
To obtain a standard ECG, a patient is connected to the machine with three electrodes
(a) One to each ankle and to the left wrist
(b) One to each wrist and to the left ankle
(c) One to each wrist and to the left chest region
(d) One to each ankle and to the left chest region
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: ECG or electrocardiogram is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart that spans each cardiac cycle. For this, it requires the attachment of three leads at body parts where action potentials from skeletal muscles can be avoided.
Complete answer:
ECG is a non-invasive and painless way to determine and diagnose any common heart problems by detecting any abnormal heart rhythm, blocked arteries or veins, etc. A standard ECG is obtained by attaching three electrodes- one to each wrist and another to the left ankle. This is done in order to minimize any noise detection by the activity of action potentials generated by the skeletal muscles. These electrodes are further attached to electrical leads or wires that are finally connected to the ECG machine.
Additional Information: -A cardiac cycle is in a continuous phase of cardiac muscle depolarisation and repolarisation. These are detected by each electrode and thus analyze cardiac electrophysiology.
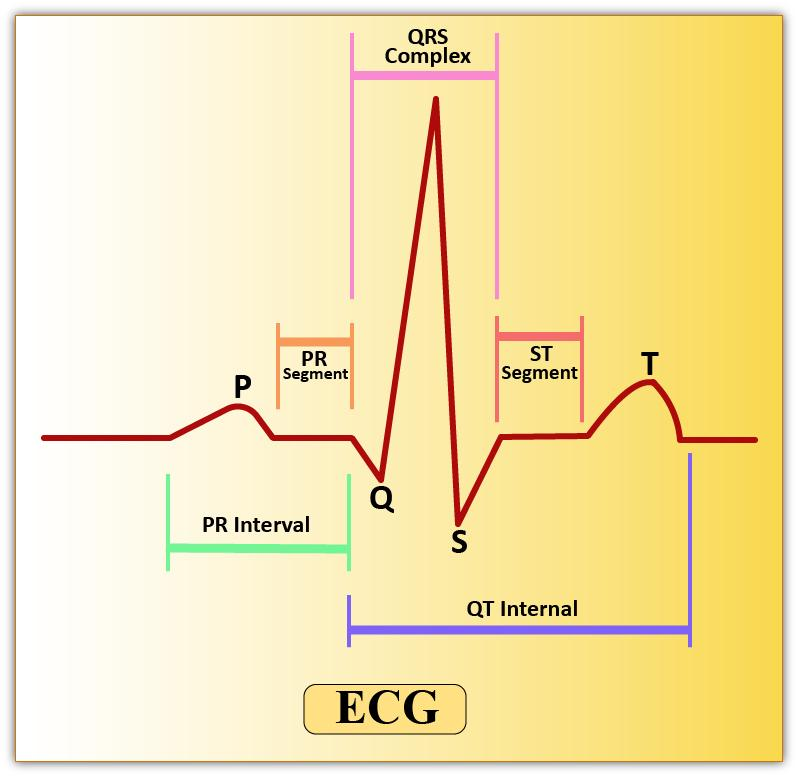
-The first wave in ECG is a ‘P’ wave. Activation of SA or Sino-Atrial Node is indicated by the P-Wave. It lasts for about 0.1 seconds. SA node activation further leads to atrial depolarization.
-Atrial depolarization is followed by ventricular depolarization which is represented by the QRS complex. The contraction of the ventricles starts shortly after Q.
-‘T’ wave is the final wave in an ECG representing a ventricular relaxation. It is produced due to the repolarization of ventricular musculature.
So, the correct answer is ‘One to each wrist and to the left ankle.’
Note: -By counting the number of QRS complexes, one can obtain the number of heartbeat per minute. Any deviation from this shape indicates abnormality.
-Elevation of QR Wave indicates myocardial infarction.
-A flat T-wave represents an insufficient concentration of oxygen received by the cardiac muscles.
Complete answer:
ECG is a non-invasive and painless way to determine and diagnose any common heart problems by detecting any abnormal heart rhythm, blocked arteries or veins, etc. A standard ECG is obtained by attaching three electrodes- one to each wrist and another to the left ankle. This is done in order to minimize any noise detection by the activity of action potentials generated by the skeletal muscles. These electrodes are further attached to electrical leads or wires that are finally connected to the ECG machine.
Additional Information: -A cardiac cycle is in a continuous phase of cardiac muscle depolarisation and repolarisation. These are detected by each electrode and thus analyze cardiac electrophysiology.
-The first wave in ECG is a ‘P’ wave. Activation of SA or Sino-Atrial Node is indicated by the P-Wave. It lasts for about 0.1 seconds. SA node activation further leads to atrial depolarization.
-Atrial depolarization is followed by ventricular depolarization which is represented by the QRS complex. The contraction of the ventricles starts shortly after Q.
-‘T’ wave is the final wave in an ECG representing a ventricular relaxation. It is produced due to the repolarization of ventricular musculature.
So, the correct answer is ‘One to each wrist and to the left ankle.’
Note: -By counting the number of QRS complexes, one can obtain the number of heartbeat per minute. Any deviation from this shape indicates abnormality.
-Elevation of QR Wave indicates myocardial infarction.
-A flat T-wave represents an insufficient concentration of oxygen received by the cardiac muscles.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




