
Transpiration efficiency / transpiration ratio is :
(A)Water absorbed to water transpired
(B)The unit weight of dry matter is synthesized in relation to units of water transpired by the plant.
(C)The unit weight of dry matter is synthesized in relation to units of water consumed.
(D)The unit weight of water transpired to the unit weight of dry matter synthesized.
Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint: Transpiration ratio or transpiration efficiency is the ratio of weight per unit volume of the water to the mass of completely dry matter in which the moisture content is absent.
Complete answer:
Transpiration efficiency/transpiration ratio is the unit weight of water transpired to the unit weight of dry matter synthesized. It was observed that the transpiration ratio of crops mostly falls between the range of 200 and 1000 i.e., crop plants transpire 200 to 1000 kg of water for every kg of dry matter produced.
Additional Information: The term transpiration is defined as the process of movement of water molecules through a plant and then further its evaporation from aerial parts of the plants, like leaves, stems, and flowers. Water is important for every organism and the same is for the plant but only a little amount of water haunted by the roots is employed for growth and metabolism. The remaining 97–99.5% of water is lost by transpiration and one more process known as guttation. Leaf surfaces have many tiny pores called stomata (singular "stoma"), and in most plants, they're more numerous on the undersides of the foliage. The stomata are surrounded by special types of cells known as the guard cells and their stomatal accessory cells ( that open and shut the pore. Transpiration occurs through the stomatal apertures and may be thought of as a necessary "cost" related to the opening of the stomata to permit the diffusion of $CO_2$ gas from the air for photosynthesis. Transpiration also helps in cooling the temperature of plants, helps in changing the pressure of cells, and also helps in the mass flow of mineral nutrients and water from roots of the plants to shoots.
So, the correct answer is ‘the unit weight of water transpired to the unit weight of dry matter synthesized’.
Note: Two major factors that influence the speed of water to flow from the soil to the roots: the hydraulic conductivity of the soil and therefore the magnitude of the pressure gradient through the soil. Both of the above factors influence the speed of bulk flow of water moving from the roots to the stomatal pores within the leaves via the xylem.
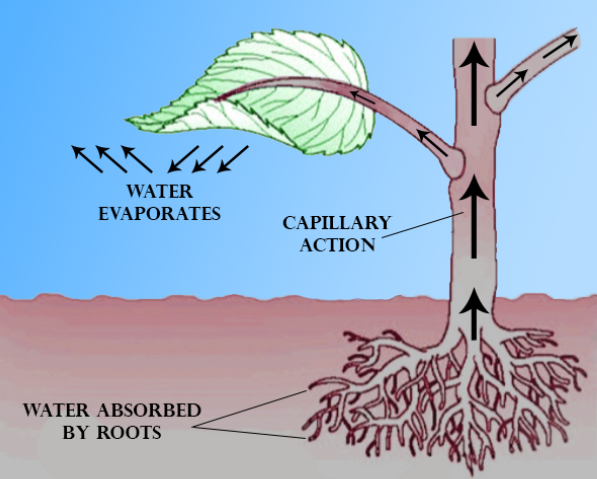
Complete answer:
Transpiration efficiency/transpiration ratio is the unit weight of water transpired to the unit weight of dry matter synthesized. It was observed that the transpiration ratio of crops mostly falls between the range of 200 and 1000 i.e., crop plants transpire 200 to 1000 kg of water for every kg of dry matter produced.
Additional Information: The term transpiration is defined as the process of movement of water molecules through a plant and then further its evaporation from aerial parts of the plants, like leaves, stems, and flowers. Water is important for every organism and the same is for the plant but only a little amount of water haunted by the roots is employed for growth and metabolism. The remaining 97–99.5% of water is lost by transpiration and one more process known as guttation. Leaf surfaces have many tiny pores called stomata (singular "stoma"), and in most plants, they're more numerous on the undersides of the foliage. The stomata are surrounded by special types of cells known as the guard cells and their stomatal accessory cells ( that open and shut the pore. Transpiration occurs through the stomatal apertures and may be thought of as a necessary "cost" related to the opening of the stomata to permit the diffusion of $CO_2$ gas from the air for photosynthesis. Transpiration also helps in cooling the temperature of plants, helps in changing the pressure of cells, and also helps in the mass flow of mineral nutrients and water from roots of the plants to shoots.
So, the correct answer is ‘the unit weight of water transpired to the unit weight of dry matter synthesized’.
Note: Two major factors that influence the speed of water to flow from the soil to the roots: the hydraulic conductivity of the soil and therefore the magnitude of the pressure gradient through the soil. Both of the above factors influence the speed of bulk flow of water moving from the roots to the stomatal pores within the leaves via the xylem.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




