
Three girls Reshma, Salma and Mandip are playing a game by standing on a circle of the radius $5m$ drawn in a park. Reshma throws a ball to Salma, Salma to Mandip, Mandip to Reshma. The distance between Reshma and Salma and between Salma and Mandip is $6m$ each, what is the distance between Reshma and Mandip?
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: Here we will first construct a diagram based on the given data, first we will draw a circle of radius $5m$ and then we will mark the places where Reshma, Salma and Mandip stood as $R,S,M$ on the circle. Now we will list all the lengths of the parameters we have in the circle. Now we will calculate the required distance by using the triangles that are formed by joining the points on the circle with each of them and with the center of the circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that,
Three girls Reshma, Salma and Mandip are playing a game by standing on a circle of the radius $5m$ drawn in a park. Reshma throws a ball to Salma, Salma to Mandip, Mandip to Reshma.
The diagrammatical representation of the above data is shown below
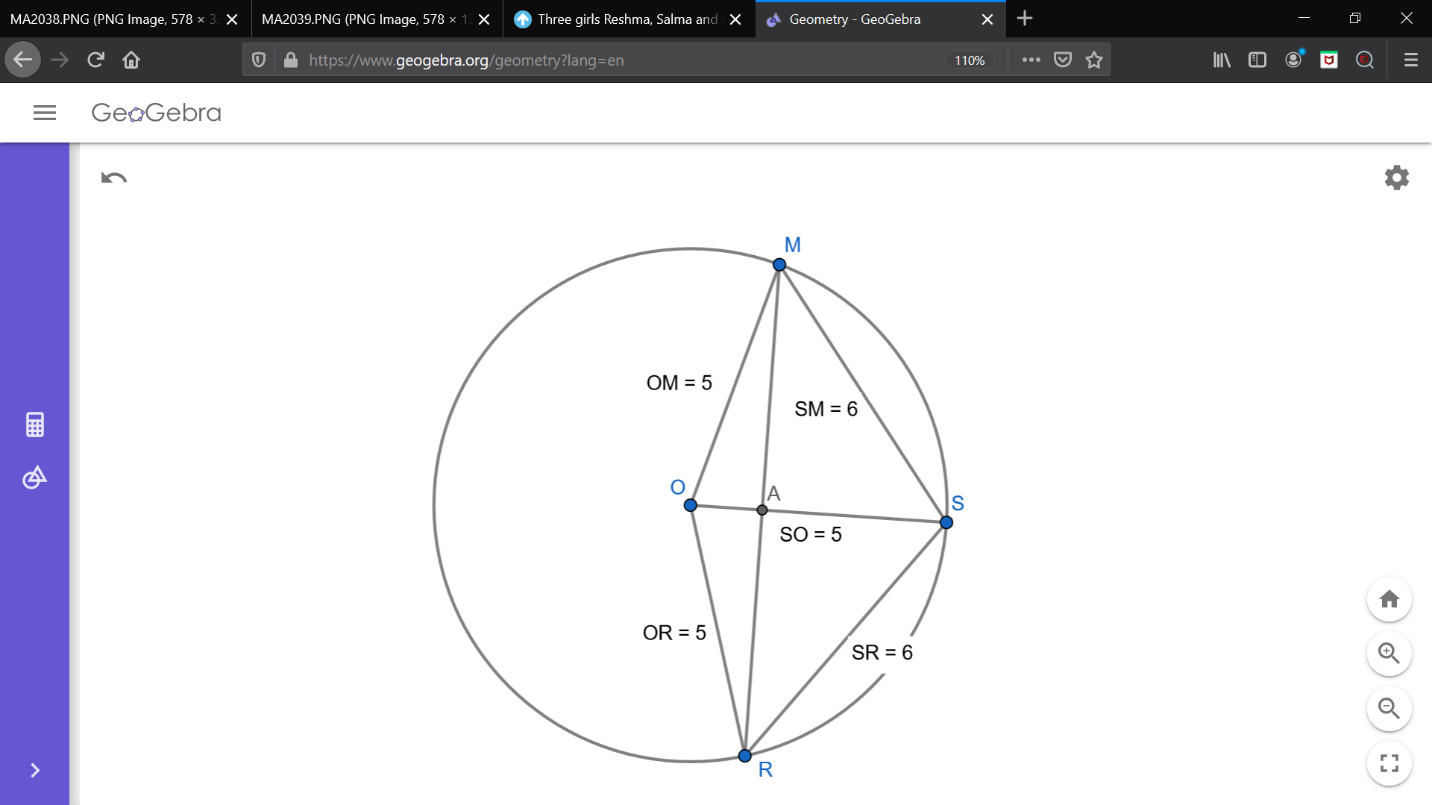
Here the points
$O$ is the center of the circle.
