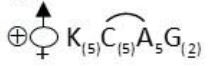
A. Asteraceae
B. Brassicaceae
C. Fabaceae
D. Solanaceae
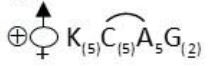
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Floral formula – (i) It represents a flower’s structure by using specific symbols, letters and numbers. It is the simple way to present salient features of a flower.
(ii) It depicts the interrelationship between different floral parts which are corolla, calyx, androecium and gynoecium, it also provides information about the type of flower, its symmetry, type of ovary, fusion etc.
Complete Answer:
A) (i) Floral diagram helps in making up the floral formula.
(ii) Floral diagram is a diagrammatic representation of the pooled up information from transverse sections of the flower bud in relation to the mother axis.
(iii) The floral formula of the solanaceae family is
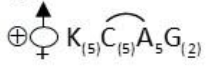
Examples of solanaceae are: Solanum tuberosum (Potato), Lycopersicon esculentum (Tomato), Solanum melongena (Brinjal), Capsicum annum (Chillies)
Family Description:
- Inflorescence: Salutary, ancillary or cymose.
- Flower: Bisexual, actinomorphic.
- Calyn: Sepals five, united, persistent and valvate aestivation.
- Corolla: Petals five, united, valvate aestivation.
- Androecium: Stamens five, epipetalous.
- Gynoecium: Bicarpellary, Syncarpous, ovary superior, bilocular swollen placenta with many ovules.
- Fruits: Berry or capsule.
- Seeds: Many, endospermous
B) Asteraceae: The floral formula is
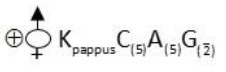
Example: Sunflower
C) Brassicaceae: The floral formula is
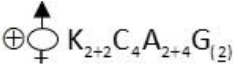
Example: Mustard
D) Fabaceae: The floral formula is
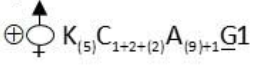
Example: Pea
Note:
1) Asteraceae: (i) Calyx is rudimentary or absent and called as pappus.
(ii) Fruit of Araceae is known as achenes or cypsela.
2) Brassicaceae: Brassicaceae or curcifireae family flowers are actinomorphic, bisexual, sepals are 4 and are dimerous i.e. arranged in two whorls, petals 4 and arranged in single whorl, stamens are 6 and are tetradynamons (two lateral stamens are smaller and four median are larger, carpels are 2 i.e. bicarpellary, syncarphons, ovary superior.
3) Fabaceae have five sepals (fused), five petals (upper posterior petal or the venillum, two lateral free petals or wings, and two anterior petals or the keel. Stamens are ten, superior ovaries.
(ii) It depicts the interrelationship between different floral parts which are corolla, calyx, androecium and gynoecium, it also provides information about the type of flower, its symmetry, type of ovary, fusion etc.
Complete Answer:
A) (i) Floral diagram helps in making up the floral formula.
(ii) Floral diagram is a diagrammatic representation of the pooled up information from transverse sections of the flower bud in relation to the mother axis.
(iii) The floral formula of the solanaceae family is
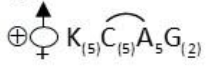
Examples of solanaceae are: Solanum tuberosum (Potato), Lycopersicon esculentum (Tomato), Solanum melongena (Brinjal), Capsicum annum (Chillies)
Family Description:
- Inflorescence: Salutary, ancillary or cymose.
- Flower: Bisexual, actinomorphic.
- Calyn: Sepals five, united, persistent and valvate aestivation.
- Corolla: Petals five, united, valvate aestivation.
- Androecium: Stamens five, epipetalous.
- Gynoecium: Bicarpellary, Syncarpous, ovary superior, bilocular swollen placenta with many ovules.
- Fruits: Berry or capsule.
- Seeds: Many, endospermous
B) Asteraceae: The floral formula is
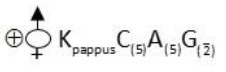
Example: Sunflower
C) Brassicaceae: The floral formula is
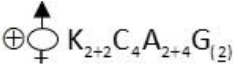
Example: Mustard
D) Fabaceae: The floral formula is
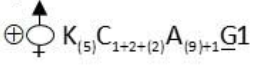
Example: Pea
Note:
1) Asteraceae: (i) Calyx is rudimentary or absent and called as pappus.
(ii) Fruit of Araceae is known as achenes or cypsela.
2) Brassicaceae: Brassicaceae or curcifireae family flowers are actinomorphic, bisexual, sepals are 4 and are dimerous i.e. arranged in two whorls, petals 4 and arranged in single whorl, stamens are 6 and are tetradynamons (two lateral stamens are smaller and four median are larger, carpels are 2 i.e. bicarpellary, syncarphons, ovary superior.
3) Fabaceae have five sepals (fused), five petals (upper posterior petal or the venillum, two lateral free petals or wings, and two anterior petals or the keel. Stamens are ten, superior ovaries.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




