
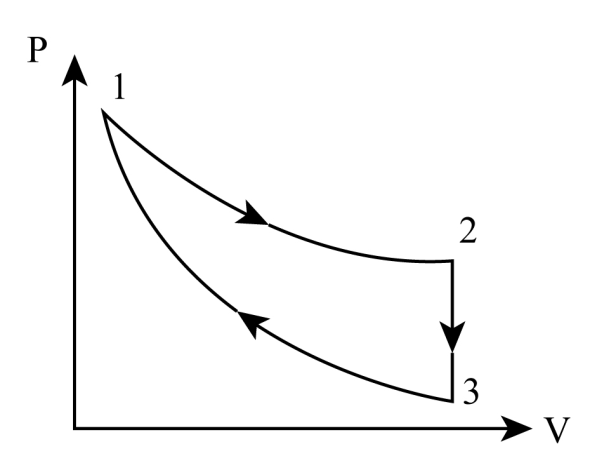
Three processes for a thermodynamic cycle as shown on P-V diagram for an ideal gas. Process 1 takes place at constant temperature (300K). Process 2 takes place at constant volume. During this process 40J of heat leaves the system. Process 3 is adiabatic and temperature T3 is 275K. Work done by the gas during the process 3 is
A. -40J
B. -20J
C. +40J
D. +20J

Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: We know that there are four thermodynamics processes isobaric, isochoric, isothermal and adiabatic. In isothermal process temperature remains constant, in adiabatic process there is no transfer of heat, also in isochoric process volume remains constant and isobaric process pressure remains constant. Also we apply here first law of thermodynamics.
Complete step by step answer:
Given, process 1 is an isothermal process. (300K)
2 is an isochoric process. (40j of heat leaves the system)
3is adiabatic process. (T3 is 275K)
Now, in the isothermal process $\Delta {{\rm{U}}_{12}} = 0$.
According to first law of thermodynamics $\Delta {\rm{Q = }}\Delta {\rm{U + }}\Delta {\rm{W}}$
(Here $\Delta {\rm{Q}}$ Is heat, $\Delta {\rm{U}}$is internal energy, $\Delta {\rm{W }}$ is work done)
$\Delta {{\rm{Q}}_{23}} = \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{23}}$ Because in isochoric process $\Delta {\rm{w = 0}}$
$ \Rightarrow - 40 = \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{23}}$
Thus for a cyclic process $\Delta {\rm{U = 0}}$
$\therefore \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{12}} + \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{23}} + \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{31}} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow (0) + ( - 40) + \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{31}} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{31}} = + 40{\rm{J}}$
In process 31we will apply first law of thermodynamics,
${{\rm{Q}}_{31}} = {{\rm{W}}_{31}} + \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{31}}$
Since 3$ \to $1 is an adiabatic process therefore heat transfer ${{\rm{Q}}_{31}} = 0$ and we are substituting $\Delta {{\rm{U}}_{31}} = + 40{\rm{J}}$ to find the value of work transfer. So we will get,
$ \Rightarrow 0 = {{\rm{W}}_{31}} + 40\;{\rm{J}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\rm{W}}_{31}} = - 40\;{\rm{J}}$
So, the work done by the gas during process $ = - 40{\rm{J}}$
Therefore the correct option is (A).
Additional Information: In Physics, when the system(gas) does work(i.e it loses energy) it is taken as positive and when work is done on the gas(i.e it gains energy) it is taken as negative.
Note: In thermodynamics cyclic process takes place when a system in a given initial state goes in different changes of state and finally returns to its initial state. Some variables in a thermodynamic system are path functions, like work and heat which depend on the path taken. On the other hand there are state functions, like internal energy which only depend on the states and not on the path taken.
Complete step by step answer:
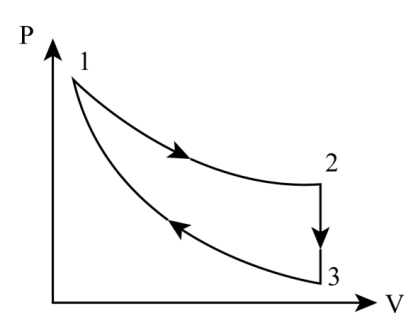
Given, process 1 is an isothermal process. (300K)
2 is an isochoric process. (40j of heat leaves the system)
3is adiabatic process. (T3 is 275K)

Now, in the isothermal process $\Delta {{\rm{U}}_{12}} = 0$.
According to first law of thermodynamics $\Delta {\rm{Q = }}\Delta {\rm{U + }}\Delta {\rm{W}}$
(Here $\Delta {\rm{Q}}$ Is heat, $\Delta {\rm{U}}$is internal energy, $\Delta {\rm{W }}$ is work done)
$\Delta {{\rm{Q}}_{23}} = \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{23}}$ Because in isochoric process $\Delta {\rm{w = 0}}$
$ \Rightarrow - 40 = \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{23}}$
Thus for a cyclic process $\Delta {\rm{U = 0}}$
$\therefore \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{12}} + \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{23}} + \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{31}} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow (0) + ( - 40) + \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{31}} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{31}} = + 40{\rm{J}}$
In process 31we will apply first law of thermodynamics,
${{\rm{Q}}_{31}} = {{\rm{W}}_{31}} + \Delta {{\rm{U}}_{31}}$
Since 3$ \to $1 is an adiabatic process therefore heat transfer ${{\rm{Q}}_{31}} = 0$ and we are substituting $\Delta {{\rm{U}}_{31}} = + 40{\rm{J}}$ to find the value of work transfer. So we will get,
$ \Rightarrow 0 = {{\rm{W}}_{31}} + 40\;{\rm{J}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{\rm{W}}_{31}} = - 40\;{\rm{J}}$
So, the work done by the gas during process $ = - 40{\rm{J}}$
Therefore the correct option is (A).
Additional Information: In Physics, when the system(gas) does work(i.e it loses energy) it is taken as positive and when work is done on the gas(i.e it gains energy) it is taken as negative.
Note: In thermodynamics cyclic process takes place when a system in a given initial state goes in different changes of state and finally returns to its initial state. Some variables in a thermodynamic system are path functions, like work and heat which depend on the path taken. On the other hand there are state functions, like internal energy which only depend on the states and not on the path taken.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