$S$ is the point where Salma stood on the circle.
$R$ is the point where Reshma stood on the circle.
$M$ is the point where Mandip stood on the circle.
Here the lengths
$SM$ is the distance between Salma and Mandip, according to problem $SM=6m$
$SR$ is the distance between Salma and Reshma, according to the problem $SR=6m$
$MR$ is the distance between Mandip and Reshma, we need to calculate this length.
We know that the distance between the center of the circle to the any point on the circle is called as the radius, hence
$OM=OR=OS=r=5m$
From the diagram we can observe that, $OS$ is the angular bisector of $\angle RSM$ and it is also passing through the center, so we know that it will perpendicularly bisects the chords of the circles i.e. $OS$ is the perpendicular bisector of the line $MR$ and it bisects the line $MR$ at point $A$, hence
$MA=RA...\left( \text{i} \right)$
From the right-angled triangle $SAR$, using Pythagoras theorem
$\begin{align}
& S{{R}^{2}}=R{{A}^{2}}+S{{A}^{2}} \\
&\Rightarrow R{{A}^{2}}=S{{R}^{2}}-S{{A}^{2}} \\
&\Rightarrow R{{A}^{2}}={{6}^{2}}-S{{A}^{2}}...\left( \text{ii} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now from the right-angled triangle $OAR$, using the Pythagoras theorem
$\begin{align}
& O{{R}^{2}}=O{{A}^{2}}+A{{R}^{2}} \\
&\Rightarrow {{5}^{2}}=O{{A}^{2}}+A{{R}^{2}} \\
&\Rightarrow A{{R}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}-O{{A}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now from the diagram we can write $OA=OS-SA$ in the above equation, then we will have
$\begin{align}
& A{{R}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}-\left( O{{S}^{2}}-S{{A}^{2}} \right) \\
& ={{5}^{2}}-{{\left( 5-SA \right)}^{2}}....\left( \text{iii} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Equating the equations $\left( \text{ii} \right)$ and $\left( \text{iii} \right)$, then we will get
${{6}^{2}}-S{{A}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}-{{\left( 5-SA \right)}^{2}}$
Using the formula ${{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab$ in the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& 36-S{{A}^{2}}=25-\left( 25+S{{A}^{2}}-2.5.SA \right) \\
&\Rightarrow 36-S{{A}^{2}}=25-25-S{{A}^{2}}+10SA \\
&\Rightarrow 36-S{{A}^{2}}+S{{A}^{2}}=0+10SA \\
&\Rightarrow 36+0=10SA \\
&\Rightarrow 10SA=36 \\
&\Rightarrow SA=\dfrac{36}{10} \\
&\Rightarrow SA=3.6 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the value of $SA=3.6$ in equation $\left( \text{ii} \right)$, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& R{{A}^{2}}={{6}^{2}}-{{3.6}^{2}} \\
&\Rightarrow R{{A}^{2}}=36-12.96 \\
&\Rightarrow R{{A}^{2}}=23.04 \\
&\Rightarrow RA=\sqrt{23.04} \\
&\Rightarrow RA\simeq 4.8m \\
\end{align}$
Now from the equation $\left( \text{i} \right)$, we can write that
$\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow RM=2RA \\
&\Rightarrow RM=2\times 4.8 \\
& =9.6m \\
\end{align}$
Hence the distance between Reshma and Mandip is $9.6m$
Note: For this problem diagrammatic representation takes a major part. After plotting the given data into picture, we can use any of the triangles in order to get the solution. Students must mark the given distances properly in the figure. By mistake, if they mark OR = OM = 6 instead of 5, then the results will vary. We are supposed to find the distance between Reshma and Mandip, so we must find the total length RM by adding RA and AM.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that,
Three girls Reshma, Salma and Mandip are playing a game by standing on a circle of the radius $5m$ drawn in a park. Reshma throws a ball to Salma, Salma to Mandip, Mandip to Reshma.
