
Total number of bones in the axial skeleton of a man is
A. 206
B. 120
C. 406
D. 80
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: The axial skeleton is one of the two parts of the whole human skeleton. It consists of the skull bones, the vertebral column, and the ribs. It acts to protect vital organs like the brain and the heart. The 28 skull bones, 26 vertebral bones, 24 ribs, a sternum, and a Hyoid bone make up the axial skeleton in man.
Complete answer: The axial skeleton is the uppermost part of the skeleton excluding the limbs. It is made up of the skull bones, the vertebral columns, and the ribs. It functions to protect the organs involved in digestion and breathing. The main function of the axial skeleton is to provide protection to the brain and the heart. Also, the axial skeleton plays a significant role in the movement of other bones.
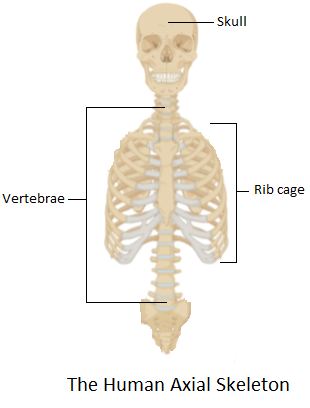
The total number of bones in the axial skeleton of a man is 80. These bones consist of 28 skull bones, 26 vertebral columns, and 24 ribs. The bones in the skull, the vertebrae, and ribs are further classified based on their position and functions. The skull is made of 6 ossicles of the middle ear, 8 cranial bones, and 14 facial bones. 1 Hyoid bone is the additional skull bone. The vertebral column is made of 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, 5 lumbar vertebrae, 1 sacral region, and 1 coccyx. This makes a total of 26 bones of vertebrae. But sometimes when fused vertebrae are counted along with the vertebral columns the total number of vertebrae makes up to be 33 in number. The ribs are 24 in total with a thoracic cage consisting of 1 sternum. Hence, the total number of bones in the axial skeleton is 80 in number.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note: The ossicles of the middle ear consisting of the body’s three smallest bones have a major role in sound signal transfer. These are the malleus, incus, and stapes. These bones are responsible for transferring the vibrations produced by sound waves directly to the inner ear.
Complete answer: The axial skeleton is the uppermost part of the skeleton excluding the limbs. It is made up of the skull bones, the vertebral columns, and the ribs. It functions to protect the organs involved in digestion and breathing. The main function of the axial skeleton is to provide protection to the brain and the heart. Also, the axial skeleton plays a significant role in the movement of other bones.

The total number of bones in the axial skeleton of a man is 80. These bones consist of 28 skull bones, 26 vertebral columns, and 24 ribs. The bones in the skull, the vertebrae, and ribs are further classified based on their position and functions. The skull is made of 6 ossicles of the middle ear, 8 cranial bones, and 14 facial bones. 1 Hyoid bone is the additional skull bone. The vertebral column is made of 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, 5 lumbar vertebrae, 1 sacral region, and 1 coccyx. This makes a total of 26 bones of vertebrae. But sometimes when fused vertebrae are counted along with the vertebral columns the total number of vertebrae makes up to be 33 in number. The ribs are 24 in total with a thoracic cage consisting of 1 sternum. Hence, the total number of bones in the axial skeleton is 80 in number.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note: The ossicles of the middle ear consisting of the body’s three smallest bones have a major role in sound signal transfer. These are the malleus, incus, and stapes. These bones are responsible for transferring the vibrations produced by sound waves directly to the inner ear.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




