
What were the three major observations Rutherford made in the gold foil experiment?
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: Ernest Rutherford was a British scientist who suggested an experiment and based on the observations of this experiment, he proposed the atomic structure of elements and gave the Rutherford Atomic Model.
This model was a big step towards describing the structure of an atom.
Complete answer:
Rutherford was a former research student of J.J. Thomson (who proposed the plum pudding model of the atom in 1904). He was engaged with alpha-particles emitted by radioactive elements. In 1906, he proposed an experiment of scattering alpha-particles to determine the structure of atoms.
On his suggestion, in 1911, H. Geiger and E. Marsden directed a beam of alpha particles emitted from a radioactive source at a thin foil made of gold. They used lead bricks to narrow the beam. The scattered particles were observed through a rotatable detector consisting of zinc sulphide screen as shown in figure. When the alpha particles struck on the screen, the screen produced light flashes which were viewed through a microscope. The distribution of the number of scattered particles was studied as a function of angle of scattering.
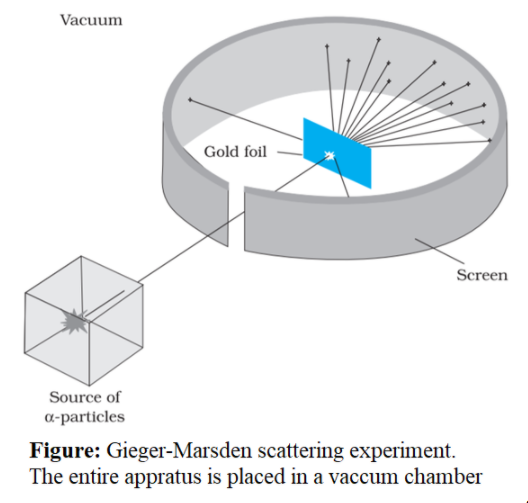
It was observed that,
1.Major fraction of alpha particles pass through the foil undeflected.
2.A few alpha-particles were scattered by very small angles.
3.A very small number of particles were deflected back by 1800.
Note:
From the observations of Rutherford’s experiment it was concluded that positively charged particles and most of an atom was concentrated in a very small volume known as nucleus. Electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom revolve around it with very high speed.
This model was a big step towards describing the structure of an atom.
Complete answer:
Rutherford was a former research student of J.J. Thomson (who proposed the plum pudding model of the atom in 1904). He was engaged with alpha-particles emitted by radioactive elements. In 1906, he proposed an experiment of scattering alpha-particles to determine the structure of atoms.
On his suggestion, in 1911, H. Geiger and E. Marsden directed a beam of alpha particles emitted from a radioactive source at a thin foil made of gold. They used lead bricks to narrow the beam. The scattered particles were observed through a rotatable detector consisting of zinc sulphide screen as shown in figure. When the alpha particles struck on the screen, the screen produced light flashes which were viewed through a microscope. The distribution of the number of scattered particles was studied as a function of angle of scattering.

It was observed that,
1.Major fraction of alpha particles pass through the foil undeflected.
2.A few alpha-particles were scattered by very small angles.
3.A very small number of particles were deflected back by 1800.
Note:
From the observations of Rutherford’s experiment it was concluded that positively charged particles and most of an atom was concentrated in a very small volume known as nucleus. Electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom revolve around it with very high speed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