The diagrammatical representation of the above data is shown below

Here the points
$O$ is the center of the circle.
$S$ is the point where Salma stood on the circle.
$R$ is the point where Reshma stood on the circle.
$M$ is the point where Mandip stood on the circle.
Here the lengths
$SM$ is the distance between Salma and Mandip, according to problem $SM=6m$
$SR$ is the distance between Salma and Reshma, according to the problem $SR=6m$
$MR$ is the distance between Mandip and Reshma, we need to calculate this length.
We know that the distance between the center of the circle to the any point on the circle is called as the radius, hence
$OM=OR=OS=r=5m$
From the diagram we can observe that, $OS$ is the angular bisector of $\angle RSM$ and it is also passing through the center, so we know that it will perpendicularly bisects the chords of the circles i.e. $OS$ is the perpendicular bisector of the line $MR$ and it bisects the line $MR$ at point $A$, hence
$MA=RA...\left( \text{i} \right)$
From the right-angled triangle $SAR$, using Pythagoras theorem
$\begin{align}
& S{{R}^{2}}=R{{A}^{2}}+S{{A}^{2}} \\
&\Rightarrow R{{A}^{2}}=S{{R}^{2}}-S{{A}^{2}} \\
&\Rightarrow R{{A}^{2}}={{6}^{2}}-S{{A}^{2}}...\left( \text{ii} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now from the right-angled triangle $OAR$, using the Pythagoras theorem
$\begin{align}
& O{{R}^{2}}=O{{A}^{2}}+A{{R}^{2}} \\
&\Rightarrow {{5}^{2}}=O{{A}^{2}}+A{{R}^{2}} \\
&\Rightarrow A{{R}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}-O{{A}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now from the diagram we can write $OA=OS-SA$ in the above equation, then we will have
$\begin{align}
& A{{R}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}-\left( O{{S}^{2}}-S{{A}^{2}} \right) \\
& ={{5}^{2}}-{{\left( 5-SA \right)}^{2}}....\left( \text{iii} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Equating the equations $\left( \text{ii} \right)$ and $\left( \text{iii} \right)$, then we will get
${{6}^{2}}-S{{A}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}-{{\left( 5-SA \right)}^{2}}$
Using the formula ${{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab$ in the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& 36-S{{A}^{2}}=25-\left( 25+S{{A}^{2}}-2.5.SA \right) \\
&\Rightarrow 36-S{{A}^{2}}=25-25-S{{A}^{2}}+10SA \\
&\Rightarrow 36-S{{A}^{2}}+S{{A}^{2}}=0+10SA \\
&\Rightarrow 36+0=10SA \\
&\Rightarrow 10SA=36 \\
&\Rightarrow SA=\dfrac{36}{10} \\
&\Rightarrow SA=3.6 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the value of $SA=3.6$ in equation $\left( \text{ii} \right)$, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& R{{A}^{2}}={{6}^{2}}-{{3.6}^{2}} \\
&\Rightarrow R{{A}^{2}}=36-12.96 \\
&\Rightarrow R{{A}^{2}}=23.04 \\
&\Rightarrow RA=\sqrt{23.04} \\
&\Rightarrow RA\simeq 4.8m \\
\end{align}$
Now from the equation $\left( \text{i} \right)$, we can write that
$\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow RM=2RA \\
&\Rightarrow RM=2\times 4.8 \\
& =9.6m \\
\end{align}$
Hence the distance between Reshma and Mandip is $9.6m$
Note: For this problem diagrammatic representation takes a major part. After plotting the given data into picture, we can use any of the triangles in order to get the solution. Students must mark the given distances properly in the figure. By mistake, if they mark OR = OM = 6 instead of 5, then the results will vary. We are supposed to find the distance between Reshma and Mandip, so we must find the total length RM by adding RA and AM.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




