
To produce the interference fringe pattern, draw a diagram of Young’s double slit experiment. Derived an expression of fringe width for bright interference fringes. If the fringe width of bright fringes \[2mm\], write the fringe width for dark fringes. Whether the center point of interference fringe pattern is bright or dark? Explain it.
Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint: In this derivation for width of bright fringes in interference pattern first we will draw a diagram showing interference as shown and then we will proceed according to diagram with the help of Pythagoras Theorem and then for bright fringe make the path difference of light rays equal to integral multiple of wavelength of light and get the desired expression.
Formula Used: -
Pythagoras Theorem
\[H = \sqrt {{P^2} + {B^2}} \]
Where \[H\], \[P\]and \[B\]are the hypotenuse, perpendicular and base of the right angled triangle.
Given data: -
Let suppose a monochromatic light coming from source \[s\]and passes through slit \[{s_1}\] and\[{s_2}\] and meet at point P on screen which is at distance \[D\] from slits and\[d\]is the distance between slits.
\[PC = x\], \[{S_1}E = {S_2}F = D\],\[CF = EC = \dfrac{d}{2}\]
\[PE = PC - EC = x - \dfrac{d}{2}\]
\[PF = PC + CF = x + \dfrac{d}{2}\]
Complete Step by step Solution:
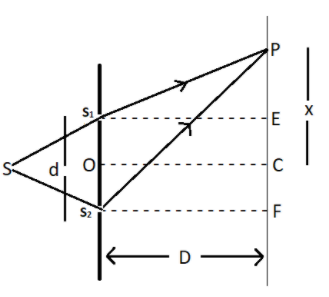
In \[\Delta {S_1}PE\] using Pythagoras theorem
\[{S_1}{P^2} = {S_1}{E^2} + P{E^2}\]
\[{S_1}{P^2} = {D^2} + {(x - \dfrac{d}{2})^2}\]…………………….. (1)
In \[\Delta {S_2}PF\]
\[{S_2}{P^2} = {S_2}{F^2} + P{F^2}\]
\[{S_2}{P^2} = {D^2} + {(x + \dfrac{d}{2})^2}\]…………………….. (2)
On subtracting (2) from (1) we have
\[{S_2}{P^2} - {S_1}{P^2} = {(x + \dfrac{d}{2})^2} - {(x - \dfrac{d}{2})^2} = 2xd\]
\[
({S_2}P - {S_1}P)({S_2}P + {S_1}P) = 2xd \\
({S_2}P - {S_1}P) = \dfrac{{2xd}}{{({S_2}P + {S_1}P)}} = \dfrac{{2xd}}{{2D}} = \dfrac{{xd}}{D}............{S_1}P \simeq {S_2}P \simeq D \\
\]
For bright fringes
Path difference \[{S_2}P - {S_1}P = n\lambda \]
\[
\dfrac{{xd}}{D} = n\lambda \\
x = \dfrac{{n\lambda D}}{d} \\
\]
where \[n = 1,2,3,.....\]
And \[\lambda \] is a wavelength of monochromatic light.
Fringe width
\[
\beta = {x_{n + 1}} - {x_n} \\
\beta = \dfrac{{(n + 1)\lambda D}}{d} - \dfrac{{n\lambda D}}{d} \\
\beta = \dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d} \\
\]
The fringe width for bright fringes and dark fringes are same so if the width for bright fringes is \[2mm\]
then it will be the same for dark fringes \[2mm\].
The center point of interference fringe pattern is bright.
Since there is no path difference of light rays coming from two slits reaching to the center point this will give the bright fringe at center point O.
Note: - In this question we should have the knowledge of the basic principle of interference and the condition for bright fringes and dark fringes. We use the Pythagoras Theorem carefully with the help of geometrical diagrams for the given situation.
Formula Used: -
Pythagoras Theorem
\[H = \sqrt {{P^2} + {B^2}} \]
Where \[H\], \[P\]and \[B\]are the hypotenuse, perpendicular and base of the right angled triangle.
Given data: -
Let suppose a monochromatic light coming from source \[s\]and passes through slit \[{s_1}\] and\[{s_2}\] and meet at point P on screen which is at distance \[D\] from slits and\[d\]is the distance between slits.
\[PC = x\], \[{S_1}E = {S_2}F = D\],\[CF = EC = \dfrac{d}{2}\]
\[PE = PC - EC = x - \dfrac{d}{2}\]
\[PF = PC + CF = x + \dfrac{d}{2}\]
Complete Step by step Solution:

In \[\Delta {S_1}PE\] using Pythagoras theorem
\[{S_1}{P^2} = {S_1}{E^2} + P{E^2}\]
\[{S_1}{P^2} = {D^2} + {(x - \dfrac{d}{2})^2}\]…………………….. (1)
In \[\Delta {S_2}PF\]
\[{S_2}{P^2} = {S_2}{F^2} + P{F^2}\]
\[{S_2}{P^2} = {D^2} + {(x + \dfrac{d}{2})^2}\]…………………….. (2)
On subtracting (2) from (1) we have
\[{S_2}{P^2} - {S_1}{P^2} = {(x + \dfrac{d}{2})^2} - {(x - \dfrac{d}{2})^2} = 2xd\]
\[
({S_2}P - {S_1}P)({S_2}P + {S_1}P) = 2xd \\
({S_2}P - {S_1}P) = \dfrac{{2xd}}{{({S_2}P + {S_1}P)}} = \dfrac{{2xd}}{{2D}} = \dfrac{{xd}}{D}............{S_1}P \simeq {S_2}P \simeq D \\
\]
For bright fringes
Path difference \[{S_2}P - {S_1}P = n\lambda \]
\[
\dfrac{{xd}}{D} = n\lambda \\
x = \dfrac{{n\lambda D}}{d} \\
\]
where \[n = 1,2,3,.....\]
And \[\lambda \] is a wavelength of monochromatic light.
Fringe width
\[
\beta = {x_{n + 1}} - {x_n} \\
\beta = \dfrac{{(n + 1)\lambda D}}{d} - \dfrac{{n\lambda D}}{d} \\
\beta = \dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d} \\
\]
The fringe width for bright fringes and dark fringes are same so if the width for bright fringes is \[2mm\]
then it will be the same for dark fringes \[2mm\].
The center point of interference fringe pattern is bright.
Since there is no path difference of light rays coming from two slits reaching to the center point this will give the bright fringe at center point O.
Note: - In this question we should have the knowledge of the basic principle of interference and the condition for bright fringes and dark fringes. We use the Pythagoras Theorem carefully with the help of geometrical diagrams for the given situation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




